In preparation for drilling a well, it is advisable to conduct preliminary exploration work. They help to find out at what distance from the earth's surface layers saturated with moisture are located. A map of the occurrence of aquifers in a particular region is useful here. If it is not, the depth of the formation can be determined by the type of vegetation from above and the type of selected rocks during drilling.
What is an aquifer?
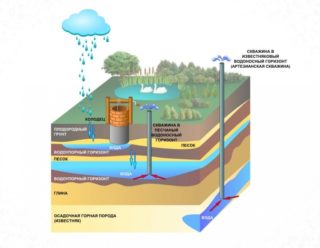 An aquifer is a plot of soil horizontally located in the earth’s thickness, in the cavities and cracks of which water moves. It is for his search that drilling is performed in order to subsequently have access to a constantly productive well.
An aquifer is a plot of soil horizontally located in the earth’s thickness, in the cavities and cracks of which water moves. It is for his search that drilling is performed in order to subsequently have access to a constantly productive well.
All aquifers can be characterized by the following parameters:
- Performance. It is determined in m3 of the volume of the resource per unit time.
- The depth of the roof and the bottom of the horizon (in meters from the surface of the earth).
- The amplitude of the fluctuation of the resource during the year. Depends on the season, temperature, rainfall, atmospheric pressure.
- Power. Thickness of soil saturated with water.
The deeper the hydrogeological formation, the more constant will be its productivity.
Types of aquifers
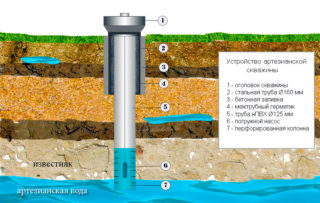 First of all, hydrogeological horizons are divided into two types - non-pressure and pressure. The first are located as close to the surface of the earth and have unstable performance. The second - are localized much deeper. Independent of rainfall or air temperature.
First of all, hydrogeological horizons are divided into two types - non-pressure and pressure. The first are located as close to the surface of the earth and have unstable performance. The second - are localized much deeper. Independent of rainfall or air temperature.
As for the depth of the aquifers, they are classified as they deepen / move away from the surface of the earth;
- High vault. You can stumble upon it as early as 5 meters from the top point of drilling. Saturation of this layer occurs solely due to precipitation. Often in hot weather, the water level here is seriously reduced, or even disappears. In addition, the liquid from the top water absorbs all the pollution from the soil, the atmosphere, close to located industrial enterprises, consumers - everything that is absorbed into the soil with rain or runoff. It is especially dangerous to use a resource from the overhead water, if there are cemeteries nearby, street toilets with a cesspool, complex chemical plants and industrial enterprises. It is important to pay attention to the fact that in the northern regions this horizon is often localized in the zone of soil freezing. Therefore, water withdrawal from here in winter will be difficult. An additional minus of the liquid from the top is the constant presence of oxygen in it. Microorganisms live and reproduce in water.
- Ground water. The layer goes to a depth of about 10 meters. Its main component as a support is clay. It is believed that this aquifer also contains insufficiently clean water, since this depth is still not enough for its high-quality filtration.
- Interstratal waters. The depth of their location can vary from 15 to 100 m. More often they are located between two waterproof horizons. The debit of such layers is stable. But it is important to take into account that the water that has reached the interstratal veins can be oversaturated with minerals, metal salts, which it absorbs all the way down. Therefore, fluid from these horizons requires a thorough analysis and a properly selected filtration system.
- Artesian waters. They are located at a depth of 100 m or more. The water here is as clean as possible, having passed many degrees of natural filtration. According to the law of the Russian Federation “On Subsoil”, artesian wells are under special control of the state.Therefore, a license is required for drilling and further exploitation of such a source.
An artesian well is best drilled for several families or households, since its flow rate seriously exceeds the needs of even 3-5 people.
Aquifer map
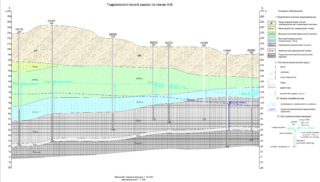 When carrying out hydrogeological studies, special documents must be compiled (including a map of the depths of artesian wells, the top water, interstratal waters) by region or area. In the future, this facilitates the search for the source and selection of equipment for drilling.
When carrying out hydrogeological studies, special documents must be compiled (including a map of the depths of artesian wells, the top water, interstratal waters) by region or area. In the future, this facilitates the search for the source and selection of equipment for drilling.
Each map contains information about the types of groundwater, patterns and their depth. Also included here are the designations of water confines and all soil layers, the direction of free flows.
The most popular hydrogeological maps:
- Hydroisogypsum. It is created for pressureless formations. It shows the system of movement of flows in aquifers. With the help of such schemes it is possible to understand what is the slope and direction of the water, where the formation is fed or unloaded, where it meets natural reservoirs.
- Hydroisopiesis. They are performed according to available accurate data. The piezometric surface is derived for artesian sources. By it is meant the height to which water is able to rise in an opened well. According to this indicator, the total length of the casing string is selected.
- Map measuring groundwater level.
- Documentation on hydrogeological sections.
- Maps of the amplitude of fluid levels in sources.
Such schemes and documents can be found in the local archives of the village. If new, previously uninhabited territories are being developed, new hydrogeological maps are compiled for them.
How to determine the water level while drilling
 Knowing folk methods and signs, you can determine the aquifer when drilling wells for water with your own hands, even without special equipment. Experienced craftsmen recommend paying attention to the vegetation in the area where the work is being carried out, since in places of close proximity to underground moisture, even in the dry season, juicy, lush greens grow abundantly. The results should be interpreted as follows, depending on its variety:
Knowing folk methods and signs, you can determine the aquifer when drilling wells for water with your own hands, even without special equipment. Experienced craftsmen recommend paying attention to the vegetation in the area where the work is being carried out, since in places of close proximity to underground moisture, even in the dry season, juicy, lush greens grow abundantly. The results should be interpreted as follows, depending on its variety:
- cattail is located where there is a topwater depth of 1-1.5 m;
- bulrushes love places with an underground layer at the level of 1-3 meters, here poplar black prefers to be located;
- sarsazan takes a fancy to zones with an underground water level of up to 5 m;
- wormwood is less whimsical and can grow freely where the layer lies 7 meters from the surface of the earth;
- sand wormwood loves places with the location of aquifers at the level of 9-10 m, it is at this depth that a well-needle is made for irrigation, the use of the resource for technical purposes;
- alfalfa feels good at a 15-meter depth of an underground aquifer.
If there are plants with a powerful root system on the site, then the level of water resources is deep. If plant crops have small roots, underground strata are not far from the surface of the earth.
You can find out the depths of water for a well by the type of sand selected during drilling. If grains of sand are large, the layer is removed by more than 8 meters. The finer the grains, the sooner the master will stumble upon an aquifer.
Accurate results from observations alone are not possible. To determine the maximum correct depth of the hydrogeological point, it is advisable to contact specialists.
How to know the depth of an already drilled well
To determine the level of the location of the aquifer, you can use the following tools:
- Special logging cable equipped with a measuring roller. Its calibration is based on the following principle: 1 meter of depth is equal to one unwinding.
- Depth meter IUGS. With its help, you can find out the angle and depth of the source due to the echo sent and reflected from the bottom of the well.
- Roulette hydrogeological RGLM. It can be used to measure up to 50 m depth.If there is no such roulette, they simply use a cord with a load (cobblestone or metal element).
When drilling a source mine, it is important to distinguish a quicksand from a real aquifer. The first has a large amount of clay in the drawn water and is difficult to drill.


