More and more city dwellers prefer to spend a weekend away from the noise of the metropolis, in the lap of nature. But, before building a country estate, it is worth paying attention to the availability and quality of groundwater in the selected area, especially if it cannot be connected to the central water supply.
What is an aquifer?
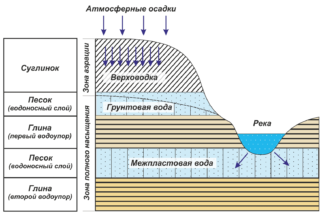 On different soil layers there is soil that can pass and store water in one way or another. It is he who is called the “aquifer”. Some of them are suitable only for household or industrial needs, others can be used to produce drinking water, others supply healing mineral water, others even contribute to the generation of electricity. Depending on the location of the aquifer, water from it can be obtained by placing a well, well, or even a powerful pump. The deeper the water, the harder it is to get it, and too deep wells are not required for everyday use.
On different soil layers there is soil that can pass and store water in one way or another. It is he who is called the “aquifer”. Some of them are suitable only for household or industrial needs, others can be used to produce drinking water, others supply healing mineral water, others even contribute to the generation of electricity. Depending on the location of the aquifer, water from it can be obtained by placing a well, well, or even a powerful pump. The deeper the water, the harder it is to get it, and too deep wells are not required for everyday use.
Types of aquifers
Soil water
A layer called a “top water” consists of gravel or sand. It is located at a depth of 1 to 4 meters from the surface, but is not available in any area. Due to the uneven size and chaotic arrangement of large and small particles of soil, water is retained in the resulting pores. It gets there by filtering sediments or water from reservoirs with the upper layers of the soil. There are several disadvantages from the point of view of a person in a leader:
- She is fickle. The presence of this layer may depend on location, season, weather and other external conditions. Accordingly, it cannot be counted on as a constant source of water.
- The high vodka is not suitable for drinking water. Typically, water from the upper aquifer is saturated with organic contaminants.
- It is not enough even for constant watering.
- The presence of this aquifer is rather a minus for the site than a plus. Where there is a sand and gravel layer that can accumulate moisture, it is difficult to lay a strong and durable foundation for the building - it is likely that the building will “float” in the coming spring, along with melting snow.
Ground water
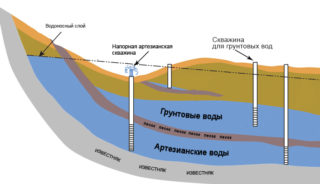 Unlike the water trap, groundwater is constant: they are everywhere, only the depth of their location and quantity differ. Water passing through the upper layers of the soil accumulates in the cavities that have become between the layers of continuous water-resistant deposits. Groundwater is replenished from water bodies, from rainfall and snowmelt. Such water is much more suitable for household and industrial needs, but the location of the aquifer should also be considered when building a building.
Unlike the water trap, groundwater is constant: they are everywhere, only the depth of their location and quantity differ. Water passing through the upper layers of the soil accumulates in the cavities that have become between the layers of continuous water-resistant deposits. Groundwater is replenished from water bodies, from rainfall and snowmelt. Such water is much more suitable for household and industrial needs, but the location of the aquifer should also be considered when building a building.
Wells built on groundwater can provide:
- Household needs, such as washing, watering, washing cars or equipment.
- Everyday needs - this water can be drunk and used for washing dishes, but only after thorough filtration and boiling.
Interstratal waters
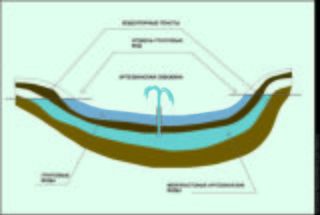 Under a layer of groundwater, separated from them by impermeable or poorly permeable rocks, there is an inter-layer aquifer. Water accumulates in cracks and cavities, where it gets through the infiltration of groundwater through poorly permeable layers of soil. Interstratal waters are pressure water and are used for:
Under a layer of groundwater, separated from them by impermeable or poorly permeable rocks, there is an inter-layer aquifer. Water accumulates in cracks and cavities, where it gets through the infiltration of groundwater through poorly permeable layers of soil. Interstratal waters are pressure water and are used for:
- Household and industrial needs.
- Recreational purposes (mineral water).
- Generation of electricity (geothermal water).
Interstratal waters are renewable natural resources; accordingly, in addition to drilling and equipping, you will also need to resolve the issue with permission to drill and register a well in its area.Such a well may be needed to obtain drinking water or its own mineral spring.
How to find an aquifer
Folk methods
 First of all, attention should be paid to the root system of plants common in the study area. The deeper the roots go, the farther the aquifer is from the surface.
First of all, attention should be paid to the root system of plants common in the study area. The deeper the roots go, the farther the aquifer is from the surface.
The second ancient and intuitive way is to observe natural phenomena: where the water is closer, its evaporation will be higher, which means that the morning summer fog will be thicker than in other places.
The third method has great accuracy - it is necessary to place 1-2 liters of absorbent material in clay dishes, for example, dried silica gel. Dishes with silica gel should be weighed, after which, tightly covering with a cloth, bury in the ground to a depth of two meters. After a few days, the silica gel absorbs a certain amount of moisture from the soil, and the heavier our pot becomes, the closer it was to the water.
Popular way
To this day, the method of searching for groundwater with the help of “frames” does not lose its popularity - aluminum wire bent at a right angle 10 centimeters from the edge. 40-centimeter wire cuts will require two, they are loosely located in the “arms”, the purpose of which is the free movement of the “frames” in the hands.
When searching for water, the frames should be kept in front of you at a small distance - so that the ends of the wire look straight ahead. With careful movement around the site, you can notice that in one or more places the frames will begin to move in opposite directions, in order to eventually intersect. The place indicated by the “cross” of these frames is most likely more suitable for the location of the well than all others.
Modern way
Today, trial drilling is used to determine the depth of soil and groundwater. The drill may have a small diameter and corresponding marking. If you need to detect soil water, then a diameter of 10 centimeters is enough. To get to the ground, you need a larger drill - up to 20 centimeters in diameter. Usually for household needs there is enough depth of 4-6 meters, for drinking water - up to 18 meters.
Determining the depth and quality of groundwater can help not only properly position a well or well, but also lay the long-term foundation of a country house or manor. Water is necessary for man, but only proper handling of it is safe.


