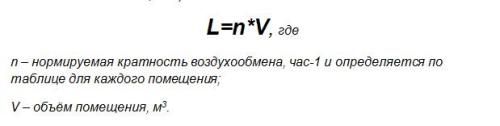To create the right microclimate in the house, you need to equip it with a system of air circulation. To ensure its effective operation, it is necessary to perform the correct calculation of the length and diameter of the pipe that removes air from the house. Calculations are performed by various methods, depending on what type of ventilation system is installed in the house.
Improper pipe height above the roof contributes to a deficiency of oxygen in the house and excess humidity. If an error was made in the design of the hood, soot and fungus will appear on the walls and furniture, and the windows will constantly be covered with perspiration.
Ventilation calculation
Ventilation usually consists of round or square ventilation ducts. If special devices are not used to remove air, then the installation of round ducts is the best option. They, in comparison with square ones, are characterized by higher strength, tightness and better aerodynamic performance. If the room is equipped with forced ventilation, then in this case it is possible to install square pipes.
Volume of incoming air
As a rule, residential buildings are equipped with natural air circulation. Outdoor air can be supplied through a window or a special valve. Outflow occurs through the ventilation duct. It can be located inside the wall or designed as an extension. It is impossible to equip the vent channel in the outer wall, since in this case condensation may form on the surface, which will lead to damage to the structure. Also, due to cooling, the air speed may decrease.
Values for ventilation pipes in residential buildings are determined by the established requirements that are regulated by SNiP. Equally important is the multiplicity of exchange, reflecting the quality of the ventilation system. So, the volume of air flowing into the room should have the following values:
- in a residential building - 3 m³ per hour per square meter of area. Moreover, this indicator does not depend on how many people are in the room. Sanitary standards established that for temporarily staying in the building, 20 m³ per hour of supply air is sufficient, and permanent residents require 60 m³;
- in an auxiliary building (for example, in a garage) - at least 180 m³ of air per hour.
To calculate the diameter of the ventilation pipes, a system is used in which only natural air intake is present, without installed forced devices. The simplest method of calculation is the ratio of the area of the room to the section of the vent channel opening.
For a living space per square meter, 5.4 m² of duct section is required, and for a utility room - 17.6 m². With a diameter of 15 m², sufficient air circulation will not be ensured. To get more accurate numbers, you need to use complex calculations.
Pipe length
All channels available in the building are connected to the ventilation pipe, through which air flows through the pipe to the street.
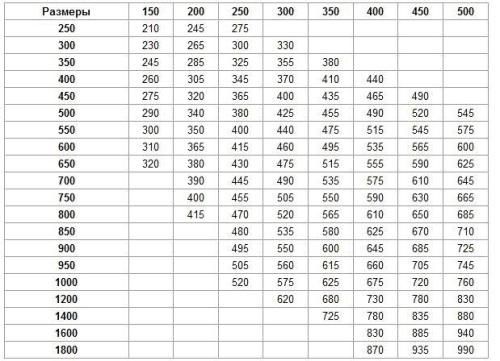
To calculate the height of this pipe, you need to know its diameter and have a special table. The cells in the tables contain the values of the cross sections of the ducts, and the left column indicates the width of the pipes. The top line shows what height the pipe should be at a certain diameter in millimeters.
It is necessary to take into account the following norms of SNiP:
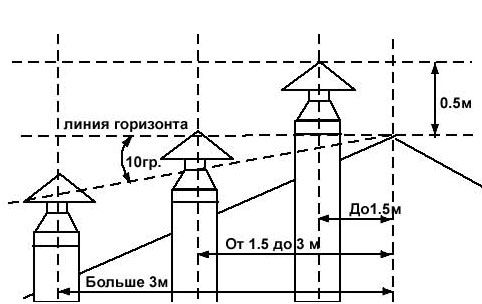
- When placed next to the chimney and ventilation pipes, their height should be the same. If this requirement is not observed, smoke from the heating unit may enter the room.
- If the duct is located no more than 1.5 m from the ridge, then its height should not exceed 0.5 m. If the pipe is separated from the ridge at a distance of 1.5-3 m, it should not be located below it.
- If the roof is flat, then the pipe should be at least half a meter.
When choosing a ventilation pipe and determining its location, it should be borne in mind that it must have sufficient resistance to wind. So, the pipe must withstand a 10-point storm, and for this its weight should be about 50 kg per 1 square meter of surface. The picture shows how the height of the ventilation pipe above the roof is calculated.
Special programs can also be used to determine natural ventilation. In this case, the calculation process is much easier. For this, it is necessary to determine the optimal amount of incoming air into a residential or utility room, respectively. The program also determines such data:
- average temperature outdoors and indoors;
- air duct shape;
- the degree of roughness of the walls inside the duct;
- resistance that is formed by the movement of air.
As a result, the program determines how long the vent pipe should be in order to ensure optimal air movement under given conditions.
When calculating the values for the duct, it is necessary to take into account the resistance indicators when moving air flows. Grids, gratings, and other structural details affect the occurrence of resistance.
Pipe diameter
To calculate the values of ventilation pipes based on the air exchange rate, the SNiP table is used. By the rate of air exchange is meant an indicator that determines how many times in one hour the air in the room changes. Before calculating the diameter of the ventilation pipe, the following steps must be performed:
- Calculate the volume of each of the available rooms.
- Determine the amount of air required for normal circulation. For this, the formula is used:
Using the above formula, the volume is calculated separately for each room.
- As a rule, for rooms, rationing of the exhaust or inflow is used. Sometimes in rooms it is necessary to organize not only the flow of air, but also its effective outflow.
- When making calculations, keep in mind that the value of L should be rounded up. After rounding, the resulting value should be divided by 5.
- After determining the required air volume for the entire housing area, a special chart is used to calculate the diameter of the pipe. At the same time, you should know that in the central ventilation pipe the speed should be no more than 5 m / s, and in its branches - no more than 3 m / s.
Requirements of SNiP to air ducts
The requirements of SNiP include checking and cleaning the chimney and ventilation pipes:
- before the onset of the heating season;
- at least 1 time in 3 months (for combined and brick channels);
- at least 1 time in 12 months (for asbestos-cement channels and chimneys, as well as for pottery pipes and pipes made of heat-resistant concrete).
During the initial inspection of ventilation ducts and chimneys, the materials from which they were made, the presence of blockages in the channels, the presence of separate smoke and ventilation passages are checked. Standards SNiP categorically prohibit the withdrawal of exhaust combustion products through the ventilation duct.
The owner of the house has the right to carry out cleaning of ventilation ducts only after passing the briefing and if there is a corresponding document on the briefing. When starting the construction of a ventilation pipe, the owner is obliged to notify the operating organization that is the owner of the house about this. Upon completion of the work, the same organization must check and give permission for the operation of the duct.
Building a quality system that allows you to control the level of moisture and provides the best living conditions is a feasible task.To do this, you just need to correctly calculate the parameters of the ventilation pipe.