The features of the operation of protective devices in power circuits are manifested in their ability to respond to increased current loads and turn off the line when they reach the maximum value. Moreover, the shutdown occurs immediately in several directions, taking into account not only electromagnetic, but also thermal effects. To understand the nature of the switching inside the device, you will need to familiarize yourself with the technical characteristics of the circuit breaker.
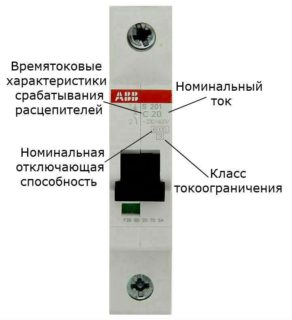
Performance data
Among the main parameters of circuit breakers that fully characterize their functionality, it is customary to include:
- rated current (normal mode);
- ultimate breaking capacity of the device (PKS);
- current limiting characteristics;
- response parameters of electromagnetic current protection.
The temperature characteristics are considered separately, which are understood as the conditions for tripping the thermal release.
The current of the standard mode is the value at which the machine can work for as long as necessary without deviations of the parameters from the given norm. This value is displayed on the instrument immediately after the letter defining its time-current characteristics. The ultimate breaking capacity of the machine is the maximum current value at which it can operate without loss of functionality. The value of the PCB is indicated on the AB housing immediately below the time-current characteristic and rating.
The current limit category characterizes the ability to disconnect the emergency line until the current reaches the overload limit. For various devices, this parameter takes the following values:
- the first category is 10 milliseconds (ms) or more;
- second category - from 6 to 10 ms;
- third category - 2.5-6 ms.
The higher the current limit category for this model, the lower the risk of wires overheating and emergency fires. On the front panel, the parameter is indicated under the PKS icon.
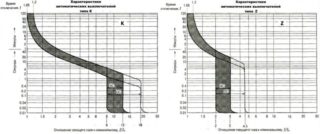
Classification by time-current characteristics
The class of the device is indicated on its panel in the form of a Latin letter before the face value. In accordance with this indicator, all known examples of protective devices are divided into a number of categories.
Automatic machines MA
The specificity of the MA machines lies in the absence of the thermal trip mechanism that is familiar to these devices. They are most often installed in the connection lines of electric motors and similar powerful devices. Especially for overload protection, these circuits use sensitive overcurrent relays. The machine itself only protects them from damage that occurs due to the impact of short-circuit currents.
Class A appliances
Automatic machines of type “A” are characterized by maximum sensitivity and reliably operate when the current exceeds the nominal by one third for the time specified by the characteristic. If its value exceeded the nominal value by 100 percent, it will take no more than 0.05 seconds to trip the coil of the e / m release. If, for technical reasons, it has not fulfilled its function, a bimetallic thermal protection comes into effect, turning off the power after 20-30 seconds. Automatic machines with this indicator are installed in the case when short-term current overloads are unacceptable.
Class B safety devices
Devices in this category have a slightly lower sensitivity than previously considered. E / m release device disconnects when exceeding the nominal by 200 percent. Its response time is not more than 0.015 seconds.It will take no more than 4-5 seconds to disengage the bimetallic plate in the disconnector. Equipment of this class is widely used in lines with wiring products (sockets and lighting devices) included in them - in circuits where starting overloads are minimal.
Category C machines
To understand the difference between automatic machines C and B, it is necessary to note: the ability to “hold” the overloads of type C devices is even higher than that of the first two categories, which makes it possible to put them in household power supplies. To disconnect the electromagnet of such devices, a current exceeding the nominal value by 5 times will be required. For reliable operation of thermal protection, a five-fold excess is required for 1.5 seconds.
Category D circuit breakers
The D characteristic of the circuit breaker indicates its high capacity to withstand overloads. For the operation of the e / m coil, a current exceeding the nominal value by about 10 times is required. To shut off the controlled line by means of a thermal release, a shutter speed of at least 0.4 seconds is required. Devices of this class are usually used as auxiliary fuses, performing the function of insurance against accidental malfunctions with other similar devices.
Category D machines are triggered in a timely manner if, for some reason, the main circuit breakers in one of the serviced rooms have failed. They can be installed in circuits with significant starting currents - to protect the windings of electric motors, in particular.
Category K and Z protective devices
Devices with the letter K are characterized by a significant variation in the operating currents of the e / m trip (relay). For alternating current, this indicator is 12 times greater than the nominal, and for lines with a constant power level, it reaches the figure 18.
The time required to turn off the e / m relay is not more than 0.02 seconds. Thermal protection tripping in these devices occurs when the load current exceeds the nominal value by 5 percent. This explains the possibility of using automatic machines of type K in circuits with inductive load.
Products with the Z index have more modest indicators of overload - no more than twice, and are used to protect electronic circuits.
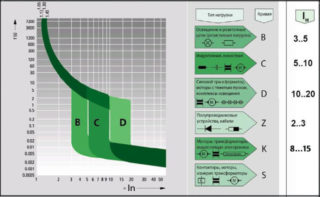
Differences AB categories B, C and D
The categories of automata A B C D belong to the main indicators that deserve separate consideration and comparison. Of particular interest among the classes of automata are the current time parameters of the last three categories.
The circuit breaker with characteristic D, unlike the categories of automatic devices A B C, is well adapted to increased overloads and is therefore installed in circuits with large inrush currents. It is traditionally used in the protection circuits of powerful electric motors. When comparing automatic machines C and B, it is important to remember that the first category of devices is more suitable for protecting household networks - for installation in a private house, for example.
Familiarity with the technical characteristics of the machines and the features of each of them will help the user to choose the right device, suitable for the mains with a given current load.