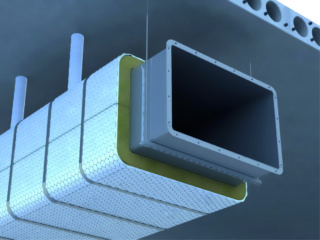
Fire protection of air ducts is an obligatory component of structural solutions used in the installation of modern ventilation systems. The use of materials with increased fire resistance significantly reduces the likelihood of the spread of burning in a fire. Fire retardant compositions are presented on the domestic market with special mastics, varnishes, as well as special dyes. For ventilation fire protection, fences made on the basis of basalt and other components are also used.
Ventilation and smoke removal requirements
A list of fire safety requirements for fire protection of ducts can be found in the rules SP7.13130.2013. When arranging ventilation systems, the combustibility parameters of flame retardants are taken into account, as well as their compliance with the object category: residential building, industrial premises, etc.
In addition, the following points are taken into account:
- fire resistance limit of the material of the air ducts themselves;
- climatic factors (temperature, in particular);
- requirements for the serviced premises.
Fire protection of ventilation ducts and air ducts according to existing standards is equivalent to materials with fire resistance not less than the same indicator for wall panels.
When choosing equipment for high-rise buildings, it is allowed to use insulation and protective slabs with combustibility characteristics of class “A”. In fire compartments it is allowed to use materials of category “B” (flame-retardant). For air ducts that do not cross evacuation routes and structural elements of the roof, class B1 coatings are acceptable.
Rules for choosing materials for fire protection ducts
The fire-retardant coating of the ducts is selected taking into account its compliance with the fire safety levels established by the standards for modern structures and materials. In this case, the operating conditions of smoke removal systems (domestic or industrial) are necessarily taken into account. To indicate the fire protection index of any material, the EI symbol is used, followed by a number corresponding to its fire resistance (within 15-150).
In accordance with SNiP the following standard markings are accepted:
- EI 150 - materials intended for “walk-through” or transit ducts;
- EI 45 - coverings and barriers for vertical discharge structures;
- EI 30 - protection elements used within the fire block.
For thermal insulation of air ducts, it is recommended to select vibration-resistant materials with good soundproof performance.
Types and features of existing heat insulators
Fire protection of ventilation ducts, which are part of forced ventilation systems, is represented by the following special materials:
- fireproof insulation;
- basalt based fibrous structures;
- thin-layer and thick-layer fences;
- elements of a combined type.
The first position is represented by mats of mineral wool or vermiculite, as well as basalt blocks of a suitable shape. For mounting these materials on ducts, separate fasteners such as self-tapping screws or steel wire are used.
Basalt based fire protection
Basalt fiber structures attract users with resistance to vibration and aggressive environments.In addition, they are completely safe for humans, are lightweight, lack of shrinkage and low moisture permeability. These coatings are applied to protected surfaces by spraying.
On the basis of the initial basalt structures, in addition to liquid coatings, mats and roll sheets that are easy to install are obtained. External protection elements increase the fire resistance of the surfaces of ducts and ducts (E1). With an increase in the thickness of the applied layer, this indicator increases and under certain conditions it can reach 150 units.
Thick Layer Structures
The following types of elements of thick-layer fire protection include:
- various types of plasters;
- special phosphate pastes;
- special mastics;
- asbestos and mineral fibers.
Liquid mixtures prepared on the basis of these materials are applied with a layer of up to 1 cm onto a metal mesh pre-fixed on the surfaces. In this case, possible deformation and cracking of materials with sudden changes in temperature and humidity are taken into account. In addition, when using massive thick-layer protection, the entire exhaust structure is somewhat heavier, which forces the use of additional fastenings and struts during its installation. When the gap between the wall and the duct is too small, it will be very difficult to do.
Combined and thin layer types of protection
To equip fire-prevention insulation of combined ducts, mastics and coils of various classes with a basalt base are used. In the process of protective treatment, the material is first applied to a pre-prepared adhesive base, and then closed with a foil sheath. Thin-layer fire protection is various dyes, as well as enamels and varnishes, prepared on an organic (water) basis.
With an increase in ambient temperature, a special carbon layer is formed in the listed compositions, which is distinguished by good thermal insulation characteristics. The advantages of liquid colorants include:
- durability;
- ease of application and low weight;
- aesthetics;
- profitability.
With the help of dyes, it is possible to process the most inaccessible places of ventilation structures. At the same time, coloring materials are inferior to other samples of protective coatings in terms of fire resistance. Another significant drawback of these products is the relatively high cost.
Fire protection installation procedure
The procedure for arranging fire protection is determined by the type of material used (slabs, basalt cotton wool or liquid mastic). Mats based on basalt fibers, for example, are mounted on pipes by means of glue using special fasteners. In this case, the sequence of operations is as follows:
- Protected surfaces are thoroughly cleaned of traces of grease and dirt, degreased with a solvent.
- Go to the preparation of mounts. To do this, pieces of soft steel wire are welded to the duct housing, by means of which a fireproof sheet is then attached.
- The protective material is cut into workpieces, the size corresponding to the diameter of the pipes. To equip the base of the protective box (its lower plane), a whole canvas is taken. The sides and cover are cut to the diameter of the pipe with a small margin for the design of the joints (up to 10 cm).
- The surfaces of the plates and the exhaust pipe are treated with a pre-prepared adhesive.
- Protective materials are applied with a layer of foil to the outside, and then fixed by means of standard hardware or wire.
If the protective material has a liquid consistency, it is applied to the treated surfaces by spraying from a spray gun, or using special rolling rollers. In the simplest case, ordinary brushes are used for these purposes. At the end of the gluing and painting operations, the treated structure is allowed to stand until the protective composition is completely dry. Only after this is the full operation of the ventilation unit permitted.
In addition to the adhesive method of attachment, there are other methods, however, mechanical options are most common. Among them, the use of special banding tapes and fastening by means of welded pins or needles stand out. When using them, special attention is paid to the fire protection of the duct fasteners, the quality of which depends on the reliability of their operation.
Typical errors
When conducting protective measures, it is important to consider such points:
- In the areas of joining of basalt sheet strips, it is not allowed to overlap it.
- The same mistake should not be made when joining the fire-retardant material with the elements of the building envelope.
- Brackets, suspensions and other components of the duct fasteners must not be left without fire protection.
Errors resulting in non-compliance of duct protection methods with current standards should be avoided.