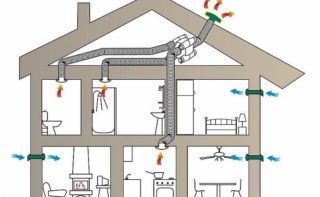
The proper operation of ventilation equipment depends on the location of the ventilation pipe. The height of the ventilation ducts above the roof must be calculated correctly. Low location will lead to reverse draft and polluted air will go back to the room, and not from it. Too high an arrangement of the duct will make the heating of the home ineffective. Warm air will go out too quickly and chill the room. The efficiency of the heating system and the change of atmosphere of the house depend on the calculation of the height of the ventilation duct.
Methods for calculating the height of the ventilation pipe above the roof
Most builders plan work on the basis of the main SNiP documents:
- No. 41-01-2003, p. 6-6-12. The document regulates the rise of chimneys.
- No. 2.04.05-91. The design of the hood in the old edition is considered.
- SP No. 7.13130.2009. Here are prescribed methods, design rules for ventilation, air conditioning.
- No. 2.04.01. Describes the outlet height for sewer risers.
There are two ways to search for the minimum height of the chimney remote from the ridge of the roof:
- Graphic. The height of the chimney section above the roof is determined by geometric constructions.
- Mathematical. The size of the outer portion of the pipe is calculated using trigonometric formulas.
Need for ventilation
The volume of transported air inside the room, the degree of heating of the room depends on the height of the ventilation duct.
From ventilation depends:
- The need for fresh air is one of the basic in human life. Efficiency, metabolism, comfort depend on it. The percentage of oxygen cannot fall below established standards. Particularly specified is its content in dormitory rooms.
- Removal of harmful substances, combustion products, smoke of the room.
- Removal of harmful suspensions, gases and impurities.
- Removing excess moisture and dust from the room.
- Reducing fire hazard by removing flammable gases and compounds. For these purposes, air handling units are the most technologically advanced, with an active spark suppression system, explosion protection, working together with gas and temperature sensors.
Reducing the intensity of ventilation increases the room temperature during heating. Accelerating the airflow reduces the temperature, decreasing the heating efficiency.
The first mechanical fan was the English Parliament steam fan. Its installation was recorded in 1734. This moment is considered the beginning of the development of ventilation systems.
Types of ventilation
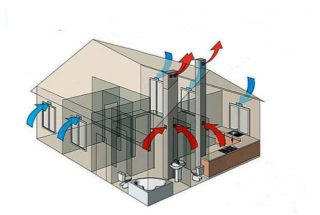
Air exchange systems are needed to provide fresh air to residential, industrial, storage facilities, and venues for public events. For the influx of fresh air and the removal of exhaust, there are 2 main types of ventilation - natural and forced. Mixed methods are sometimes used. Specific methods for cleaning indoor air are made on the basis of calculations according to the technical specifications. The terms of reference take into account the maximum number of individual factors of influence and requirements for air purity.
Natural
Natural ventilation is caused by the movement of air currents due to differences in temperature and density.Warm air has a lower specific gravity, rises up and is removed through special ventilation ducts or leaks. Cooler and heavier air descends. This method has positive and negative sides.
The plus is the simplicity and lack of additional energy. The absence of connected fans at high electricity prices is an obvious positive effect.
The disadvantages of natural ventilation are more:
- The difficulty of adjusting the rate of air exchange is highly dependent on natural conditions.
- The possibility of reverse thrust. This factor can be dangerous if ventilation is installed near boilers. The combustion products are pulled back, which negatively affects people's health and the functioning of the equipment.
In rooms with a sophisticated air conditioning system, natural ventilation is not in demand. The advantage is given to the mechanical hood.
Forced
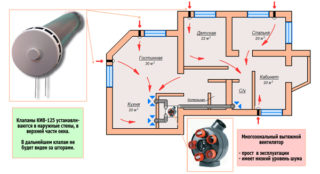
In new buildings, state standards require the use of forced hoods. Air movement is provided by axial or centrifugal fans. According to the statement of work, exhaust pipe length parameters are selected for better traction and equipment power.
Advantages of forced ventilation:
- air flow adjustment in direction, height, power;
- creation in one room of different zones for air exchange;
- exclusion of drafts and "dead" zones;
- the possibility of autonomous functioning.
Negative points:
- installation complexity;
- Energy consumption;
- the need for periodic maintenance, audits, inspections;
- search for service professionals;
- power reserve negatively affects the cost of the entire system.
The forced system is able to exactly match the specified parameters. It is divided into three types - supply, exhaust, supply and exhaust.
The main parameters affecting the height of ventilation ducts above the roof
To create the right microclimate, the house needs to be equipped with an air circulation system. Ensure proper operation will help the correct height of the ventilation shaft above the roof. Calculation methods depend on the type of ventilation. The following factors affect the size of the outside of the ventilation ducts.
- The shape of the ventilation duct. Often a combination of square and round is carried out.
- The volume of air flow. It is carried out through a window, a special supply valve mounted in a wall or an extension.
- The length of the pipe varies from the shape of the roof, the location of the ridge, the chimney. To calculate it, a multiplicity indicator is applied based on the SNiP rules.
- Requirements of norms and rules for air ducts.
When constructing ventilation ducts, the owner of the premises must notify the operating company.
