Old mechanical relays are characterized by two drawbacks - low speed and limited resource in the number of allowable switching. The electronic switches that came to replace them (another name is a solid-state transistor or triac relay) are completely devoid of these shortcomings, which attracted the attention of electronics experts. The absence of mechanical parts, as well as the simplicity of the circuit make it easy to assemble them at home. Familiarization with the task will help familiarization with the features of the device and the principle of operation of these elements.
What are solid state relays and their classification
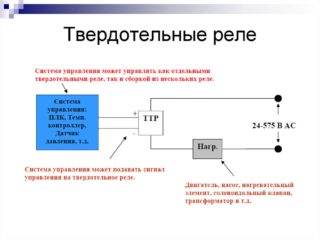
Solid state relays (or TTRs) are electronic devices with a structure that does not contain mechanical components. The principle of their operation is based on the features of the semiconductor junctions, characterized by high switching speed and security from physical fields.
Switching of solid-state relays is based on the principle of triggering an electronic key.
Commonly used electronic components such as transistors, diodes, or thyristors are traditionally used as key elements in these products. Depending on the structures used in their manufacture, the TTRs are divided into devices built on the basis of one of the listed elements (relays on triacs, for example).
In accordance with the operating modes and the type of switching voltages, samples of solid-state relays manufactured on the basis of semiconductors are divided into the following groups:
- DC switching devices;
- devices that control the operation of load lines with variable current parameters;
- universal products operating in various chains.
The first devices are characterized by constant voltage control of no more than 32 volts. Representatives of the two remaining positions are capable of switching significant potentials (up to tens of kilovolts).
Advantages of TTR
 The advantages of the relay include:
The advantages of the relay include:
- the ability to switch relatively powerful loads;
- high speed;
- work in the conditions of galvanic isolation;
- ability to withstand short-term overloads.
Not a single sample of mechanical or electromechanical products is able to compete with electronic switches. Therefore, new structures based on semiconductors completely replaced old mechanical samples.
The unique operational characteristics of the TTR allow them to be used without any restrictions while increasing the response time. All of these advantages of these devices are an excellent reason to try to assemble a solid-state relay with your own hands. The disadvantages of these products include the need for additional power, as well as the need to remove excess heat generated when working with powerful loads.
Do it yourself
To make a current relay with your own hands, you need to stock up on a number of electronic components that make up the basis of switching circuits. Also, special materials will be required from which the body of a home-made relay will be made.
Electronic elements
The following common parts are usually used as electronic components used in the independent manufacture of the simplest TTR sample:
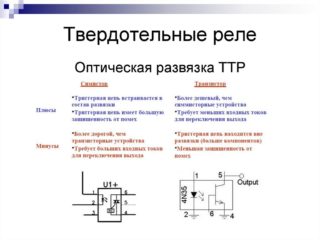
- optocoupler MOS3083;
- Triac VT139-800;
- bipolar transistor series KT209;
- a set of resistors, as well as a zener diode and an LED, which serves as an indicator of the relay operation.
