The relay is a system of switches necessary for switching, disconnecting and connecting electrical circuits. The purpose of the operation of the switching device is to create specific working conditions for the equipment. Connecting a relay means creating a load on the switch that controls the device.
Relay mechanisms
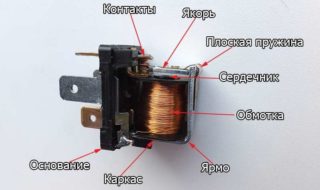
The relay device is made in the form of a coil entwined with a large amount of copper wire. Inside it is a core-rod made of metal, fixed on a yoke - a L-shaped plate. On top of the core and coil is an anchor - a metal plate that is held by a return spring. Movable contacts are attached to the anchor, and motionless contacts opposite them.
The assembly of the coil and core is an electromagnet, and the assembly of the core, anchor and bright is the magnetic circuit. Contacts provide control of the circuit, opening and closing it.
Principle of operation
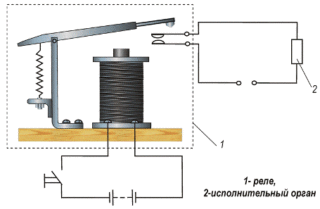
The principle of operation of the relay 4 contact or 12-volt model is similar. Without supplying voltage to the device, the anchor is distant from the core by means of a return spring.
At the moment when voltage is applied, a current begins to move along the winding, the magnetic field of which acts on the core. The magnetized element, by overcoming the forces of the return spring, attracts the anchor. Its active contacts move, opening or closing with motionless.
After the supply voltage ceases, the winding current disappears, the demagnetization of the core occurs. The return spring brings the armature and contacts to their original state.
Varieties of Relays
Relay devices are classified according to several parameters.
Number of phases
Subdivided into:
- single-phase - designed to supply voltage in residential premises;
- three-phase - suitable for industrial applications.
Three-phase switches turn off the power to all equipment during voltage surges on one of the lines.
Switch type
Available models:
- maximum - increase the voltage parameter to a certain value;
- minimum - lower the indicator to the specified value.
The voltage threshold is not set by the user.
Type of activation of the sensing element
The sensing element, upon switching on which the device will work, is an electromagnet, magnetoelectric unit, induction or electrodynamic system. Depending on its type, there are relays:
- primary with direct connection of contacts to the network;
- secondary - can be connected through measuring inductive or capacitive transformers;
- intermediate - amplify or transform the signals of primary / secondary models.
The functions of the sensing element are the conversion of voltage into the process of movement of the armature relative to the yoke.
Type of load control
To control the voltage, the following models are used:
- direct action - the load is switched by contacts;
- indirect action - the load connects the secondary elements.
The load is supplied and suspended at regular intervals.
Type of signal input
On sale you can find the following switching devices:
- electronic - provide voltage control under high load conditions. Control the lighting and components of the car;
- reed switches - small coil-shaped models. Designed for closing, switching, opening the network. Sensitive to mechanical stress and ultrasound;
- electrothermal - turn off and turn on the electric current for heating the bimetal plate. Used for electric motors in production, arrangement of single-phase or three-phase power supply;
- time delay - to create short pauses, slowdown circuits are used. Devices work in cars, traffic lights, Christmas garlands;
- light timers - allow you to program the lighting of greenhouses, aquariums, livestock complexes. Heaters, fans are connected to them;
- electromagnetic - the current of the statistical winding is activated by the influence of a magnetic field. Devices with an average load of up to 320 A and voltages of up to 1.6 kW can only work in DC networks.
Structurally, the standard regulator has the form of a bag for mounting on a din rail. Some models are made in the form of adapters and extension cords.
Contact Features
By design, the contact intermediate relay consists of three types of elements.
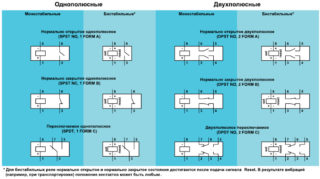
Normally open
They are in the open state until the power is supplied to the coil. The relay is activated after voltage is applied, and the contacts come to a closed state. The power grid closes.
