Regardless of which building is being designed: residential, industrial, or related to cultural use, it must have water supply and sewage systems. In this case, both networks are designed at the same time, because the amount of water used will be calculated sewage capacity. The water supply network itself is divided into two parts: internal and external water supply. The first part is the piping inside the building. The second is from the source of water intake to the building. In this case, the external wiring is laid according to State standards.
Water sources
In private housing construction, water sources can be: central water supply networks, open reservoirs, dug wells or drilled wells. In addition to the first position, in all other cases a water treatment system is organized, which includes a set of filter elements that provide water purification.
The ideal option is a central water supply, which provides houses with already purified water. But if the pipes of the system have been used for a long time, the processes of metal corrosion have affected them. Therefore, the installed coarse filter will solve this problem.
Increasingly, in private housing construction, wells or wells are used for water intake. Because the water in these hydraulic structures is cleaner than in open water. But this does not affect the design features and methods of laying an external water supply network.
Building regulations
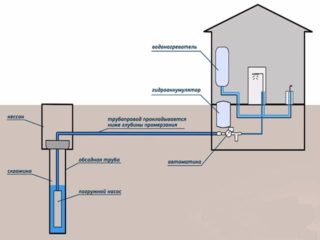
First, design a scheme for laying external water pipes. It depends on the location of the house relative to the source of water intake, on the number of consumers, for example, if, apart from the house, the water supply network extends to the summer kitchen, bathhouse, garage, pool and other facilities. The more the latter, the more complicated the wiring diagram.
It is also necessary to consider the amount of fluid consumed. It depends on the number of people living in the house. It is taken into account that 200 liters of water or 0.2 m³ should be allocated per person per day. From this indicator depends on what diameter of the pipe should be used, what power the pump should be installed. At the same time, the latter must determine the pressure - to what height the pump unit can raise water. Raising water from a well or a well is energy costs determined by the technical capabilities of the pumping equipment.
Other building codes:
- The straight-line laying of water pipes from the source of water intake to the house is a priority. Deviations from the straight line are not prohibited if there are insurmountable obstacles on the way. For example, a tree, a built object, etc.
- Laying is best done below the level of freezing. This is not a strict norm, because pipes can be insulated, since the market offers several effective and inexpensive technologies.
- If water supply is organized from central networks, a well should be organized near the connection point. A shut-off valve and a water meter are installed in it. The well must be insulated so that neither the pipe nor the water meter freezes in winter.
- Wells and wells that are sources of water intake should be located at a distance of 50 m from cesspools, gutters, septic tanks, and filtration fields.
Given all the requirements, it is important to carry out the design correctly.Pipes are selected according to the diameter of the product and the material from which they are made.
Pipe selection
 The best option for pipes for external water supply is made of low pressure polyethylene (HDPE). Specifications:
The best option for pipes for external water supply is made of low pressure polyethylene (HDPE). Specifications:
- high ductility, hence the ability to lay water pipes without using additional fittings;
- low abrasion;
- high strength;
- withstands water temperature up to + 40С;
- not subject to corrosion;
- in the process of freezing, polyethylene does not crack and does not deform;
- service life - 50 years;
- low price;
- ease of installation.
Pipes are sold in bays 50 or 100 m long. When purchased from a bay, the required quantity can be cut off.
Installation Steps
The organization of external networks and water supply facilities begins with marking on the ground exactly according to the finished project. Next is the excavation. The depth of the formed trenches is also indicated in the design. The width should be 0.5 m greater than the diameter of the pipe being laid.
If the soil at the construction site is loose, the bottom and walls of the trench are leveled, compacted. Before laying the pipe, the bottom is covered with a layer of sand with a thickness of 10-20 cm, which is also leveled and compacted.
Pipes are laid out in trenches. At the junction of pipe sections, for example, branches, a pit is made at the bottom of the trench. The very process of joining pipes is carried out in two ways: using fittings or welding. If the pipe used has a diameter of more than 150 mm, the connection is carried out by flange fittings.
Most often they use welding technology: butt welding and electrofusion. Joint to joint is the most effective way by which maximum joint strength is achieved. But if the diameter of the laid pipes is less than 63 mm, the best option is electrofusion welding.
After completion of installation work, the water supply is insulated. For this, special cylinders are used, they are also shells made by pressing various thermal insulation materials: mineral wool, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam and so on. Insulators of this type consist of two or three parts, which surround the pipe and fasten together with a knitting wire or clamps.
Another option for thermal insulation of an external water supply is a heating cable. It is under a slight voltage all the time, therefore it constantly gives off heat. The only drawback is volatility.
Plumbing testing
Any pipe connection cannot guarantee 100% leakage protection. Therefore, the water supply network is tested before installing thermal insulation. The algorithm of ongoing processes:
- the entire water system is filled with water without pressure and is in this state for 2 hours;
- pressure is created inside the pipes, which is maintained for half an hour;
- check the water supply for leaks, special attention to the joints.
The final stage after the installation of the insulating material is filling the trenches with soil. It is preliminary recommended to fill the pipe with sand with a layer thickness of 15-20 cm, then fill the trenches with the selected soil. Without fail, the water supply system is washed until the water becomes clean at the outlet.