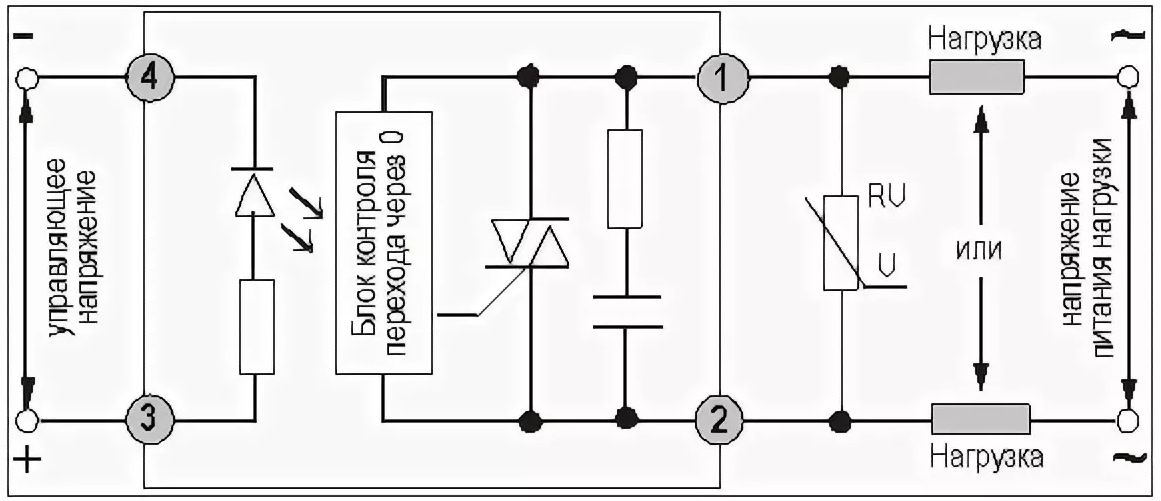
The listed electronic elements are soldered in a hinged manner according to the scheme given in the sources. Along with other components, it contains a key transistor, which supplies stabilized pulses to the control diode of the optocoupler pair.
The feed moment is fixed by an LED element, the use of which in the actuator circuit allows visual control.
Under the influence of these pulses, an instantaneous tripping of a semiconductor triac connected to a switched circuit occurs. The use of an optocoupler pair in such a circuit makes it possible to control constant potentials from 5 to 24 volts.
A boundary chain of a resistor with a zener diode is necessary to reduce the amplitude of the current flowing through the LED and the control element to a minimum value. Such a circuit solution allows you to extend the life of most of the elements used in the construction of the circuit.
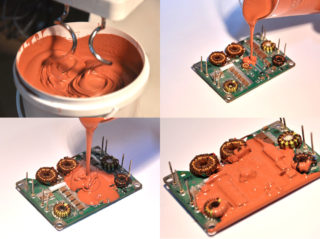
Case design (compound filling)
For the manufacture of a prefabricated housing, first of all, an aluminum plate with a thickness of 3-5 mm will be required, it will serve as the basis for electronic assembly. Dimensions are chosen arbitrarily, provided that they guarantee good heat dissipation in the environment. Another requirement for this part is a well-processed, absolutely smooth surface, polished with a special tool or polished with a sandpaper to a shine.
At the next step of preparing the case, the plate selected as the base is equipped with a border from a strip of cardboard glued around the perimeter. The result is a small box designed to accommodate the previously assembled electronic circuit. Based on its components, only a triac is rigidly attached, all other elements are held within the enclosure due to their own connections.
To connect to the load and power supply, the corresponding conductors are output to the outside of the box.
In the future, reliable fasteners of the entire assembly are provided by a liquid compound poured into the box, prepared in advance in a suitable container. After it hardens, a monolithic structure will be obtained, which is not inferior to the best industrial designs in terms of protection against vibrations and other influences. Its only drawback is the inability to disassemble for the purpose of subsequent repair of the circuit.
Varieties of TTR
 When assembling DIY solid state relay circuits, it should be borne in mind that a variety of components can be used for these purposes. Nothing prevents a person who has taken up work from choosing modern field-effect transistors, for example, which are distinguished by high speed and low power consumption. These elements are only managed by potentials, providing the ability to switch sufficiently powerful consumers. Field structures such as MOSFETs are capable of switching load circuits with power reaching tens of kW.
When assembling DIY solid state relay circuits, it should be borne in mind that a variety of components can be used for these purposes. Nothing prevents a person who has taken up work from choosing modern field-effect transistors, for example, which are distinguished by high speed and low power consumption. These elements are only managed by potentials, providing the ability to switch sufficiently powerful consumers. Field structures such as MOSFETs are capable of switching load circuits with power reaching tens of kW.
For self-fabrication of a solid-state relay, it is allowed to select other semiconductor structures that can control power circuits: thyristors, for example, or bipolar transistors. The main thing is that they comply with the requirements for the functionality of this circuit and the operating parameters of the elements included in its structure. Everything else depends on the preparedness and attentiveness of the performer.