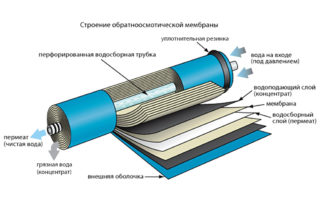
A reverse osmosis filter purifies water by passing it through a low-permeability membrane under pressure. Purification is used in domestic and industrial conditions to return to water qualities suitable for drinking and consumption in household needs. After setting up new equipment, the filtration proceeds in the current operating mode, but over time the elements become clogged with garbage and the system performance noticeably decreases. To restore the power level of osmosis, membranes are cleaned.
Signs of membrane fouling
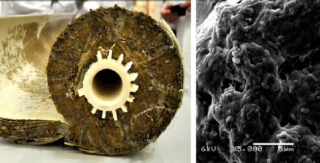
 The flushing frequency of the system depends on the level of total contamination of the incoming water. The worse the water, the more membranes become clogged. If you have to clean more than once every two weeks, you must install a pre-filter.
The flushing frequency of the system depends on the level of total contamination of the incoming water. The worse the water, the more membranes become clogged. If you have to clean more than once every two weeks, you must install a pre-filter.
To return the osmotic filter performance to its initial level, it is recommended to flush the membranes with reagents containing acids and alkalis in order to clean from accumulated dirt. With the help of professional compounds, silt deposits and accumulations of an organic nature formed during the operation of the system are removed from the surface of the filters.
The membrane in the reverse osmosis filter is located in the body of the cleaner. Quantitative capacity can be from one to seven pieces. Structurally distinguish:
- spiral wound
- fiber.
The most popular are spiral elements. By type of assembly, they are a pair of membranes wound on a central outlet pipe. With constant work after a certain time, a decrease in productivity becomes noticeable, loss of the required high-quality composition of purified water, or a large pressure drop across individual membrane elements. All these indicators speak of blockages.
The types of deposits on the filtration elements differ in their physico-chemical qualities and the method of formation. The most common are:
- Cretaceous deposits. The main sign of calcium carbonate contamination is light plaque at the edges of osmosis membranes. It happens yellow or beige, rarely white. This type of plaque is neutralized by hydrochloric acid and is accompanied by weak drilling. When sludge contains only calcium carbonate, the precipitate completely disappears, and the solvent does not change color. The color transition and the appearance of foreign fractions suggests that other substances were also contained in the plaque.
- Gypsum deposits. Calcium sulfate plaque most often comes from filtering sea and underground brackish water. After the formation of the first crystals on the membrane against the background of constant replenishment with foreign substances, a chain reaction occurs, pollution cannot be stopped. Symptoms by which calcium sulfate deposits are recognized are a light colored layer, as is the case with Cretaceous deposits. The difference lies in the fact that the clogging of the filter elements occurs much faster, and the substances cannot be dissolved by hydrochloric acid.
- Iron oxide. A brown coating remains on the membrane, the origin of which is still not reliably understood. Presumably, contamination occurs due to the fact that some bacteria leave particles of iron hydroxide on the membranes.
- Silicon deposits. During the polymerization, insoluble silica gel is formed, which enters into a chemical reaction with iron, calcium and other substances. The rate of rise of plaque increases with the influx of contaminated water. Resistant plaque cannot be removed.
- Biological trash.Black plaque is caused by mold, mildew or accumulation of sludge. Bio-pollution often accumulates in the form of mucus and film on the membrane or body of the filtration system. Such raids are dangerous in that, destroying the elements, they can get into drinking water and cause various diseases.
Biological plaque is fixed on the filters due to physical properties: roughness, hydrophobicity and surface charge. After stopping, bacteria begin to secrete polysaccharides, which leads to an increase in colony growth and increased pollution.
To prevent the appearance of biological contaminants in reverse osmosis, it is necessary to strictly monitor the purity of pre-filtration systems. The likelihood of bacterial growth increases during downtime. In industrial installations, when water treatment is delayed for a day, all membranes involved in production are seeded. To remove infection, it is necessary to carry out a complex of disinfecting measures using chemical preparations.
Symptoms for all types of pollution are:
- a general decrease in the performance of the reverse osmosis system to 20%;
- deterioration in the quality of clean water;
- significant, up to 20%, pressure difference between contaminated water and permeate.
To restore system power, it is recommended to clean the reverse osmosis membrane using chemicals.
Effective membrane flushing methods
When using reverse osmosis filtration, consumer health depends on the quality and purity of the membrane. There is a mechanical and chemical flushing.
Mechanical is carried out by changing the pressure of water in the opposite direction, which leads to the expulsion and removal of plaque. In industrial filters, such manipulations are carried out up to five times per hour for up to 30 seconds. The result achieved by machining is affected by the flow rate of the volume of incoming water. The higher it is, the better the cleaning.
Before carrying out chemical washing, it is necessary to establish the type of pollutant. Often the situation is exacerbated by the presence of different types of plaque, which leads to the use of cleaning in several stages using solutions of different acidity.
To clean the osmosis used at home, you must:
- turn off the tap on the storage tank;
- close the valve in front of the filter and unscrew the pressure relief valve;
- disconnect the JG tube and inlet fitting, remove the filter;
- rinse the reverse osmosis membrane with citric acid per 1 liter of water, 150 grams of acid, hold for 12 hours and place in the system, performing the steps in the reverse order.
Membrane cleaning in industrial systems consists of washing with chemicals and disinfection. The substances used must be safe for filters, so you need to determine in advance the necessary concentration and duration of the procedure.
For systems with low productivity, the pressure change method is used as regeneration. The valve on the concentrate section is unscrewed, which leads to its discharge in significant volumes and the removal of a large percentage of contaminating plaque. Application of this method on powerful installations is not always possible. To carry out high-quality cleaning, you must:
- analyze the composition of the incoming water;
- to monitor the condition of the equipment;
- select the desired type of washing solution and its concentration;
- set the frequency and duration of washing;
- remove residual solution from the membrane by washing.
The use of a reverse osmosis filter requires strict adherence to operating conditions. Therefore, cleaning the membranes is necessary to ensure the smooth operation of the system and to prevent the appearance of contaminants.