When carrying out installation work related to electrical wiring, various conductors are used - cables, cords. During operation, it may be necessary to install new or replace old conductors, and then you need to know their labeling. It consists of a symbol, as well as colors that describe the different characteristics of the device. To understand the labeling, you need to understand what each of its components is responsible for.
Labeling purpose

When buying electrical equipment, you should understand what the letters and numbers in the name mean. This code is a marking that gives the electrician the following useful information about the conductor:
- The material of the veins, their quantity. Most often, aluminum and copper conductors with one or several conductors are used.
- Type of insulation. Shows what material the insulating layer is made of.
- Section of the conductor. From this indicator directly depends on what load can be connected to the wire. Copper and aluminum conductor with equal cross-section withstands various loads.
- Rated electrical values. This is the operating voltage, current, power.
- Resistance to environmental factors. For the street, models are taken with resistance to moisture, UV, mechanical stress. Home conductors are usually installed in a switchboard or cabinet, on walls or inside them, so they do not require a high level of resistance to adverse effects.
- Design.
- Flexibility.
The marking can also indicate the type of conductor - cable, wire or cord. A wire is understood to mean a product from a monolithic or multiwire current-carrying component with insulation or its absence. A cord is a series of multi-wire insulated wires that are used to connect electrical appliances to a power point. A cable is a product with both single-core and multi-core wires, with insulation, armor, or other design features. They are distinguished by purpose - power, control, used in radio frequency installations. Cable types, types of wires and designation must be present both on the conductor itself and in the documentation for it.
Labeling is different. There is domestic and foreign - the decryption principle is the same, only letters differ. The material used is the same. There is also a color designation of wires. Among domestic products, you can always find an analogue of a foreign conductor and vice versa.
Cable marking
All materials from which cable products are made are designated by a certain letter. The location of the letter is also important - it shows what is made of this material.
The first character in the cable marking indicates the core material. A - aluminum, pass - copper. The following 3 characters indicate isolation, armor and protection. First you need to figure out what is meant by each of these concepts.
The insulating layer is used to protect the cores from short circuits. Various dielectrics are used - rubber, PVC and others.
A protective inner shell is a layer that fits under the armor. It can also be an external protective layer to protect insulation and increase protection against negative influences (UV, temperature, liquid, fractures). Not used on all cables.
Armor is a steel tape or wire braid. Increases the mechanical strength of the product.It is not used in all cables, but only when there is a high risk of damage or constant loads. Application - underground, underwater, aerial wiring.
Cable marking is as follows:
- 1 sign - what veins are made of. A - aluminum, pass - copper.
- 2 sign - insulation material. B - PVC, P - polyethylene, P - rubber, HP - non-combustible rubber, F - fluoroplastic, G - bare (without insulation), C - film, K - control cable (purpose), KG - flexible.
- 3 sign - type of protection, if present in the cable. A - aluminum, C - lead, P - polyethylene hose, PU - reinforced polyethylene hose, B - PVC, P - rubber.
- 4 sign - armor, if present.
- 5th sign - outer cover, cable construction. G - waterproofing, in the absence of the letter G - protection against mechanical stress; E - shielding; O - insulated wires that are connected by a winding; B - if the last letter, then paper insulation, otherwise PVC.
A numerical value is written after the letters. The numbers show the working voltage of the cable (if there is no value, the voltage is equal to the mains 220 V), the number and cross section of the cores.
As the cross-section of the wire is indicated, depends on the thickness of all cores. If they have the same cross section, such a pair of numbers in the designation is one. If there is a grounding, thinner core, a second pair of numbers is placed after the + sign.
Temperature and GOST
Important information about operating conditions and the name of GOST, according to which the conductor is produced, can be applied to the cable. Temperature conditions play an important role in laying the cables in an external way. It is indicated on the labeling of electrical wires in the case of special purpose products.
GOST and TU are also not always indicated in the marking. This does not mean that the product is not in compliance with standards.
Wire marking
The method of marking the wires does not differ from the designation of the cable. These two electrical equipment are similar in their purpose and characteristics.
The wire designations are as follows:
- The first position is the material lived. Similarly to cables with the presence of the letter A, one can judge that the cores are made of aluminum, in its absence - from copper.
- The second position - shows which wire it is. P - ordinary (most often single-core), PP - flat (two, three or more cores), W - cord. Also, heating wires, which are designated as PN, have recently appeared on the market.
- The last third position is insulation material. Design information and designation may also be provided here. G - flexible, C - connecting, T - gasket is permissible only in pipes.
- Next is a digital code. The first digit is the number of cores, the second is the cross section.
