To understand why difavtomats are needed, first of all you will need to familiarize yourself with the purpose of the protective devices used in existing electrical networks. These include varieties such as circuit breakers and residual current circuit breakers. In addition, universal circuits replacing them under the general name "differential automaton" are installed in power circuits.
What is a differential automaton and how does it work
Difavtomat is a combined device in the body of which two devices are combined at once - a circuit breaker and an RCD. The machine, like all other products of this class, is triggered by overload and short circuit on the line. The RCD circuit works on the principle of comparing current components flowing through its coil in the forward and reverse directions. In case of violation of the equality of these values, the differential signal is supplied to the executive relay, which disconnects the emergency section of the power circuit in a split second.
The combination in one case of two functionally interconnected devices provides the following advantages:
- the ability to reliably protect power lines from overloads, short circuits and dangerous earth leakage currents;
- their use as devices for protection against electric shock;
- space saving when mounting on a DIN rail (two seats instead of three);
- price gain when comparing with the separate use of modern models of machines and RCDs.
The only drawback relating only to electronic modifications is considered to be the loss of performance when the zero bus is broken. In this case, the phase core remains energized, which under certain conditions can lead to electric shock.
Difavtomats are installed like conventional devices immediately after the electric meter. Each of them ensures the safety of a separate supply line. By their functional capabilities, these devices completely replace the devices replaced by them; the principle of operation of the difavtomats is the same.
Types of difavtomatov
By the number of simultaneously serviced phases, all differential automatic machines are divided into single-phase and three-phase devices. The first of them are installed in 220 volt networks by supplying phase and neutral wires to them.
According to the requirements of the PUE, conductors supplied to bipolar devices should only be connected to the upper terminals.
Phase and zero conductors connected directly to the consumer (to the load) will be connected to the lower contacts. The need to enter two buses at once is explained by the requirement of operation of a differential device for protection against current leakage. Depending on the brand of device used and the series, two or more places will be required for mounting on a DIN rail.
For installation in three-phase networks of 380 Volts, 4-pole difavtomats are used. Three phase wires and a zero bus are connected to their upper terminals from the side of the electric meter. And from the lower terminals in the direction of the load depart three working conductors and zero.
In accordance with the design features and the internal circuit of these devices, they are all divided into electromechanical and electronic samples. In the first models, the separation of the differential current and tripping is carried out in a combined way, and in the second models, the built-in electronics is “responsible” for this.
According to the possibilities of protecting the power supply line from a dangerous potential, all known types of difavtomats are divided into devices connected to the grounding device and dispensing with it.
Parameters of residual current machines
The universality of differential automata, which allows combining the functions of two devices at once, is explained by their design and the capabilities embedded in them. The main parameters characterizing a differential circuit breaker include:
- type of electromagnetic release;
- rated current at which the device can operate for a long time;
- performance indicator and operating voltage;
- earth leakage current;
- breaking capacity and current limit class.
 The releases used in devices of this class are conventionally divided into main and auxiliary devices. The first of them belong to the circuit breaker and can respond to overcurrents, completely disabling the switching circuit. The second type of releases (circuit breakers) allows you to expand the functionality of the protective device.
The releases used in devices of this class are conventionally divided into main and auxiliary devices. The first of them belong to the circuit breaker and can respond to overcurrents, completely disabling the switching circuit. The second type of releases (circuit breakers) allows you to expand the functionality of the protective device.
Usually it is installed only in special devices made to order, which can be:
- independent type with the possibility of remote shutdown by a special signal;
- minimum voltage - triggered when it falls below an acceptable level.
- zero potential devices.
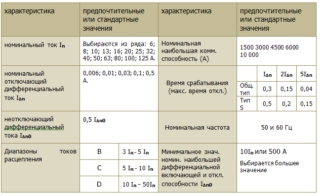
According to the current indicator, all known samples of difavtomats, like AB, are divided into a number of devices that have strictly normalized values from the following series: 6, 10, 16, 25, 50 Amperes, etc.
In addition, a current indicator indicated by the letters “B”, “C” or “D” is used in their marking. They are located in front of the marking code of the rated current (amperage) and indicate the speed of this model.
Another group of technical characteristics includes the trip current of the RCD circuit (differential indicator), called "leakage". For most samples of circuit breakers, these values fit into the standard series: 10, 30, 100, 300 and 500 milliamps.
On the case of a typical device, leakage currents are indicated by a “delta” icon with the corresponding number.
The following characteristic of protective diflift machines is the value of the operating voltage at which they are able to function in normal mode: 220 Volts for single-phase circuits and 380 Volts for their three-phase analogues. Its value is indicated under the denomination or under the key of the device.
According to the leakage current and the selectivity index, the known types of differential current switches have the following notation:
- “A” - samples reacting to leakage of alternating (ripple) current.
- "AC" - models of electric machines that are triggered by leaks with a constant component.
- "B" - a combined option that combines both of these features.
The characteristic "type of RCD" is indicated by an alphabetic index or a symbolic pattern.
By analogy with AB, difavtomaty work when overloaded in the wiring according to the selective principle, taking into account the time delay. This approach allows you to disconnect the network selectively at the maximum current and provides good electrodynamic stability of the entire protective system. According to this most important indicator for human safety, differences of differential current devices are taken into account by the following icons:
- the “S” symbol, meaning a delay of approximately 200-300 milliseconds;
- the English letter "G" (a temporary pause of 60-80 milliseconds).
The operating conditions of single-phase electric machines are determined by the place of their placement in the control cabinet on a DIN rail. According to the requirements of the manufacturer, humidity and air temperature, as well as dustiness in the room where the cabinet is located, are subject to regulation.
Electronic or electromechanical
To select a suitable model, you first need to decide what type of machine to choose: a traditional electromechanical or a more modern electronic one. The right choice will help familiarity with the features of each of these performances.
Electromechanical machines
These models are non-volatile, that is, they retain their functionality even in the absence of electricity. In contrast, electronic models can only work if there is a supply voltage consumed for own needs.
In the first samples, the following electrical and mechanical components are “responsible” for disabling and generating useful signals:
- electromagnetic circuit breakers;
- thermal releases;
- inductive coils emitting differential current;
- electromagnetic relays and other modules.
All these elements have nothing to do with electronic circuits and work at the expense of their own energy reserves. For the operation of a difavtomat of this class, a leakage current or short circuit in the serviced line is sufficient.
Electronic variant
Electronic devices need additional power supply and have greater speed in comparison with their electromechanical counterparts. An electronic circuit, usually assembled on a microprocessor or transistors, is “responsible” for isolating the differential currents and generating control signals in them.
This circuit is conventionally called electronic, since electrical nodes are still present in it.
To isolate leakage currents in these devices, a differential transformer of electromagnetic type is used, and to disconnect the power circuit, a relay of the same class is used.