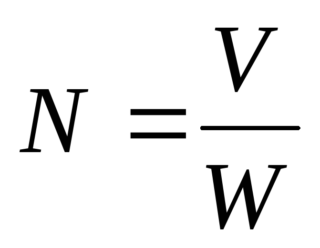Air conversion is an essential hygienic indicator of the microclimate in a room, along with temperature and humidity. The air exchange rate shows the ratio of the volume of air that enters the room or is removed from it in 1 hour (m3 / h), to the total cubic capacity. Air changes in a natural way through the cracks of openings or by the method of organized supply and exhaust ventilation.
What is the air exchange rate
Outside, the atmosphere is always cleaner than indoors. The endogenous space receives air from the street with dust and adds impurities to it from human life. Residents spend about 80% of the time in the house, so the exchange of air with the environment is of great importance.
The multiplicity of air exchange in residential premises shows the intensity of convection of air flows and is determined by the number of exchanges per unit time. It can be calculated by the formula expressing the ratio of the supplied volume for 1 hour to the cubic capacity of the room where it enters. In other words, the multiplicity indicates how many times in an hour the microclimate in the room changes.
Standard indicators of air exchange are prescribed in the documents SNiP, codes of rules. In Russia, the amount of exchange is measured in cubic meters per hour. For a more accurate determination, the calculation of cubic capacity per person is used, according to the volume and area of the room, the amount of clean and the amount of air removed are regulated.
The hood is standardized depending on the functionality of the room. The flow in and out is correlated according to the standard ventilation principle - in clean rooms the flow prevails, and in problem rooms more polluted air is removed.
Calculation Methods
The indicator means how many times it is necessary to change the air in the endogenous microclimate in 1 hour in order to clean it to the maximum MPC (indicator of permissible concentration) of impurities.
The rate of air exchange can be calculated by the formula N = V / Wwhere:
- N - air exchange rate (times);
- V - cubic meter of outdoor air entering the room in 1 hour (m3 / h);
- W - volume of the room of interest (m3).
The method of natural convection usually changes the microclimate up to 3-4 times. For greater value do mechanical ventilation.
The volume of incoming flows, which is intended to dilute harmful impurities and gases to the maximum permissible concentration, is calculated by the formula V = B / (pb - po)where:
- V - cubic capacity of air flow (m3);
- B - the amount of pathogenic substance entering in 1 hour (mg / h);
- pb - MPC of the undesirable component in the atmosphere of the workshop (mg / m3);
- po - concentration of the same component in the incoming stream (mg / m3).
The production uses welding, laser or plasma cutting, soldering of metals with the release of harmful gases. To reduce the concentration, high-quality extraction and ventilation of local areas near the workplace is done. The amount of gas is measured per unit volume using a gas analyzer device.
The scale of the harmful component is calculated by the formula B = a bwhere:
- B - volume of harmful impurities (m3);
- and - leakage rate (for workshops - 1, for garages - 2);
- b - gas ratio in the atmosphere (mg / m3);
- W - cubic capacity of the workshop (m3).
Contaminated streams should be cleaned before being vented out using a filtration system.
Other air exchange calculations
The heat exchange air exchange rate is calculated if there is a large amount of heat in the room that needs to be removed from the room.
The index is calculated by the formula L = 3.6 · Q / (p · c · (t - k))where:
- L - air exchange (m3 / h);
- Q - the heat released in the room (W);
- p - density of internal air (kg / m3);
- c - air heat capacity;
- t - temperature of the removed stream (° C);
- k - temperature of the incoming stream (° C).
The moisture exchange rate of air exchange is determined if a large amount of moisture is released in the room as a result of vital activity or technological processes.
The calculation is carried out according to the formula L = W / (p (d - do))where:
- L - air exchange by humidity (m3 / h);
- W - moisture concentration (%);
- p - density of the internal atmosphere (kg / m3);
- d - moisture content in the removed stream (g / kg);
- do - moisture content in the supplied air (g / kg).
