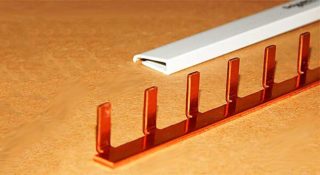
For the installation of electrical products installed in power distribution cabinets, prefabricated and connecting buses of various types are used. A special comb for automatic machines is one of those elements that are difficult to do without when arranging switching lines. It is used for the convenience of combining a line of automatic devices in an electrical panel, allowing you to do without complicated wire jumpers in installation.
Types of connection busbars
Known types of combs for circuit breakers (AB) are classified according to a number of characteristics, the main of which are:
- total number of poles available on them;
- number of plug-in installation modules, taking into account a fixed width;
- type of working contacts - bends or pins.
According to the first feature, the connecting bus can have several designs, among which there are single-pole, double-pole, as well as 3-pole and 4-pole strips.
By the number of modules connected to the combs, they are designed for 12/24/36/48/60 seats. According to the type of contacts used in the products (this division relates to the design features of the combs), they are all divided into pin or gear samples. The first of the varieties belongs to the universal type, as it is suitable for any modular automaton or similar device.
Design features
Differences in the performance of electric combs are associated with the following features of their device:
- The number of insulated plates in the comb bus is equal to the number of its poles.
- Each variety of connecting comb is used only for certain purposes.
- Single-pole connectors are used exclusively for single-phase machines, and 4-pole connectors are used for switching 3 phases and zero, for example.
Known patterns of combs have two designs that differ in their pitch (18 mm and 27 mm). The first is designed to connect single-module machines, the declared width of which is exactly equal to 18 mm. Combs with a pitch of 27 mm allow combining devices with a body width of 1.5 modules (18x1.5 = 27 mm).
The design of the connecting devices is designed for the installation of a large number of machines with a total number of outputs from 12 to 60. This explains why using them to install 2 or 3 devices, for example, is impractical. Traditionally, these auxiliary products are used to assemble switchboards with a significant number of switching devices.
When acquaintance with the design of the combs, special attention is paid to the cross section of the phase connecting rail made of copper, which should not be less than 16 square mm. An approximate calculation of the amount of wire that is saved on such a replacement removes all doubts about the advisability of using these copper products.
Types of bends
There are two types of discharge contacts that are part of the connecting combs.
- Bends made in the form of pins and designated as “Pin”. They are used very often, because they fit most automatic devices.
- Fork bends marked with the Fork badge.
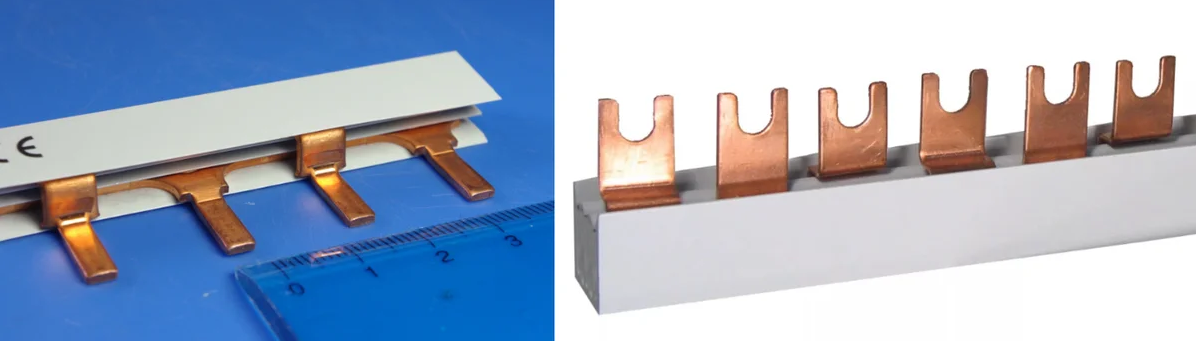
The second type of contact is used much less often, because their installation will require a special clamp, which is not available for all connected AVs. The cross-section of the outlet pins is selected so that it is enough to work with load currents up to 63 amperes inclusive.
When choosing single-phase tires, as well as any other dimensions that differ in the type of bends, it will be necessary to take into account a number of design features. For each class of connected devices, only a specific bus model is suitable. When they try to install a connecting comb, the outlets of which do not correspond to this device, they may simply not fully enter the sockets. In this case, some part of the tire plane remains open, which poses a threat to users and installers.
As an example, there are automatic machines of the ABB brand, the body of which is available in two versions: S200 and a simpler model - S200L. For the first of these samples, a bus under the designation PSH is suitable, and for the S200L its other type PS is required.
Chinese combs with standard bends may not fit the pitch at all, which results in the inability to use them. Experts advise not to save on the quality of these products and purchase only after consulting with sales managers.
Advantages and disadvantages
 The advantages of using copper combs are:
The advantages of using copper combs are:
- Simplicity and high speed of assembly.
- Getting high-quality and reliable electrical connections.
- Reducing the total number of contacts in half, which increases the reliability of the resulting compounds.
When installing standard jumpers made of electrical wires, two bare contact ends fall on one clamp at once. When using a single-phase comb, for example, only one tooth (retraction) is used.
Specialists in their own way solve the problem of saving contacts - they connect the machines not with separate jumpers, but with a solid wire. For this, loops with the desired bending radius are made in the zones of electrical connections.
The disadvantages of the connection method, in which electric busbars are used, include:
- The inconvenience of replacing the automatic protection device, since in this case it is necessary to remove the entire comb as a whole.
