Any living or working space requires fresh air. There are sanitary and hygiene standards, according to which the air masses must be updated every two hours. The lack of sufficient oxygen saturation is especially noticeable when performing physical work in production. To ensure the supply of fresh air to the workshop, as well as to clean the room from dust and fumes, the installation of powerful professional ventilation systems is required.
Features of industrial ventilation
Workshop, site and other production facilities require a special air conditioning system. It will be different from household or office. This is due to the features of the premises. In production, dust and dirt are often formed during operation, harmful fumes in chemical plants, excess moisture appears. A professional ventilation system can cope with these problems. It represents a whole range of engineering solutions aimed at the uninterrupted cleaning of air masses and the flow of oxygen without disrupting the process.
The main tasks that industrial ventilation performs:
- Support for air exchange with a given frequency. According to sanitary standards, the air should be updated every two hours. This indicator may vary depending on the type of production.
- Ensuring the advancement of air flow.
- Removal of dust, odors, gases, excess heat from the room.
- Creating a suitable microclimate for work.
The engineering complex of industrial ventilation can be divided into two types:
- Local. Its main task is the local elimination of harmful substances in the place of their formation. The source of harmful fumes is closed on all sides by shields in the form of a cap, due to which the substances do not enter the air.
- General exchange. Responsible for cleaning air masses in all production facilities.
According to the principle of action, production systems can be divided into the following types:
- Supply ventilation. Provides free fresh air to the room. In such systems, duct fans are widespread.
- Exhaust type. Contaminated air currents are removed, and new air enters unorganized through doors, windows, crevices and other openings. Exhaust ventilation of industrial premises is used in workshops where work is carried out related to harmful substances, excess moisture or heat, and also where many people work.
- Supply and exhaust type. Combines both of the previous types.
If ventilation is selected, there is a classification according to the settings:
- Monoblock. The devices are easy to operate and maintain, but have a high cost. Air ducts and power are connected to the unit.
- Typesetting. Devices requiring special skills for installing ventilation in the workplace. Differ in the low price.
It is better to install a supply and exhaust system. But before its installation, calculations are required so that air flows do not enter adjacent rooms and are not removed from there.
Air distribution methods
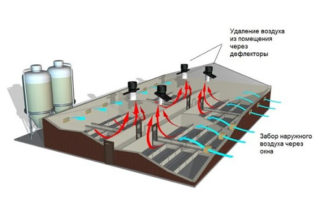
In any room, air circulation can occur by mixing or displacing.In the first case, diffusers are placed on the ceiling and wall platforms, through which fresh air flows. Inside the building, they are mixed with spent ones and then removed through a diffusion valve.
When displacing in the lower part of the room, air distributors are installed at a low speed, due to which a forced supply of fresh air is carried out. New chilled air flows are distributed in the lower part, warm flows upward and are removed naturally through the roof ventilation.
Organization of natural ventilation in the workplace
Natural ventilation in the room occurs due to the appearing difference in the pressure of the air flows, their temperature and direction of movement. An example of this type is airing a room by opening windows and doors. A similar method is also called unorganized, as there are natural physical phenomena that a person cannot control.
The positive qualities of natural air exchange include the low cost of organization. No installation of filters, professional fans, diffusers or other technical equipment is required. But due to the impossibility of control, such a system cannot be the only one in production. Also, the volume of air mass renewal is insufficient to maintain an optimal microclimate.
Mechanical ventilation
Mechanical or artificial ventilation is created using fans. Ventilation systems for industrial premises of this type require energy resources and financial costs. The main advantages include:
- Creating an air intake from the required space of the enterprise. In a room that needs enhanced air purification, you can put more powerful equipment.
- The ability to adjust.
- Creating an air supply directly to the workplace, removal with filtration.
The choice of the desired industrial mechanical system depends on the volume of production, purpose and its capabilities.
Calculation of supply and exhaust ventilation
The first step in designing a system is to identify the source of hazardous substances. Next, calculate how much air should be diverted for the safe work of employees. Under ideal conditions, the calculation is made according to the formula L = N x mwhere:
- L - amount of air used;
- N - number of employees;
- M - air consumption per person per hour.
In the case of a ventilated room, M is 30 cubic meters / hour, and in an unventilated room at least 60 cubic meters / hour.
If various substances are used, their permissible concentration must be calculated. The air flow in this case is calculated by the formula L = Mв / (yпом - yп). Here L - the required amount of fresh air; Mv - harmful substances entering the room mg / h;yp - specific pollution of the whole area, mg / m3; yp - amount of substance in the air stream, mg / m3.
Welding ventilation
During welding, air masses of impurities that are harmful to human health. Constant removal of nitric oxide, carbon, fluorine and other chemical compounds through ventilation systems is required. The type of ventilation depends on the volume of production, the capacity of the equipment and its operating time.
If the production is small and the capacity of the welding shop is small, local ventilation can be arranged. It is enough for air purification in confined spaces.
In the case of technological processes over the entire area of the workshop, local ventilation will not be effective. In this case, it is advisable to use a general exchange duct.This can be a hood in the upper and lower parts, as well as the creation of forced flows and space heating.
Basic requirements for a ventilation system in the workplace
To create the optimal scheme of air exchange at production facilities, the norms of SNiP "Ventilation of special and industrial buildings" are used. They contain the following provisions:
- Installation of the system is carried out in any production site, despite its pollution and the number of employees. This is required for safety in the event of an emergency.
- The system should not become a source of pollution.
- Noise should not go beyond the norms established by SanPiN.
- In the case of work with harmful substances and high air pollution, it is necessary to increase the number of extraction devices. In a clean room requires a greater influx of air masses. In other cases, a balance must be maintained.
- At least 30 cubic meters / hour of fresh air per person. More accurate calculations take into account room humidity, excessive heat, pollution, heating in the cold season.
If all the rules are observed, any system can be installed that will provide the necessary efficiency for the removal of polluted air and the influx of fresh.