The heater provides and maintains the desired temperature in the room. It is installed in the system of forced ventilation, air conditioning and heating, is able to heat large areas, as it is characterized by high power and performance. In order for the device to function correctly, it is necessary to calculate the power of the heater before purchasing it.
Classification of heaters
The devices operate from different energy sources and are classified by type of coolant. Three types are widely used:
- water;
- steam;
- electric.
The former themselves do not heat the air, but only transfer heat to the air flow, since the heat carrier is brought to the air heater. Electrical appliances do not use a coolant, they heat the air thanks to electricity. The main elements in such devices are heating elements.
Water
Water heaters are a budget option. Their price and maintenance costs are low. It is necessary to bring a water supply system to the device, so installation requires certain skills. Quickly transfer it to another place will not work. The coolant (water or ethylene glycol) can come from a heating system, hot water or boiler. To adjust the air temperature, it is necessary to take into account the power, the level of heating of the coolant and air mass. Control is carried out using a thermostat.
When installing water and steam heaters, polymer and metal-plastic pipes cannot be used, since they will melt. Steel galvanized pipes are recommended.
In addition to efficiency, the water device is different:
- ease of use;
- high efficiency;
- security
- simple principle of action.
The disadvantage is the restrictions on the minimum temperature and dust content of the input stream.
It is advisable to install a water device in spacious production rooms, warehouses, catering establishments, cottages with good ventilation. It quickly warms up large volumes of air.
Steam
In addition to the coolant, steam heaters are practically no different from water heaters. An insignificant difference is the 2 mm thickness of the tube walls versus the 1.5 mm. The need for additional amplification is associated with high pressure in a steam system. It varies from 0.5 to 1.2 Pa. Use carbon and stainless steel.
Steam heaters are also installed in enterprises, and those where steam is formed during the production process. The maximum steam temperature is 180 ° C.
Electric
The electric heater does not need to be connected with a heat carrier; it has small dimensions and weight, therefore it is easier to install.
The advantages of electrical devices:
- the convenience of use;
- mobility;
- compactness.
Disadvantages:
- work on electricity;
- dry the air.
High energy costs make the constant use of devices of this type unprofitable. They are less powerful than steam and water appliances, so they are not suitable for heating rooms with an area of more than 100 m2, but are optimal for heating apartments. Electrical appliances use three times more energy than water heaters, but they have lower performance. Often they are used as temporary heaters.
To adjust the temperature of the air mass at the outlet, it is only necessary to install a temperature sensor.
To save energy, you must install the recuperator.
Advantages and disadvantages
Water and steam heaters designed for heating industrial premises are extremely beneficial because they do not require additional investments. Financial resources are spent only on the purchase of the device. Their advantages:
- rapid achievement of the desired air temperature;
- simple installation;
- safety;
- reliability;
- the ability to adjust the heating level.
Of the shortcomings are noted:
- use in rooms with positive air temperature;
- the inability to use for heating apartments;
- equipment required to provide air traction;
- if the coolant flow stops, the system stops working.
The last point is also valid for electric heaters, only for power outages.
Design of different types of heaters
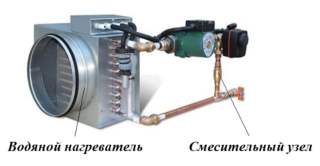
A heater is a heat exchanger that transfers heat carrier energy to an air heating stream and works on the basis of a hair dryer. Its design includes removable side shields and heat transfer elements. They can be connected in one or more lines. The built-in fan provides air draft, and the air mass enters the room through the gaps that exist between the elements. When air from the street passes through them, heat is transferred to it. The air heater is installed in the ventilation duct, so the device must match the shaft in size and shape.
Water and steam heaters
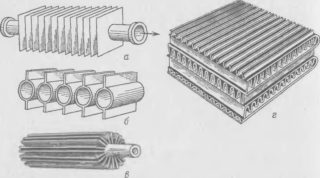
Water and steam heaters can be of two types: ribbed and smooth tube. The first, in turn, are divided into two types: lamellar and spiral-wound. The design is one-way or multi-way. In multi-way devices there are partitions, due to which the direction of flow changes. Tubes are located in 1-4 rows.