Normally closed
They operate according to the opposite principle, being in a closed state at the time of de-energization of the relay. After the appearance of voltage, the relay operates, the contacts and the circuit open.
Loose-leaf
When the coil is de-energized, the average common contact of the armature is closed to stationary. After the relay is activated, the middle element together with the armature moves in the direction of the stationary contact and closes with it. Communication with the first stationary contact is broken.
Multiple contact group models provide multi-chain management.
Relay circuit diagram
The circuit diagram of the relay is applied to the cover by the manufacturer. The device itself has the form of a rectangle, marked with a marker K with a number. The letter K with two numbers separated by a dot is used to designate contacts without applying a load. The first is the serial number of the device, the second is the serial number of the contacts.
Contact groups next to the coil are marked with a dashed line. Under the electrical circuit also indicate the parameters of the contacts, the value of the maximum switching current. A variety of currents and voltage under operating conditions are applied to the relay coil.
Wiring diagrams
The module is connected to consumers depending on the design and the number of contacts.
With multiple contacts
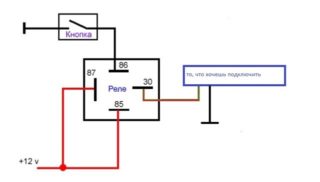
Scheme of activation and operation of the light relay, consisting of 4 pins allows you to connect foglights through a fuse:
- Search for additional voltage by cutting the red wire on the safety block and soldering additional.
- Installation of an outboard fuse.
- Connection of the power relay according to the numbering of contacts. 30 - cable after the fuse, 87 - cable to the PTF directly, 86 - wire with a bolt to the bolt near the relay.
- Creation of a management system. The PTF button is pulled out without removing the pad.
- The wiring of the wire with a multimeter and its attachment to the body.
- Check headlights and dimensions.
- Re-dial with a multimeter and search for the numbers 12+.
Contact 85 pops up only on the wire, when touched which appeared 12+.
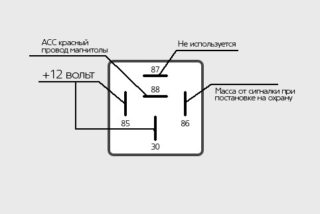
Wiring diagram five-pin The relay is suitable for creating an alarm. The connection is as follows:
- Identification of contacts. 85 and 86 are responsible for the coil, 30 - common, 87-a - normally closed, 87 - normally open.
- The supply contact 85 is connected to the signal wire.
- 12+ Volts is supplied to coil contact 86 with the ignition on.
- Contacts 87-a and 30 snap into the open circuit.
- Inverted polarity.Minus is supplied to coil contact 85 and contact 87, plus to contact 86 from limit switches. On the 30th there is a plus.
As a blocker, a gas pump, starter, injector power, ignition can be used.
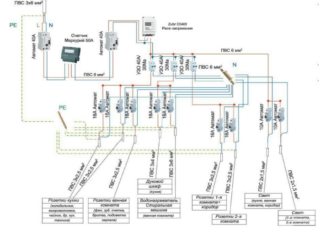
For voltage relay
The voltage relay connection diagram provides for the installation of the device on a DIN rail in the switchboard. For a three-phase network, the following applies:
- The connection cable is determined - copper, with a cross section of 1.5-2.5 mm2.
- Input contacts are connected via a starter or contactor.
- The phase is located at markers A, B, C and zero terminal N.
- Three-phase conductors snap into the corresponding upper terminals of the device.
- The conductor of terminal No. 1 is connected to the output of the coil.
- Terminal No. 3 is connected to the phase bypassing the voltage relay.
- The output No. 2 of the contactor coil must be connected to the neutral conductor of the network.
- The load conductors are connected to the terminals of the starter at the output.
- The zero conductors in the distribution box pop up on a common neutral.
For ease of connection, refer to the diagram on the relay housing.
Relay settings
The circuit to turn on any relay will only work if the settings are correct. The user can set the threshold for the maximum and minimum values, select the activation delay and re-enable after a reboot.
Having decided on the type of switching relay and understanding its circuit, you can independently create an electrical circuit. When working, you should consider the type of contacts, the type of device and the principle of its operation.