To account for electricity in three-phase circuits, special design counters are used that record its consumption for each phase. Features of the operating modes in power lines force the use of special transducers - current transformers (CT) for taking readings. Direct connection of a three-phase Mercury counter, for example, in such a circuit is allowed only under one condition. The presence of restrictions is explained by the fact that the currents flowing in the controlled line should not exceed the limit value of 60 Amps.
Advantages of installing and operating the product Mercury 230
The electric meters of the class in question are metering devices with which it is possible to measure the energy spent in three-phase circuits. The advantages of this type of electronic device include:
- the ability to meter electricity at various rates;
- permissibility of operation in three-phase networks, the inclusion of which is carried out directly or through current transformers;
- the ability to work individually or as part of dispatch equipment;
- advanced functionality provided by the features of inclusion in the overall power system.
Devices are successfully operated not only at industrial enterprises and other production facilities, but also in private homes, where three power phases are used quite often.
The power requirement of 380 volts is explained by the use of power equipment, which includes electric motors. They successfully work only in the presence of three phase voltages and are used in borehole pumps, machines and other types of equipment used for personal purposes.
Electric meter specifications
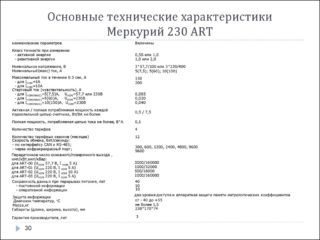 The operational characteristics of the Mercury 230 device, fully characterizing it as a metering device, include the following features:
The operational characteristics of the Mercury 230 device, fully characterizing it as a metering device, include the following features:
- Display on the display of data on consumed electricity for any of the envisaged operating modes: night, day, preferential, etc.
- Accounting for energy consumption in one of 4 tariff modes with 16 zones of overlap in time.
- Counting and recording current and frequency parameters.
- Control of consumption through the interface (from the central control room).
- Saving up to 10 major events in the device’s memory, as well as moments of the disappearance of individual phases, their excess of permissible values, opening dates and changes in the tariff regime.
The meter also provides a special type of protection, eliminating the possibility of unauthorized entry during attempts to steal electricity. In these devices, the readings are carried out according to the "cumulative total" algorithm, which is independent of the instantaneous direction of the current.
Why do I need TT
The connection of three-phase meters through current transformers Mercury makes it possible to expand the range of measured parameters to several hundred amperes. This can be achieved through the use of converting devices with a fixed transformation ratio (most often it is 20). Since the Mercury type meters are designed for currents of not more than 60 Amperes - using a transformer allows you to take readings at their values in the supply circuits, reaching many hundreds of Amperes.
For other TT models, the transformation coefficient has “its” values (5, 30, 40, etc.).
The choice of a specific converter model depends on the calculated current load level in the consumer network.If the current value does not exceed 60 Amps, which is extremely rare, direct connection of the meter to a controlled circuit is allowed.
Wiring diagrams
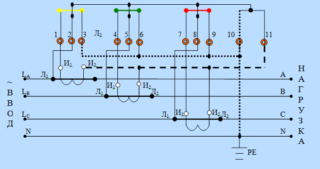
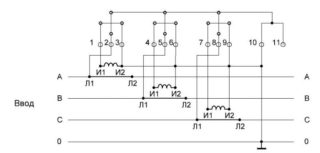
The connection diagram of the meter through current transformers Mercury 230 provides several ways to turn it on, differing by switching linear conductors: semi-indirect connection; direct inclusion; indirect way.
Semi-indirect inclusion
Semi-indirect is the type of connection in which only one converter is used for taking readings - a current transformer, made in the form of a separate module. This device allows you to lower the value of the current component that directly affects the Executive node of the electric meter. With its help, it is possible to expand the range of capacities to be accounted for in existing electrical networks. In addition, their use ensures the normal functioning of the equipment connected to them.
Direct connection
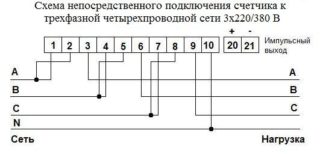 In the simplest connection scheme of the Mercury 230 counters, the principle of direct connection of its working windings to the gap of the phase supply wires is used. It is allowed to connect electric meters in this way only on condition that the current flowing in the controlled circuits does not exceed a value of 60 amperes. This restriction applies to each of the phases subject to mandatory accounting.
In the simplest connection scheme of the Mercury 230 counters, the principle of direct connection of its working windings to the gap of the phase supply wires is used. It is allowed to connect electric meters in this way only on condition that the current flowing in the controlled circuits does not exceed a value of 60 amperes. This restriction applies to each of the phases subject to mandatory accounting.
This method is used extremely rarely, since with three-phase power the starting currents in electric motors, for example, often reach hundreds of amperes.
Indirect inclusion
In an indirect connection, the electric meter is included in the controlled circuit according to several schemes developed specifically for this method. One of them is the connection through ten separate conductive cores. With its help, it is possible to implement separate metering of current and voltage, which increases the efficiency and safety of the device in all modes. The disadvantage of this method is the large number of switching elements that reduce the reliability of the counter performing its functions.
This category includes a circuit that allows you to connect the meter to a three-phase three-wire network using 2 current transformers and 2 voltage converters. With its application, it is possible to slightly reduce the number of necessary switching and increase the reliability and safety of operation of accounting equipment.
The nuances of connecting the meter via TT
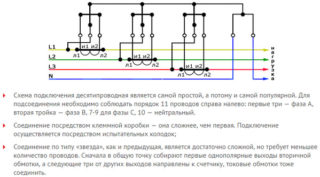 In the most common (semi-indirect) method, the voltage reading chains are switched on directly, and the current ones through the CT. In this situation, it is important to learn to distinguish the following switching methods:
In the most common (semi-indirect) method, the voltage reading chains are switched on directly, and the current ones through the CT. In this situation, it is important to learn to distinguish the following switching methods:
- Ten wire circuit.
- Seven-wire analogue of it.
- Scheme with combined circuits.
In the first case, three wires from each of the phase lines plus neutral and two conductors from 3 CTs are connected to the meter junction box. The advantages of this approach include the optional disconnection of the supply line if it is necessary to replace the meter or during repair work. In addition, with this switching method, the reliability of its operation and the safety of operation are increased. The disadvantage of this method is the greater the number of connecting wires.
When applying the seven-wire circuit, the three response ends of the current transformers are combined and connected to the "ground" (10-3 = 7). Simultaneously with the convenience of repairing electrical equipment in this case, the number of switched wires decreases. This simplifies the installation and repair of electrical equipment and significantly reduces the risks during its operation in normal conditions. You can also connect an electric meter according to a combined scheme, when voltage circuits are combined with current taps due to the installation of jumpers at the corresponding points of the transformers.Usually they are located between the taps I1 of current transformers and the corresponding phase line. The number of connecting conductors in this case remains the same - seven cores.
When choosing the appropriate option for connecting an electricity meter, the Mercury 230 is primarily based on safety considerations. Only after fulfilling this requirement are questions of profitability and ease of maintenance or repair considered.