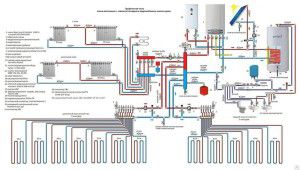
Effective operation of a water heating system is possible only with the right choice of coolant. Before creating a heat supply project, it is necessary to determine its type in advance, find out the main technical and operational characteristics. There are certain parameters specific to the heat carrier of the heating system: temperature, volume of thermal expansion, viscosity.
Coolant functions in the heating system
How to choose the right heat transfer fluid for heating? To do this, determine its purpose for heat supply systems. The calculation of its characteristics is included in the design. Therefore, it is necessary to know the functional features of water or antifreeze in heating.
The main task that a safe coolant for heating systems must perform is the transfer of thermal energy from the boiler to batteries and radiators.
In autonomous heating, this process is carried out using a heating element, which raises the temperature of the coolant to the required level. Then the temperature expansion and the operation of the circulation pump create the proper speed of hot water for its transportation to the radiators of the system.
Before calculating the volume of coolant in the heating system, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with its secondary functions:
- Partial corrosion protection of steel elements. This will occur only with a minimum oxygen content in the water and no foaming. It has been observed that in unfilled heating, rusting is much faster;
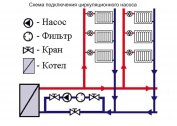
- Circulation pump cooler. The most common pump model has the so-called "wet rotor". Even if the maximum temperature of the coolant in the heating system is reached, it will still reduce the heating level of the pump power unit.
These functions are affected by the parameters of the heating medium. Therefore, when choosing, you should carefully study the characteristics of water or antifreeze. Otherwise, the actual heat supply parameters will not coincide with the calculated ones, which will lead to an emergency.
Even if simple water is flooded in the heating system, it cannot be used for hot water supply at home. During operation, the content and parameters of the heating medium coolant change
Types of heat carrier for heating
As the circulating fluid, you can use water and some types of antifreeze. This does not affect the amount of coolant in the heating system, but affects the heat transfer, travel speed and system safety requirements.
To identify the most acceptable option, a comparison of the coolants for heating systems is necessary. Most often, ordinary water is used. This is due to its affordable cost, good indicators of heat capacity and density. When the boiler stops working, it can still accumulate the received heat for a while to transfer its surface to the batteries. In this case, the volume of coolant in the heating system will remain the same.
However, despite its positive properties, water has several disadvantages:
- Freezes. When exposed to negative temperatures, crystallization and volume increase occur. This is what causes damage to pipes and radiators.Therefore, the optimum temperature of the coolant in the heating system must be maintained;
- Impurity content. This applies to ordinary water. Often, this is precisely what causes scale to appear on the batteries, radiators, and boiler heat exchanger. Experts recommend the use of distilled liquids, in which the percentage of alkali, salts and metals is minimal;
- With a high oxygen content, it provokes a rusting process.. This is more common for open heating systems. But even in closed heating circuits, over time,% of oxygen content in water can increase.
At the same time, water can be used as a coolant for aluminum heating radiators. Subject to the composition of the liquid and the minimum amount of oxygen, destructive processes will not occur in it.
If the operating conditions of the heating system imply the possibility of exposure to negative temperatures, a different type of circulating fluid should be used. How to choose a coolant for heating systems in this case, and what criteria should be followed?
One of the determining parameters is the freezing temperature. For antifreezes, it can be from -20 ° C to -60 ° C. This allows you to operate the heat supply even at low temperatures without causing breakdowns.
However, antifreezes have a higher density than water - the optimal coolant speed in the heating system in this case can be achieved only with the installation of a powerful circulation pump.
The following types of antifreeze agents are available depending on the composition and components:
- Ethylene glycol. It is characterized by low cost, but extremely toxic. Not recommended for autonomous heating of a private house;
- Propylene glycol. It is completely safe for human health. It has a worse coefficient of thermal conductivity than a liquid based on ethylene glycol. It has a high cost;
- Glycerin based antifreeze. It is he who is most often chosen as a heat transfer fluid for heating. The price is much lower than that of propylene-glycol compounds, non-toxic, has a good heat capacity.
You need to know that calculating the amount of coolant in the heating system for antifreezes will be more difficult. This is due to their foaming when reaching maximum temperature. To minimize this phenomenon, manufacturers add special inhibitors and additives to the composition of the liquid.
Before purchasing a safe coolant for heating systems, you should read the recommendations from the manufacturers of the boiler and radiators. Not all types of anti-freezing fluid can be used for aluminum radiators and gas boilers.
Main characteristics of the heat carrier for heating
It is possible to determine in advance the coolant flow in the heating system only after analyzing its technical and operational parameters. They will affect the characteristics of the entire heat supply, as well as affect the operation of other elements.
Since the properties of antifreezes depend on their composition and the content of additional impurities, the technical parameters for distilled water will be considered. For heat supply, it is the distillate that should be used - fully purified water. When comparing coolants for heating systems, it can be determined that the flowing fluid contains a large number of third-party components. They negatively affect the operation of the system. After use during the season, a layer of scale forms on the inner surfaces of the pipes and radiators.
To determine the maximum temperature of the coolant in the heating system, attention should be paid not only to its properties, but also to restrictions on the operation of pipes and radiators. They should not be affected by increased heat exposure.
Consider the most significant characteristics of water as a coolant for aluminum heating radiators:
- Heat capacity - 4.2 kJ / kg * C;
- Mass density. At an average temperature of + 4 ° C it is 1000 kg / m³. However, during heating, the specific gravity begins to decline. Upon reaching + 90 ° С it will be equal to 965 kg / m³;
- Boiling temperature. In an open heating system, water boils at a temperature of + 100 ° C. However, if you increase the pressure in the heat supply to 2.75 atm. - the maximum temperature of the heat carrier in the heat supply system can be + 130 ° С.