Calculation of air exchange for gas emissions is performed if an accumulation of air impurities is required in the workshop, which must be timely removed outside the premises.
The formula applies L = K / (K0 - K1)where:
- L - required air exchange rate (m3 / h);
- K - weight of emitted gases (m / m3);
- K0 - MPC of gases (from the directory for a specific room);
- K1 - gas concentration in the incoming stream.
Air exchange rates according to sanitary standards (number of people) are determined from the condition of supplying people with the necessary volume of fresh oxygen. For public buildings, 20 m3 / h · people are provided for short visits. For a long stay, it is calculated at 40 m3 / h · people, gyms require air exchange of 80 m3 / h · people.
The value of the ratio of air exchange
Utility rooms in the apartment are among the high sources of microclimate pollution. According to SNiP, outdoor air is supplied to the rooms, and humid and gas polluted air is drawn from the toilet, kitchen and bathroom.
The amount of air to be removed from the premises:
- a kitchen with a gas stove - 90 m3 / h;
- kitchen with electric stove - 60 m3 / h;
- bathroom and toilet - 25 m3 / h.
If the calculated air exchange rates of the required supply and exhaust do not match, the power of the devices is taken at the maximum value. A balance is considered balanced if the indicators are similar. The supply and exhaust system, which uses fewer incoming flows compared to the outlet, has a negative balance, and vice versa.
A system with recirculation is considered economical, while the output streams are partially used a second time after treatment with humidifiers, filters, and cleaners. This reduces costs, but the ratio of harmful impurities should not exceed 30% of the MPC.
Recycling is not used indoors:
- with the release of air impurities 1 - 2 hazard categories;
- in the atmosphere of which pathogens are present in excess concentration or there are pungent odors;
- where there are harmful gases that sublimate during the passage of heaters, if there are no corresponding filters in front of the heating elements.
In laboratories where harmful steam and airborne contaminants are released, ventilation is done so that the air does not enter neighboring rooms after cleaning. For workshops where there is a concentration of explosive additives in the atmosphere, air is removed from the 3 m zone around the source.
Air exchange rate
Air exchange indices vary for industrial workshops, public spaces and residential premises. Modern windows with hermetic double-glazed windows provide only 10 - 20% of the necessary air exchange. In standards and regulations there are indices tied to the area, the volume of the room, the number of people.In different countries, the required values differ, although a person breathes the same way.
The norms of the multiplicity of exchange are given in the documents:
- residential premises - SNiP 2.08.01 - 1989, GOST 30.494 - 1996;
- medical organizations - SP 158.133.30 - 2014;
- kindergartens, schools, institutes, schools - SanPiN 2.4.1.3049 - 13, SNiP31 - 06 - 2009, SNiP II - L.6 - 67, SNiP 2.04.05 - 1986;
- administrative buildings - SP 44.13331 - 2011, SNiP 2.08.02 - 1989;
- baths, saunas - SNiP II - L.13 - 1962;
- Airports, cars and railway stations - VNTP 3 - 81, SNiP 2.04.05 - 1991.
Regulatory values do not take into account that living quarters are empty during the day, and office and work at night. On-site coordination of ventilation or natural ventilation works to save costs.
Normative indicators
When designing the inflow and cleaning system, the purpose of the building, the technical premises of a separate apartment, office or bathroom are taken into account. In housing in the multi-apartment sector, a minimum volume of supplied air of 30 m3 / person is accepted.
Table of air exchanges for the premises of GOST, SNiP
| Name | The rate of multiplicity (m3 / h) |
| Living common room (hall) | 3 |
| Kitchen in an apartment or hostel | 6 – 8 |
| Bath, shower | 7 – 9 |
| Restroom | 8 – 10 |
| Household laundry | 7 |
| Wardrobe and pantry | 1 – 1,5 |
| Garage, cellar | 4 – 8 |
| Cinema hall, theater, conference hall | 20 - 40 m3 per person per hour |
| Office | 5 – 7 |
| A restaurant | 8 – 10 |
| Cafe, bar, billiard room | 9 – 11 |
| Supermarket, trading floor | 1,5 – 3 |
| Auto repair shop workshop | 6 – 8 |
| The gym | 80 m3 per athlete or 20 m3 per viewer |
| Public bathroom | 10 - 12 m3 / h or 100 m3 per toilet |
Rules for creating indoor air exchange
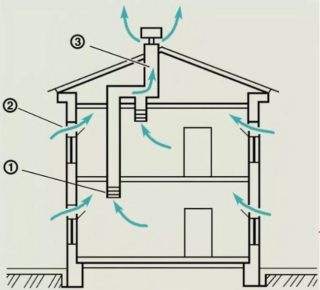
In urban apartments, the scheme of natural and supply and exhaust ventilation is used. The waste streams are discharged through the internal channels in the building through the hoods. The system requires replenishment of the atmosphere with the same cubic capacity of fresh air. External flows come through leaks in window and door openings or when opening transoms and vents.
The natural air exchange system works due to different specific masses of cold and warm air. It matters the wind on the street to create traction in the internal ventilation ducts. In warm weather, the draft becomes less, so many residents put electric fans in the exhaust vents in the kitchen and in the bathroom.
The norms of air exchange in office premises stipulate that interior doors should have a clearance between the canvas and the floor of about 1.5 - 2.0 cm for natural convection or lower transfer grilles. Windows are considered in a single system as supply devices.
Constructive solution
The structure of the canals in the multi-storey sector changes depending on the development of new construction technologies. Previously, individual ducts went from each hood to a common column. The transition to increased number of floors necessitated a bundle of vertical pipes on 4 - 5 floors with horizontal passages, and from them there are channels to a common shaft.
The compact vertical combines 1 - 2 prefabricated channels, the waste stream does not go directly to the output vertical, but is brought there only above the next floor or higher. The design of the pulling shafts in structure resembles a Christmas tree. The design takes up little space, but the structure makes it dependent on weather conditions.
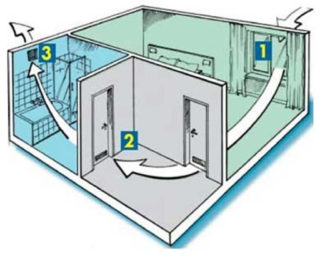
Modern decoration materials in apartments emit harmful substances to the body, sealed windows do not allow enough oxygen. Natural ventilation systems do not comply with sanitary standards applicable to housing. Supply and exhaust ventilation systems are installed in the apartments, which remove air from each room.
In a private building
In a private house, ventilation is provided with a forced supply and exhaust system, as It is necessary to supply fresh air to the boiler room, cellar, kitchen, and other rooms.The microclimate suffers if they put only a hood without organizing an influx. In this case, there is a lack of oxygen. Another mistake is to supply air without forcing. In this case, the internal air is diluted with fresh streams, but odors and harmful components remain in the house.
Artificial ventilation does not allow polluted outdoor air, as filters are provided in the system that eliminate the flow of allergens, bacteria and germs. In the bathroom, integrated ventilation eliminates humidity, in the kitchen removes odor, stuffiness. The equipment operates in automatic mode, controlled manually or by electronic devices. The cost of a forced system is higher than the installation of internal or external channels. To save money, only those functional components of the system that are necessary for a particular house are selected.
The effect of plastic windows on air exchange rate
A rarefied atmosphere is created in the home due to the dense insulation of the metal-plastic window openings and modern airtight doors. Under these conditions, the draft in the sewer can overturn if such a hole is located above the others, in one of the rooms the temperature is higher than the others, or the difference in wind pressure acts.
Modern windows become uncomfortable, breathless and cause trouble in the form of poor ventilation. Many remove gaskets and make extra slots in the frame. This solution gives the result in the form of drafts, heat loss and icing transoms. There is a special solution in the form of prefabricated structural elements that are inserted into the frame for organized control of air passage.