In the process of installing electrical circuits in switchgear and power units, a busbar trunking or electrical bus is used. So they call the design - a conductor made of metal with low resistivity.
Benefits of Using Busbars
The use of tires in electrics instead of cable products provides significant savings in material, energy and labor resources:
- Installation takes 2 times less time than laying the cable.
- Service life - up to 30 years without the need for complex maintenance.
- Flexible configuration allows you to perform high-quality and safe installation of the network, depending on its path.
- The busbar has a more aesthetic appearance than a group wiring.
- Shielding the conductor eliminates the effects of electromagnetic fields on nearby office equipment.
- The design is fireproof and complies with safety requirements for protection level IP55.
The scope of electric buses is to connect electrical circuits in low-voltage networks or high-voltage discharge devices, substations, etc.
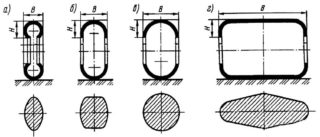
Sectional tire classification
Depending on the shape of the cross section of the busbar, distinguish:
- tubular structures;
- rectangular models;
- box conductors;
- two- or three-way models.
The advantages of conductors with a rectangular cross-section are efficient heat dissipation and low current resistance, which reduces active and limits reactive energy. Thus, it is possible to ensure significant savings in expensive energy resources, which is important for large commercial and industrial facilities.
The scope of the busbar of rectangular cross section is the installation of networks and switchgears with a current strength in the range of 2000-4000A. It is possible to connect several flat tires to obtain two- or three-lane configurations.
Flat and box modifications of the busbar trunking are used in networks operating under voltage up to 35 kV.
An optimal modification is considered to be a tubular electric bus. Among its main advantages are efficient heat removal, high strength and uniform distribution of the generated electric field.
Metals used in tire manufacturing
Depending on the purpose and the required operating parameters for the manufacture of conductors can be used:
- copper;
- aluminum;
- steel;
- steel-aluminum - a steel core coated with a wound of aluminum wires.
Among the advantages of aluminum tires are corrosion resistance, excellent conductive properties, low weight and reasonable cost. For their manufacture, low-alloyed aluminum alloys with a low content of silicon and magnesium are used to improve the ductility and strength of the metal.
Copper tires with a copper content of up to 99% are in no way inferior to aluminum, but have less distribution due to the relatively high cost.
Tire marking
The application of color marking on busbars is regulated by current standards. Compliance with their requirements is mandatory for each manufacturer. Labeling can be carried out both at the production stage and after its completion.In the first case, color insulation is used, in the second - color insulation tape indicating different phases of the conductor.
The color designation of tires allows you to accurately determine their type and purpose:
- The ground conductor is marked in yellow and green in the form of alternating longitudinal stripes.
- The neutral and working conductors are marked with blue.
- The connection of the conductors implies the use of all three shades in different versions: insulation with longitudinal yellow and green stripes and a blue line at the end or blue insulation with a yellow-green strip at the junctions and at the ends of the conductor.
In three-phase current networks, phase A is marked in yellow, phase B in green, phase C in red.
According to the requirements of current standards, along with the color marking of conductors for AC networks, the following letter designation of conductors is used:
- in a single-phase network - L;
- in a three-phase network - L with numbers from 1 to 3;
- medium - M;
- neutral, or zero - N;
- grounding - PE;
- combined working and zero - PEN (combination of designations of each of the used conductors).
Models for DC networks are marked with the letter L with a + or - sign, respectively - a positive or negative conductor.
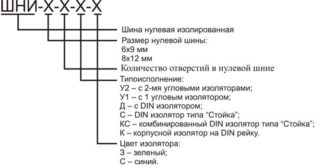
Zero tire
The grounding and neutral working conductors are connected using the zero bus. Its design consists of a conductive core and a plastic base, which is mounted on a DIN rail. The core is made of special electrical copper or brass. The design of the conductive element has holes and clamping bolts. Their presence allows for accurate and safe cabling in switchgear assemblies. Models of zero tires are made of different lengths, which allows you to make the required number of mounting holes in the core. The main area of their application is AC or DC networks, designed for operating voltage up to 400V.
Thanks to the use of a zero tire, it will be possible to:
- increase the efficiency of used protective automatic devices;
- create at the same time several points of connection of loads to the neutral conductor;
- neatly and safely separate the neutral and working conductors;
- ground the visible type using a plastic device with a cover to protect the terminals;
- mount a single circuit from the ground point to each load.
An important condition when choosing a zero bus is to take into account restrictions on the maximum allowable cross-sectional area of wires. This will ensure the safety of network operation and uninterrupted power supply at the facility. In addition, the selection of the optimal modification of the conductor is carried out taking into account the maximum number of connected loads.
The installation of the zero bus is carried out directly inside the electrical panel or on the metal rail using a bolted connection. Distinguish between outdoor and indoor installation methods. The first option is provided for electrical cabinets with a closed design, which eliminates the access of unauthorized persons to the internal contents. Installation in a closed way is optimal for networks to which expensive energy-intensive equipment is connected - machines and mechanisms, power tools, etc.