An important parameter in the operation of heat supply is the optimal coolant speed in the heating system. It directly depends on the diameter of the pipelines. The minimum value should be 0.2-0.3 m / s. Maximum speed is not limited by anything. It is important that the system maintains the optimum coolant temperature in the heating throughout the circuit and that there are no extraneous noises.
However, professionals prefer to be guided by the burrows of the old SNiP of 1962. It indicates the maximum values of the optimal coolant speed in the heat supply system.
|
Pipe diameter mm |
Maximum water speed, m / s |
|
25 |
0,8 |
|
32 |
1 |
|
40 and more |
1,5 |
Exceeding these values will affect the flow rate of the coolant in the heating system. This can lead to an increase in hydraulic resistance and “false” triggering of the drain safety valve. It should be remembered that all the parameters of the heat carrier of the heat supply system must be pre-calculated. The same applies to the optimum temperature of the coolant in the heat supply system. If you are designing a low-temperature network - you can not give this parameter value. For classic circuits, the maximum value of heating of the circulating fluid directly depends on the pressure and restrictions on the pipes and radiators.
For the right choice, the coolant for heating systems pre-compile the temperature schedule of the system. Maximum and minimum values of water heating should not be below 0 ° С and above + 100 ° С
Calculation of the volume of coolant in heating
Before filling the system with coolant, it is necessary to correctly calculate its volume. It directly depends on the heat supply scheme, the number of components and their overall characteristics. They affect the amount of coolant in the heating system.
First, the parameters of the supply line are analyzed. Of great importance is the material of its manufacture. To calculate the volume of coolant in the heating system, you need to know the inner diameter of the pipe. According to modern standards, the article of steel pipelines gives the internal size of the section, and for plastic adopted the outer. Therefore, in the latter case, it is necessary to subtract two wall thicknesses.
In order to independently calculate the volume of coolant in the heating system, you do not need to do calculations. It is enough to use the data from the table below. With its help, you can calculate the amount of coolant in the heat supply system.
|
Diameter mm |
Heat carrier volume (l) in 1 m.p. pipes, depending on the material of manufacture |
||
|
Steel |
Polypropylene |
Metal-plastic |
|
|
15 |
0,177 |
0,098 |
0,113 |
|
20 |
0,314 |
0,137 |
0,201 |
|
25 |
0,491 |
0,216 |
0,314 |
|
32 |
0,804 |
0,353 |
0,531 |
|
40 |
1,257 |
0,556 |
0,865 |
Having this information, it is enough to determine the length of pipes of a certain diameter according to the heat supply scheme and multiply the resulting value by a volume of 1 mp In this way, the volume of coolant in the heat supply system is calculated, but only in pipes.
But in addition to the supply lines in the heating circuit there are radiators and batteries. They also affect the volume of coolant in the heat supply system. Each manufacturer indicates the exact capacity of the heater.Therefore, the optimal calculation option is to study the battery passport and determine the amount of required coolant liquid for heat supply.
If this is not possible for a number of reasons, you can use approximate numbers. It is worth noting that with a large number of batteries, the calculation error will increase. Therefore, to accurately calculate the amount of coolant in the heat supply system, it is recommended to find out the passport characteristics of the battery. This can be done on the manufacturer’s website in the technical information section.
The table shows the average volume of coolant for one section in aluminum, bimetallic and cast-iron heating radiators.
|
Radiator type |
Center distance mm |
||
|
300 |
350 |
500 |
|
| Aluminum |
– |
0,36 |
0,44 |
| Bimetallic |
– |
0,16 |
0,2 |
| Cast iron |
1,1 |
– |
1,45 |
These figures must be multiplied by the total number of sections in the heating system. Then, the already calculated volume of water in the pipes should be added to the data obtained and the total amount of coolant in the heating system can be determined.
However, it should be remembered that when comparing coolants for heat supply systems, it was noted that, from time to time, the volume may decrease for objective reasons. Therefore, to maintain the operability of the system, a coolant should be periodically added to it.
For an accurate calculation of the volume of water calculation in the heating system, it is necessary to take into account the capacity of the boiler heat exchanger. For solid fuel models, this figure can be several tens of liters. In gas, it is slightly lower.
Ways to fill the heating system with coolant
Having decided on the type of coolant and calculating its volume in heating, it remains to solve its one problem - how to add water to the system. This is an important point in the design of heat supply, since when the critical water level is reached, the boiler heat exchanger and radiators may fail.
For an open heating system, water can be added through an expansion tank located at the highest point in the system.
To do this, it is necessary to draw the supply line and connect it to the tank structure. When reducing the volume of coolant, it is enough to turn on the supply of a new portion of water to supplement the system.
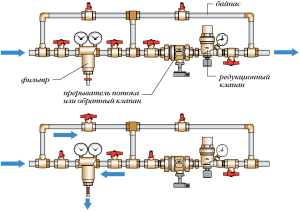
Filling a closed system is carried out according to another scheme. It should include a make-up unit. This component is located on the return pipe, in front of the expansion tank and the circulation pump. The supply components include the following components:
- Shutoff valves installed on the connected branch pipe;
- Non-return valve, preventing the change in the direction of flow of the coolant;
- Strainer
To automate the operation of the unit, a servo mechanism can be installed on the crane. It connects to a pressure sensor. With a decrease in pressure, the servo mechanism opens the tap and thereby adds coolant to the system.
The video describes the options for choosing a coolant for the heating system: