An auxiliary structure made of various materials gives shape to concrete products and determines their location in space. The formwork for the foundation is made of elements that limit the size, support the building mixture until it hardens. The auxiliary structure is usually disassembled after curing, and the fixed shell becomes part of the base.
Conditions for assembling the formwork for the foundation and its functions
The construction formwork for the strip foundation must be strong, have stable dimensions. The texture of the future base and the number of cracks on the surface depend on the quality of the inner plane. Accuracy of assembly is a significant condition during installation.
Formwork performs the following functions:
- controls the shape of the concrete mass before solidification;
- aligns the surface texture of the foundation;
- isolates the basis from soil.
The installation and use of formwork is regulated by the State Standard No. 52085-2003 “Formwork. General technical conditions ”, which began to be applied by resolution of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated May 22, 2003 No. 43.
Formwork device
The formwork is removed from the individual parts, and the shields made of wood, metal, and other material form the basis. The inside is cleaned of debris and leveled to minimize the finishing process.
Attention is paid to the strength of the fastening elements to each other, because the concrete mass is heavy and may violate the integrity of the structure. The base of the house is formed correctly if the shell does not let water through. The height of the auxiliary structure is made more than the foundation level by 15 - 20 cm. The panels are strengthened with wooden posts that are hammered into the ground and placed after 0.7 - 1.0 meters.
Drawing and scheme
Concreting the foundation includes selecting the type of formwork and performing a schematic layout in plan for its precise installation. The laying of the foundation is of great importance, the process is controlled by specialists, and installation begins with the design.
Drawings of the molding system are developed taking into account:
- the size and material of the shields;
- fixing devices.
Formwork assembly schemes are part of the project for the production of PPR works, which also includes plans for the placement of tape elements, time-bound organizational charts, and process maps. The marking drawing contains a strategy for the arrangement of elements with reference to the central axes of the building by numbers.
The choice of material for formwork
The restrictive design is selected taking into account the type of foundation, its massiveness, length, type of concrete. The material should be affordable and have an acceptable cost.
Used specialized types:
- wood;
- metal;
- reinforced concrete;
- polystyrene foam.
Small bases are poured using improvised means for which you do not need to spend money. For example, old boards, dismantled door leafs, furniture parts, pieces of slate are used. Formwork from such items is difficult and not always popular, because it is difficult to choose the appropriate parts and sizes.
Metal
The metal mold is a suitable option for monolithic and strip substrates.The reinforcing racks are welded to steel shields, and a reliable collapsible design is obtained, the blocks of which are bolted. Galvanized or galvanized metal is also used. The coating on the steel surface protects the material from corrosion, therefore, such panels have multiple turns, are easily cleaned and removed.
Aluminum sheets are lightweight and convenient in the construction industry, but have a high cost. The material differs from steel in lower strength and increased fluidity, so it quickly loses its shape. Aluminum panels are almost not repaired, so their use is limited.
Reinforced concrete
Such formwork is unconventional, rarely installed due to the complexity of installation and high cost. To properly make the formwork, ready-made reinforced concrete slabs are taken. The advantages include the fact that the powerful shell is not removable and can reduce the transverse size of the foundation body.
Another option for a reinforced concrete shell is the case when a reinforced layer is concreted on top of fixed plates made of foam or another insert made of plastic material. A grid of metal rods encloses the insert on both sides and is connected by wire pallets. Concrete is sprayed with special equipment.
Expanded polystyrene
A shell of this material stably maintains its technical properties during operation over a long period of operation of the building. Formwork has high strength and protects concrete from freezing and moisture in harsh climates.
PSB-S polystyrene plates with a density of 25 - 35, a thickness of 40 - 100 mm must be set in the design position in accordance with the step-by-step instructions. Plates are connected by monolithic partitions. Overlying blocks engage with the lower elements due to special locks, and concrete is laid in the inner space.
Wood
Used boards or boundary sheets of particleboard, OSB impregnated with moisture. The plywood formwork for the foundation is assembled using screeds and wooden supports, which are connected by nails or screws. Blocks must be placed in rows so that there are no voids between them, and at the end set limit plates according to a similar principle.
The top of the structure is connected by reinforcement so that the concrete does not break apart the edges. A frame of reinforcement or mesh of metal rods is installed inside. Heat-resistant foam inserts are used to coordinate thermal resistance. Concrete is poured into the resulting space, after hardening, the panels are removed.
Varieties of formwork for the foundation
By designation, the shell is vertical, for example, formwork for a columnar foundation, and horizontal. The sheer structure moves up as it is filled with concrete, as when pouring a pile foundation.
The frame system consists of shields on a metal frame and supports, connected by nails, bolts, screws. The design is rigid and is applied many times. The beam system includes formwork panels, beams, a crossbar, scaffolding, where the elements are joined by welding. This design is used for the construction of walls, and for concrete concreting is not used.
