For exterior finishing work, much attention is paid to the technique of insulation of facades for plaster. Various heat-insulating materials, traditionally used in construction, are suitable for these purposes. It is useful for an interested user to get acquainted with the main types of insulation for facades for plaster, as well as find out how they are mounted on the walls of the house.
Materials for the facade
The most common insulation for facade plastering is polystyrene foam (polystyrene). Its benefits include:
- lightness of material;
- good heat capacity;
- relative cheapness.
The technology of facade insulation with styrofoam for plaster has one drawback. This material is characterized by low permeability for steam penetrating from the premises, which has to be compensated by artificial ventilation of the facades of the house. A good alternative to such heaters is mineral wool heat insulators, the classic representative of which is ordinary stone or environmentally friendly cotton wool. This material has increased hygroscopicity, which forces the use of waterproofing elements in the form of membranes of various classes during its installation. In addition, polyurethane foam is used as a facade insulation for plaster, only slightly inferior to mineral wool and polystyrene.
Mounting Methods
The facade insulation for exterior decoration of the house under the plaster can be equipped in the following types:
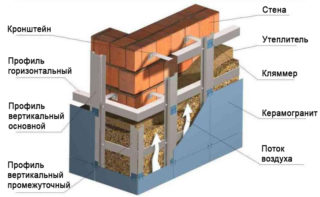
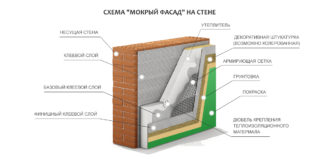
- Ventilated facade, which consists of a frame and external cladding, as well as layers of steam and wind insulation.
- Wet facade, upon arrangement of which the insulation is fixed directly on the wall of the house. A reinforcing layer is attached to it, in which quality a steel or synthetic mesh is used, on top of which a layer of plaster is applied.
Which of the presented methods to choose depends on the preferences of the owner of the house and the material chosen for the facade plastering with insulation.
A convenient option is the use of modern thermal panels. But their cost is significantly higher than that of other materials.
Calculation of insulation thickness
In order to calculate the desired thickness of the insulation, you need to determine the indicator of thermal resistance of the outer wall (facade). It is found by the following formula:
R ave. = (1 / α ext.) + R1 + R2 + R3 + (1 / α ext.)
- R1, R2, R3 represent the values of thermal transfer resistance of all protective layers (it is believed that there are three, but in practice this number can be any),
- α (internal) and α (external) - absolute values of the thermal return of the inner and outer surfaces.
Following this, the minimum thermal resistance is calculated by the formula:
R min = δ / λ
- δ - the thickness of the insulation layer,
- λ - thermal conductivity of a particular material.
Both indicators are compared in absolute value. If Rmin slightly less or approximately equal Rpr, there is no need to insulate the wall. Otherwise, there is a difference between these two values. ΔR, which is the initial parameter for determining the thickness of the insulation (δS) The latter is found by the following formula:
δS = ΔR x λwhere λ corresponds to the thermal conductivity of the insulation.
The methodology considered is rather complicated for an unprepared person; calculations on it rarely do without serious errors.
It’s easier to use a standard online calculator that allows you to quickly get the desired result.To do this, the data proposed by the program records the wall material and the selected type of insulation material.
Workflow
 It is better to install insulation for the walls of the house outside under the plaster in dry weather at an air temperature of + 5 ° to + 30 °. The selected range is most suitable for the adhesives used and for the thermal insulation material itself. When buying it, special attention is paid to the presence of marking by parameters. Mineral wool, for example, should have a density of 150, and PPS - the designation "F" (front).
It is better to install insulation for the walls of the house outside under the plaster in dry weather at an air temperature of + 5 ° to + 30 °. The selected range is most suitable for the adhesives used and for the thermal insulation material itself. When buying it, special attention is paid to the presence of marking by parameters. Mineral wool, for example, should have a density of 150, and PPS - the designation "F" (front).
The most suitable insulation options are polystyrene foam or basalt wool in slabs. Both materials are very similar in their characteristics. Therefore, the sequence of their installation is almost the same:
- From the facades of the building, all hinged elements are dismantled: slopes, outdoor lights and drainpipes.
- Old paint and the remnants of other coatings are removed from them.
- Small cracks and dents present on the walls are putty.
- If there are significant flaws in size, leveling plastering is used.
The maximum value of the unevenness of the treated surface is not more than 1 cm per 1 meter of length. If areas with a crumbling surface are found, they should be treated with a deep penetration primer.
Immediately before installing the insulation in the lower part of the wall, it is recommended to fix the profile, which serves as a support for the first row of plates. Thanks to him, it is possible to facilitate the fixation of the workpieces and strictly maintain a horizontal line. For their fastening, special glue is used, which, after application to the wall, is immediately leveled with a notched-type spatula. Following this, the plate is pressed to the plane and fixed with dowels of a special design, called “fungi”.
Insulation plates for walls outside under the plaster are placed as densely as possible one to the other, so that cracks or gaps are minimal. All subsequent rows are laid with overlapping, providing displacement of joints in adjacent rows. To facilitate the installation of heat-insulating blanks, metal profiles are used that perform the function of guides. Plates are closely stacked between them and fixed on the adhesive, and the gaps between them are sealed with the same glue. Subsequently, these same guides are used as supports for the plaster rule, by means of which an even surface of the coating is formed.