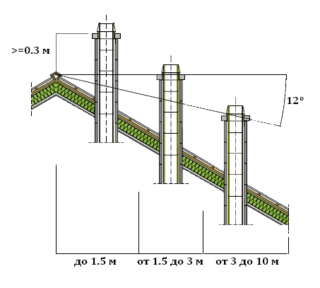
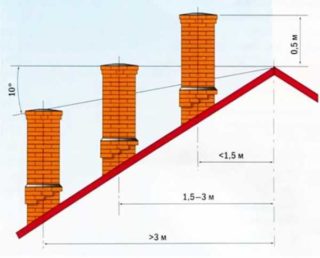
Dimensions relative to the ridge
When the duct is located near the ridge - no further than 1.5 m, the external height of the pipe should not exceed 50 cm. If the ventilation channel is referred to the edge of the roof at a distance of 1.5 to 3 m, it should be flush with the ridge of the house. When the ventilation channel is assigned further than 3 m, its height decreases in relation to the ridge of the house by no more than 10 degrees.
Roof structure
The height of the ventilation pipe above the roof without a slope must be at least 50 cm. The ventilation pipe must withstand a squally wind and a 10-point storm. For this, its weight must be at least 50 kg / sq. m. surface.
Section
In the absence of forced removal mechanisms, a round pipe is the best option. This type of duct is stronger, more airtight, more aerodynamic than a rectangular or square section.
Before calculating the diameter, the following parameters are laid:
- the volume of each of the ventilated rooms;
- air volume for normal circulation for each room.
The diagram calculates the diameter of the pipe after determining the total volume of the premises. In this case, the flow velocity in the central highway should not exceed 5 m / s, and in the lateral - 3 m / s.
Ventilation
No ventilation duct is installed on the outside of the wall, as condensation forms and the flow rate decreases. The inflow volume should be 3 m³ / h per 1 sq. M in the living room. m., regardless of the number of people. According to sanitary standards, temporarily located 20 m³ / h is enough for permanent residents - 60 m³ / h. In utility rooms - from 180 m³ / h.
Fire safety regulations
SNiP rules provide for checking, cleaning chimneys and ventilation pipes as follows:
- before the heating season;
- 1 time in 3 months or more often for combined and brick ducts;
- Once a year or more often for asbestos-cement pipes, ceramic and products made of heat-resistant concrete.
Initial verification evaluates not only the materials of manufacture. It analyzes the absence of blockages, pipe irregularities, the presence of separate smoke and ventilation outlets. SNiP rules prohibit the discharge of combustion products into ventilation channels. Self-cleaning is allowed after training with the receipt of paper on the completion of training.
Calculation of duct diameter and duct height
The calculation of the rectangular or circular cross section of the ventilation duct is carried out in the presence of 2 parameters - air flow rate and air exchange in the premises. With forced exhaust, the air exchange is replaced by the fan power. The parameter is written in the accompanying documents to the product. Air exchange is calculated based on the multiplicity of SNiP for a particular room. The flow velocity in the duct usually should not exceed 5 m / s, but sometimes increase to 10 m / s.
Regulations
During normal ventilation operation, indoor air is constantly updated. According to the requirements of SNiP and SanPiN, norms are established in residential and non-residential rooms, bathtubs, toilets, kitchens, and other special rooms.
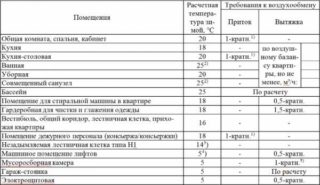
Minimum standards - multiplicity per hour or cubic / h for single-family residential buildings:
- residential premises with a constant presence of residents - at least one volume per hour;
- kitchen - 60 m³ / hour;
- bathroom, bathroom - 25 m³ / hour;
- other premises - at least 0.2 air volumes per hour.
Requirements for the "Code of Practice SP 60" come from the norms for 1 person in premises with a permanent stay:
- with an area of less than 20 square meters. m / person - 30 m³ / hour, but not less than 0.35 volume per hour;
- with an area of more than 20 square meters. m / person - 3 m³ / hour per 1 sq. km. m
The “Code of Practice SP 54" for residential multi-apartment buildings provides other conditions:
- bedroom, living room - 1 exchange per hour;
- cabinet - 0.5 volumes;
- utility rooms - 0.2 volumes per hour;
- sports facilities - 80 m³ / hour;
- kitchen with electric stove - 60 m³ / hour; 100 m³ / h is added to the gas;
- bath, toilet - 25 m³ / hour;
- Sauna - 10 m³ / hour for each visitor.
The rules in the documents are slightly different. The calculation comes from the volume of premises or the number of people. Better to choose the maximum values.
According to the table
A special algorithm allows you to calculate the diameter of the ventilation pipe, based on the table in SNiP. The height of the ventilation pipe above the roof of a private house depends on the diameter and is determined by the cells of the table, where the pipe width is packed in the left column and the height in the top row in mm. This takes into account the location of the house from the ridge, the shape of the ceiling, the remoteness of the ventilation duct from the chimney pipe.
By electronic calculator
A special calculator calculates the norms depending on the entered indicators: the area of the room, the height of the ceiling, the number of people, the type of room. The calculator takes into account the main indicators. It is advisable to conduct several calculations and choose the maximum values for each of the rooms.