Removable
Replaceable systems differ only in material, because the design is always made similar and contains decks, a connecting belt, supports and braces. In construction, modular or inventory versions of panels are used, which are manufactured at the factory. Such formwork is quickly mounted, removed and is characterized by high accuracy of geometric dimensions.
In private housing construction, the turnover of the structure does not play a role, therefore, wood is more often used, for example, formwork of a strip foundation from a board is made. After removal, the material will no longer be used.
Inventory formwork can be rented if such a decision is justified economically.
Fixed
The design consists of formwork easily assembled parts, which, after concrete hardening, go into the category of working elements and perform the specified functions. The shell protects the foundation from soil fluid, the base withstands freezing and thawing without damage.
Factory modules are used, which are assembled using grooves and spikes in appropriate places. External supports are not used, as inner tabs hold the structure and provide resistance to the load. Most often, non-removable options are made of materials that save heat and poorly transmit moisture, but metal, fiber-reinforced concrete, ceramic granite or plastic are also used.
Collapsible
The system is intended for disassembly after application and relocation to the next plot. You can design such a formwork for the foundation with your own hands, purchase a multi-turn in the market, or rent it. The formwork consists of shields and a power frame. Supports, braces support the boards in the working position, so that the concrete does not spread during the hardening process.
The disassembled version differs in the way of fastening the elements. The panels are connected by bolts that are removed if necessary, and the stationary formwork is fastened with nails or by welding the frame, which makes it impossible to remove it without destruction.
Small shield
The design is used on small objects so as not to use cranes for installation. Boards weighing less than 50 kg are put into the design position manually in the construction of private houses, where a large amount of concrete work is not provided for pouring the foundation.
Small-panel formwork contains elements of standard sizes, is connected using the shock lock method and with the help of clamping screws. The advantage of the device is the repeated use and long life. The labor of workers is saved, the installation technology is clear and simple, in each element there are grooves, mounting holes for fitting parts.
Sliding
This type of shell is rearranged in height and is used in the construction of buildings with monolithic concrete walls, columns. Rigid boards of the selected design are mounted at a certain height, concrete mix is fed inside. After solidification, the shell is disassembled and rearranged above to accept a new portion.
For rearrangement jacks, hoists, hoists are used.
The use of sliding formwork is effective in buildings with a constant perimeter of walls in plan and for structures with a minimum number of window and door openings, for example, elevator walls, water towers, lighthouses.
Features of the calculation of formwork
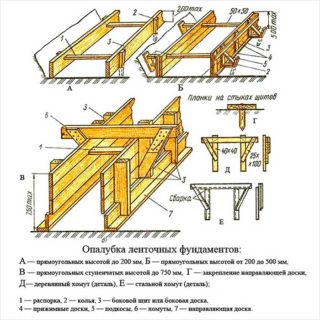
Standard calculations are reduced to determining the number of boards or sheets of chipboard and comparing their value. For this, the area of the side wall of the strip foundation is divided by the area of the element. For example, the surface of the base on the side is 7 m² (length - 10 m, height - 0.7 m). The board has an area of 0.9 m² (length 6 m, width 0.15 m). The number of boards is 7 / 0.9 = 8 boards (7.77).
Typically, a private house takes 40 - 50 pieces of boards per 1 m³ of concrete mix. For this, the volume of the entire foundation is calculated. It is equal to the perimeter multiplied by the height and width of each freestanding or turning section, then the volumes add up.
Preparatory stage and do-it-yourself production technology
The initial stage includes the acquisition of materials, preparation of the tool.Before the do-it-yourself formwork is installed, it is necessary to level the construction area.
The operation includes:
- cutting of plant soil;
- digging trenches;
- cleaning the bottom of the pit to the design level.
The ditch for the strip base or the pit for the posts is chosen so that there is a margin of 10-15 cm on the sides for installing the shields together with the spacers. Vertical barriers for flat screens are placed after the sand and gravel bedding device at the bottom of the trench.
DIY formwork installation for the foundation
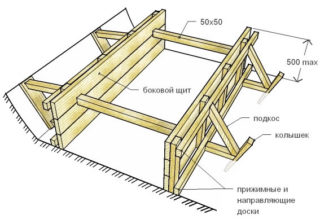
 All horizontal and vertical parts of the structure are set according to the level or a building level is used.
All horizontal and vertical parts of the structure are set according to the level or a building level is used.
Phased sequence of actions:
- installation of uprights;
- hitching and fastening of shields;
- installation of emphasis and connection of the upper edges.
Shields on vertical bars are hung so that between them no cracks appear more than 5 mm, through which moisture will leak from the concrete. Stops and braces are placed to strengthen the formwork, boards or bars are used.
The encircling frame is placed in two tiers, at the bottom (10 cm high) it takes the initial load from concrete, and at the top (40 cm), the shields will simultaneously prevent the boards from spreading to the sides. The inner surface of the formwork is covered with polyethylene from leaks and absorption of moisture into the wood.