A water heater, consists of a metal, often rectangular frame, inside which there are rows of tubes and a fan. Connection is made to the boiler or central heating plant using outlet pipes. The fan is located on the inside, it pumps air into the heat exchanger. To control power and output air temperature, 2 or 3-way valves are used. Devices are installed on the ceiling or on the wall.
There are three varieties of water and steam heaters.
Smooth pipe. The design consists of hollow tubes (diameter from 2 to 3.2 cm) located at small intervals (of the order of 0.5 cm). They can be made of steel, copper, aluminum. The ends of the tubes communicate with the collector. Heated coolant enters the inlet, condensate or cooled water enters the outlet. Smooth-tube models are less efficient than others.
Features of use:
- the minimum temperature of the inlet stream is –20 ° C;
- requirements for air purity - not more than 0.5 mg / m3 in terms of dust content.
Ribbed. Due to the ribbed elements, the heat transfer area increases, therefore, ceteris paribus, ribbed heaters are more productive than smooth tube ones. Plate models are distinguished by the fact that plates are mounted on the tubes, further increasing the heat transfer surface area. In navivny steel corrugated tape is wound.
Bimetal with fins. The greatest efficiency is achieved through the use of two metals: copper and aluminum. Manifolds and nozzles are made of copper, and fins are made of aluminum. Moreover, a special type of finning is performed - spiral-rolling.
In electrical appliances, air is heated due to its contact with red-hot plates or spirals. Heating elements are made of refractory metals.
Calorifier power calculation
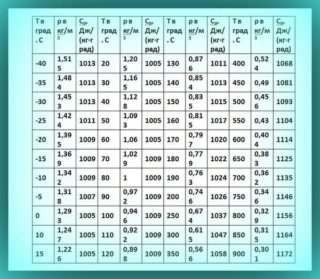
For the correct calculation of the air heater it is necessary to determine the initial data: performance, air density, street temperature and the desired room temperature. The latter indicators are extremely important, since the amount of heat spent on heating 1 m3 of air depends on them. Part of the data can be found in special tables.
Water device
To calculate the cross-sectional area of the water heater, use the formula Af = L × ρst/3600 (ϑρ). The values used are:
- L - productivity, which is expressed in m3 / h or kg / h;
- pst - street air density according to the table;
- ϑρ - mass air velocity in cross section.
Having obtained the result, one standard-sized air heater or several devices is selected for the ventilation system so that the area or the sum of the areas is equal to or slightly larger than the calculated value.
The mass air flow rate in kg / h is calculated by the formula G = L × pwed:
- pwed- air density at medium temperature.
pav calculated by the formula (tst+ tcon)/2:
- tst - Outdoor air temperature in the coldest five-day week;
- tcon - desired room temperature.
Then for the average indicator determine the density according to the table.
The heat consumption for heating the air is calculated by the formula:Q (W) = G × c × (tcon–Tst)
For example, data will be calculated if it is known:
- L - 10000 m3 / h (performance is indicated in the documentation);
- tcon - 21 ° C;
- tst - –25 ° C.
pav = (- 25 ° C + 21 ° C) / 2 = –2 ° C
The density of air at this temperature is 1.303.
The mass flow rate of air mass is G = 10000 m3 / h × 1.303 kg / m3 = 13030 kg / h
From here Q = 13030/3600 × 1011 × (21 - (- 25)) = 168325 W.
To this value, it is necessary to add 10-15% for the power reserve.
Steam heater
The power of the steam heater is determined in the same way, only for calculation G use the formula G = Q / r. r - specific heat generated during condensation of steam in kJ / kg.
Electric air heater
For electrical appliances, most of the necessary data is usually indicated by the manufacturer, which greatly simplifies the calculation of air heating and the choice of air heater. Despite the relatively low thermal power, the electroheater system consumes a lot of electricity, so it often has to be connected with a separate cable to the shield. Heaters with a power of more than 7 kW are supplied by 380 V.
The current consumption is calculated by the formulaI = P / UwhereP - power, and U - voltage. Value U depends on the features of the connection. If the connection is single-phase, U = 220Vif three phase U = 660V.
The heating temperature is calculated by the formulaT = 2.98 × P / Lwhere L - as in other calculations, system performance.
To heat small areas, it is recommended to purchase an electric air heater, it is more convenient and does not require complex installation. If the heating area is more than 100 m2, it is more profitable to use a water or steam device. In any case, in order to perform the selection of the air heater correctly, it is necessary to make preliminary calculations.