When constructing an autonomous water supply network for a private house, you need to think about a sufficiently large number of parameters that will make the water supply network a network that works for a long time and does not require large maintenance costs. One of the important factors is the speed of movement of water in the pipelines of water supply.
Why speed should be a certain value

If the speed is insufficient, undissolved particles that come with water from the well or well will settle on the pipe walls. This will lead to siltation and a reduction in the bore. As a result, the pressure and productivity of the entire system as a whole will decrease.
If the water velocity in the water supply is large, this leads to an increase in the pressure of the pumped liquid on the pipe walls and their joints. It is likely that a leak will occur at some point in the pipeline.
Typical Speed Values
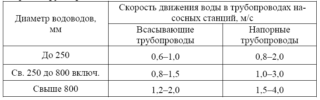
There are recommended values for the water flow rate in the water pipes, which depend on the material from which the water pipes are made, whether they are new or have already been in operation. Here are a few dependencies to help you make the right choice.
|
Pipe diameter mm
|
Speed in a plastic pipe m / s
|
Speed in a steel pipe, m / s | |
| new | the old | ||
| 50 | 22 | 0,7 | 0,062 |
| 100 | 11 | 0,74 | 0,068 |
| 200 | 7,6 | 0,82 | 0,076 |
The speed directly depends on the diameter of the pipes. Moreover, any liquids moving through pipes obey the laws of physics. In plumbing, these laws seek to stop the movement of water. The force that is applied to this is called the resistance force. It leads to pressure losses, and, consequently, to a decrease in speed.
Usually, the formula for the flow rate of water in pipelines, as such, is not used anywhere. Because it makes no sense to calculate what has already been proven and is freely available in the tables. It is taken as the standard recommended value.
The parameter of water flow rate in pipelines is used to calculate several characteristics of the water supply network. For example, when calculating the flow of water or choosing the diameter of the pipes.
Water supply should be understood as a network of drinking water, hot water supply and fire protection system.
Calculation Examples
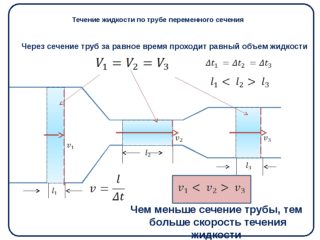 More often, the flow rate or pipe diameter is calculated using speed. To do this, use the formula:
More often, the flow rate or pipe diameter is calculated using speed. To do this, use the formula:
W = V × Swhere W - expense V - speed, S - sectional area of the selected pipes.
According to one of the tables, the speed of water movement is selected. If it is a fire water supply system, this parameter must be within 3 m / s. Quite a large value, but for a water supply system of this type, the value is averaged, and sometimes more.
For example, you need to calculate the cross section of the pipe. To do this, you need to additionally determine how much water will be consumed through the sprinklers or drenchers of the fire system. This is also a tabular value, depending on the protected area of the building or structure. Let it be a fire system in one stream, in which the flow rate is usually 3.5 l / s or 0.0035 m³ / h.
Knowing all the required parameters of the water supply, it is possible to calculate the cross section of the pipes that will be mounted in the network:
S = W / V = 0.0035: 3 = 0.0012 m².
Knowing the cross section of the pipe, you can calculate its diameter. The area formula is as follows: S = πD² / 4, hence the diameter formula:
D = √4S / π = √ (4 × 0.0012: 3.14) = 0.0038 m or 38 mm. There is no such value for the diameter of the pipes, so you need to choose a standard larger - 40 mm.
This is the simplest example.In reality, most water supply systems are complex schemes in which there are taps, connected sections, installed shutoff valves and other obstacles that reduce the speed of movement of water in the water supply system. At the same time, pumping stations are installed in many networks, which form the capacity and pressure. Often, how many pumping units are installed in the system, which operate alternately: two, three, one at a time, in different on and off sequences.
In such cases, the calculation is carried out stepwise, for each section separately. At the same time, additional coefficients that level the obtained values, as well as the pressure loss at the fittings and in the places where the shut-off valves are installed, are necessarily taken into account.
Flow rate
 The water velocity in the pipe has two values: at the walls it is zero, at the axis - the maximum parameter. The farther from the axis, the weaker the water moves.
The water velocity in the pipe has two values: at the walls it is zero, at the axis - the maximum parameter. The farther from the axis, the weaker the water moves.
If we consider the cylinder along which the fluid moves as an imaginary model, we can say that no forces will act on the water inside the pipe. But in reality, this is not so. The first force that acts on the water flow is the friction force on the inner walls of the pipeline. It decreases with distance from the walls.
The second force is the pumping force acting from the pump in the direction of flow. If this parameter is always unchanged, the flow of fluid inside the pipe occurs laminarly. The speed remains unchanged, at the walls it is zero. This is an ideal situation.
In practice, this rarely happens. There are many factors for this, for example, turning the pump on and off, clogging of the filter, and so on. In this case, at the walls of pipelines the speed changes dramatically: more or less, sometimes with a huge difference. In the rest of this characteristic changes less.
Many online portals offer calculators with which you can calculate the flow rate of a fluid passing through a cylinder. This will require only two parameters:
- pipe inner diameter in mm;
- the performance of the water supply system, or rather, the volume of fluid passing through the pipe over a certain period of time (m³ / hour).
But such calculators do not take into account the material from which the pipes are made, as well as the presence or absence of fittings, additional circuits and valves. These settlement services can be taken as a basis, but you should not expect the exact value from them.
Solving the issue related to the speed of movement of the water flow inside the water supply network, it is necessary to clearly determine the complexity of the system, the productivity of pumping stations and the types of pipes used. The easiest way is to select this value according to the table in which the indicators have long been calculated and are guaranteed to be reliable.