When decrypting, you need to understand exactly where the wire is and where the cable is. Otherwise, you can get confused, because in the first case, the letter P will mean "wire", and in the second - material. You can understand where the conductor is, by the number of letters in the designation. Wires usually contain no more than 4 letters, unlike cables with a longer code.
Optical Cable Labeling
These types of conductors have a different designation scheme in contrast to classic cables. The first two letters indicate the destination - OK (optical cable). This will allow the wizard to accurately identify the conductor.
Further, the algorithm is similar. There is a set of letters and numbers that indicate specific characteristics.
- Cable laying condition.
- Modular design. M - multi-module, C - single-module.
- Flammability. NG - non-combustible material for group laying, N - non-combustible for single laying, without a letter - combustible.
- After the letters H and NG, the type of shell is prescribed. LS - halogen-free polyethylene with reduced smoke emissions. HF is a non-halogen-free polyethylene that does not spread when burning corrosive gases.
- Design.
- The number of optical modules x the number of fibers in the module.
- Type of optical fiber. They can be single and multimode. The letter E denotes a single-mode, M - multimode.
- Permissible tensile reinforcement.
Optical cables are used for internal and external installation. Cables for special purposes are laid in the ground, under water: swamps, ponds, river terrain and other water bodies.
Color coding
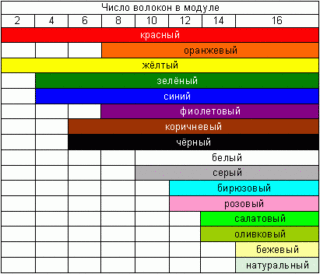
 You can determine the purpose of the wire by its color. Color marking is used for this. Thanks to the developed standards, the master, during installation and repair, can understand in a matter of seconds which wire is phase and which is zero or ground.
You can determine the purpose of the wire by its color. Color marking is used for this. Thanks to the developed standards, the master, during installation and repair, can understand in a matter of seconds which wire is phase and which is zero or ground.
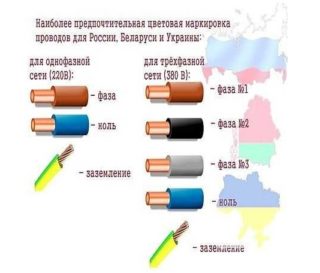
Earth according to accepted standards should be painted in green-yellow. The insulation can either be painted completely in such a color, or have a strip along the entire conductor of the yellow-green gamut. Grounding letter PE. When determining it is important to pay attention to the name - the land can also be equipped with zero protection. This core must not be confused with the usual zero, so as not to violate the correct connection.
Zero is usually dyed blue or blue. The phase can be of different colors (except those assigned to zero and ground), depending on the manufacturer.
According to GOST 31947-2012, it is better not to paint the conductors in red and white. The recommended staining scheme is as follows:
- Three-core conductors - yellow-green, blue, brown, blue, black.
- 4-core - yellow-green, blue, brown, black, brown, black and gray.
- Five-core wires - yellow-green, blue, brown, black, gray, brown, black, gray, black.
A prerequisite is the ease in distinguishing the color scheme.
In the absence of color coding, you will have to use special tools - multimeters that determine the purpose of the core. The phase can also be determined using an indicator screwdriver.
There is also non-standard coloring, which depends on the brand of wires. In this case, zero must be blue to simplify the search. The earth in this case can be black or white, as it was painted before. The remaining wire will be phase. This method of determination with non-standard staining is dangerous, so it is better to use a tester.
Foreign marking
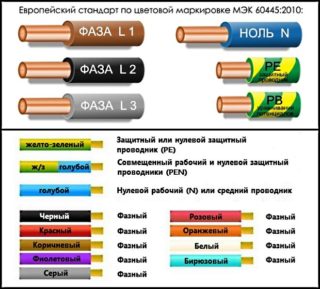 The foreign designation of the conductors differs from the Russian one.
The foreign designation of the conductors differs from the Russian one.
Wire and cable marking:
- A type. N - power, H - consistent.
- Rated voltage. Marking of electric wires is registered with a digital code.
- Material lived. No designation or Cu - copper, A - aluminum.
- Insulation material. Y, PVC, V - PVC; G, R - rubber; N - polychloroprene rubber.
- Conductive layer. H is semiconducting.
- Screen, filler in power cables. C, S- concentric conductor or shield, copper. A is aluminum. F - core in a shell with hydrophobic filling.
- Shell. V - PVC, R - rubber, N, Y, PVC - polychloroprene rubber, 2Y - polyethylene.
- Design. U - round monolithic, R - round multiwire flexible, H - multiwire increased flexibility.
- Armor. B - flat steel tape, SWA - round steel wire.
Some manufacturers may have foreign wire decryption.