- The inability to add another automaton (this will require a new dimension).
One of the possible solutions to the problem of the second case is to install backup devices with frequently used values of 10 and 16 Amps in advance. Their output contacts remain unused until a certain point in time, and they themselves constantly remain in the off state.
Given the special techniques of mounting machines and their redundancy, the use of connecting dies is advisable in any situation, despite the shortcomings.
Schemes of connecting automatic machines through a connecting comb
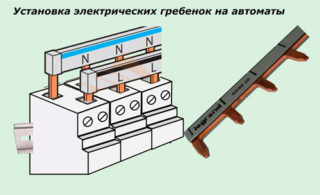 A comb busbar is introduced into the connecting chain according to certain rules defined by the electrical circuit for its inclusion.
A comb busbar is introduced into the connecting chain according to certain rules defined by the electrical circuit for its inclusion.
Since the union of automata in 220 Volt networks is carried out only in phase (without zero) - this bus is usually called phase.
Depending on the type of power circuit, into which jumpers for automatic machines are connected, they are calculated for operation either in a single-phase line (220 Volts), or in a three-phase network. In the second case, the switching circuit is a triple copy of a single switching. The difference between the two options is manifested only in the design of the bus connector itself.
According to the PUE, the element is designed to create reliable contact between the upper (supply) terminals of automatic devices, the voltage from the output of which enters the load line. To do this, the bus must withstand significant currents, which determines the circuit for its inclusion in the common power circuit - all machines are connected with its help in parallel at the input. This rule is valid for single-phase (single-row) tires, as well as for three-phase combs for automatic machines.In the second case, the copper product has three isolated rows offset by a step corresponding to a distance of 380 volts between the phase terminals of the switching device.
Features and installation rules
 A typical comb bus is mounted within the boundaries of the inlet or distribution panel very simply, without causing particular difficulties for the contractor. However, in this case there are a number of nuances, which must be taken into account when installing the comb for circuit breakers.
A typical comb bus is mounted within the boundaries of the inlet or distribution panel very simply, without causing particular difficulties for the contractor. However, in this case there are a number of nuances, which must be taken into account when installing the comb for circuit breakers.
According to the requirements of regulatory documents, the phase bus is located only on the upper contacts of the machines, combined in one line.
Features of connecting the bus under the comb also appear in the following subtleties:
- Since its conductive part during installation falls between the lower pressure plate and the comb itself, the plastic insulating protrusion on it should be turned towards the screw mount.
- In violation of this requirement, it is not possible to obtain an aesthetic connection that is devoid of bending of the plate.
- When installing a 3-phase type comb, it is important to monitor the correct location of the insulators, which eliminates the possibility of interphase circuit.
In the process of installing connecting busbars for machines instead of standard jumpers from a wire, observance of generally accepted marking is mandatory. It is applied to the housings of the mounted products and must comply with the requirements of current standards.
Typically, such combs are sold already measured standard rulers, the number of mounting contacts on which is different. Therefore, before connecting, the total number of connected machines is calculated and, taking into account their thickness, an unnecessary part of the bus is cut off.
Connection of RCD and differential machines
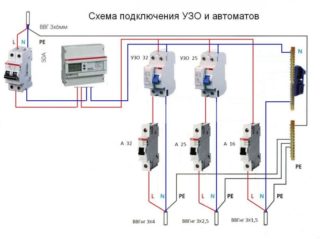 By means of a double-pole comb, designated as (L + N), as well as its 3-pole analogue, it is convenient to combine not only ordinary ABs, but also add residual current devices (RCDs) to them. When simple disconnecting AB and RCD are installed in a cabinet in one ruler, the installation of a combination of protective devices is noticeably complicated. The difficulties that have arisen are explained by the features of the supply busbar connection to various types of devices, which manifest themselves differently in the following two options:
By means of a double-pole comb, designated as (L + N), as well as its 3-pole analogue, it is convenient to combine not only ordinary ABs, but also add residual current devices (RCDs) to them. When simple disconnecting AB and RCD are installed in a cabinet in one ruler, the installation of a combination of protective devices is noticeably complicated. The difficulties that have arisen are explained by the features of the supply busbar connection to various types of devices, which manifest themselves differently in the following two options:
- Together with a line of several machines, one or more RCDs are installed.
- Instead of automatic devices and RCDs, differential devices completely replacing them are built in the line.
Difavtomat is an RCD combined in a single housing and a conventional circuit breaker.
The first case, in turn, involves two mounting options: the comb is used in a single-phase circuit or installed in a three-phase power line.
Single phase switching
The peculiarity of such a connection is that for machines it will require a single-pole line, and for RCDs - a two-pole line. The condition for the operation of the latter is joint phase and zero switching. In this case, they proceed from the principle of maximum capabilities, that is, they choose a two-pole bus, and the earth taps on the machines simply bend.
3 phase connection
In this case, it is necessary to use a 4-pole comb made of copper, the three phase contacts of which are used both on the machines and on the RCD. The fourth "zero" row is used to connect to the RCD, and in the area of "earth" contacts of conventional disconnecting devices, it simply bends. When installing one diflavomat in any situation, the taps of the comb are connected to all the contacts involved in the circuit.
A connecting comb for circuit breakers and RCDs is a convenient way to combine them into a single structural unit. It can be used both in standard enclosed switchgear cabinets and in any other place reserved for the installation of switching devices.