Any heating network includes a heat source - a boiler room, a heating plant, primary or secondary pipelines for transferring a heat carrier, and a consumer - a house, an apartment, an enterprise. The indicators of hot water in the highway differ significantly from the temperature of the liquid that is supplied to the batteries. A heat point is a complex in which a heat carrier is prepared for supply to the consumer.
Types and features of the heat point

The heat point includes equipment that allows you to connect power plants to heating systems, fluid supply systems, measuring and control devices. Typically, the heating unit is placed in a separate room or building.
The purpose of any type of TP is to regulate the flow of coolant. All elements of the system - highways, pipelines, servicing apartments, radiators - are designed to work with a coolant of a certain temperature, purity, gas contamination. Violation of these indicators leads to clogging and failure of the system.
TP controls the performance of the incoming and outgoing water. The consumer receives a liquid of optimal temperature under the pressure for which the heating, ventilation, water supply systems are designed. If some indicators change to an unacceptable value, the control system turns off the water supply.
Here, the coolant is converted, for example, steam condensation and conversion into superheated water.
TP can serve a different number of consumers, include different heat consumption systems. The methods of installation and installation of equipment also differ.
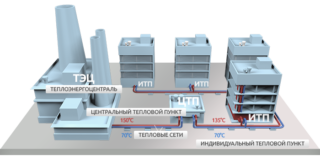
Central heat point
The feature of the heating unit is a large number of connected consumers. The central heating center serves several houses, an enterprise or even a whole microdistrict. Usually it is placed in a separate building, but installation in the basement is allowed, if its dimensions allow it.
This option is not too convenient for the average consumer - the occupant of the apartment. The central heating system sets the same coolant temperature, not taking into account that the length of the pipelines is not the same. The nearest buildings, as a rule, overheat, the distant ones get very cool water. During preventive and repair work, a whole microdistrict immediately remains without heat.
Individual heat point
ITP is an individual heat point. It performs the same functions as the TSC, but to a lesser extent. It supplies the coolant to 1 building or even to one of its parts. Since its dimensions are much smaller, place the heat center in the basement or in another technical room.
A plus of an individual heating station is the supply of the same temperature to water consumers. The length of the pipeline, even in a tall building, is not so long as to affect the temperature. This option is more economical because less heating is required to maintain the optimal mode in apartments.
Modular Heat Point
Block or modular thermal unit is a finished factory product. The blocks are compact, assembled and work in the same way. You can place them on the smallest plot. They install the blocks very quickly: you just need to connect the external wires. In terms of the number of consumers, a modular point can be either individual or central.
Advantages and disadvantages
Each type of TP has its own advantages and disadvantages. Advantages of TSC:
- coolant parameters - temperature, pressure, are maintained and controlled automatically;
- The item serves a large number of consumers.
The disadvantages of this solution are much more:
- Each consumer receives a strictly metered amount of heat. However, these shares are equal only at the level of TSP. Due to the different lengths of the pipeline, residents of buildings receive water with different temperatures.
- The longer the pipe, the greater the heat loss. Because of this, it is necessary to increase the temperature on the central heating system, which leads to an increase in the cost of heating and hot water.
- During the repair, a large number of residents remain without heat.
- The circulation of hot water is uneven. In houses located far from the central heating center, it is necessary to drain cold water for a long time before getting heated. The counter takes into account all this volume as a hot consumption.
ITP is much more profitable:
- Less heat loss during heat transfer. Installing ITP in a building saves from 15 to 30% of the cost.
- All apartments receive the same amount of heat, taking into account the area.
- From the tap, the water goes really hot and immediately.
- Since the heating unit operates without a high load, the probability of damage is lower. Installation and repair of equipment takes less time.
- When the TP fails, fewer residents suffer.
The disadvantages of an individual complex are associated only with its limited capabilities. TP serve 1 house, sometimes even part of it. To modify the whole microdistrict, a lot of money will be required.
Advantages and disadvantages of the ICC are determined by its purpose. However, such a system has its advantages:
- The finished module takes up minimal space. Even if it is a central heating facility, it can be installed in the basement.
- Installation is extremely simple - it only needs to be connected to the heating main and the power grid.
The higher the degree of automation of the heating unit, the lower the cost of its maintenance and maintenance.
Principle of operation
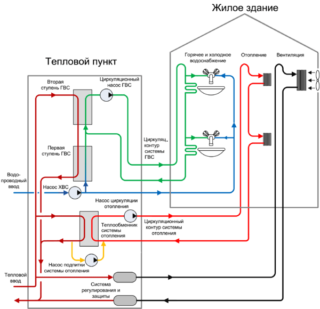
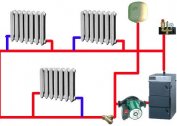
The principle of operation of a modern heating station is simple. The liquid from the line transfers its heat through a heat exchanger to the hot water supply and heating system. Then the coolant is transferred via a return pipe to the boiler room or power center, where it is heated again. Heated liquid from TP is distributed among users.
The heating station supplies users with heating media and hot water. The schemes of the systems are different.
Tap water enters the TP. Part of the cold water is supplied to consumers, the other part is heated in a stage 1 heater. Heated fluid enters the circulation circuit. The pump provides a constant movement of hot water along the circuit from the heating system to users and vice versa. As needed, the inhabitants of the house take hot water.
Since the liquid is gradually cooled, it is periodically reheated in a 2 stage heater. Since the volume of water in the circuit decreases, it is necessary to constantly draw in cold water, heat it and make up for its lack.
The scheme of operation of the heating heating unit in an apartment building is somewhat different. It is simpler: water, having given heat to pipes and radiators, returns almost in the same volume as it was supplied. Leaks are possible, but small. The make-up system operating on the basis of the primary heating network compensates for the losses.
Key components of a heat point
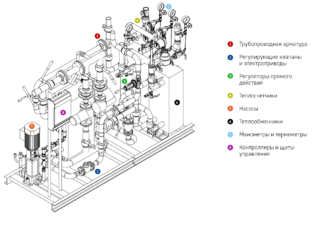
The thermal complex includes several basic elements:
- A heat exchanger is an analogue of a boiler boiler heat boiler. Here, heat from the liquid in the main heating network is transferred to the heat carrier TP. This is an element of the modern complex.
- Pumps - circulating, make-up, mixing, booster.
- Mud filters - mounted at the inlet and outlet of the pipeline.
- Pressure and temperature regulators.
- Shutoff valves - acting in case of leaks, emergency change of parameters.
- Heat metering unit.
- Distribution comb - distributes the heat carrier to consumers.
Larger TPs include other equipment.
Selection of systems
Water is prepared for transmission to users using a control unit. By the form of this element, several schemes of the operation of the heating unit are distinguished.
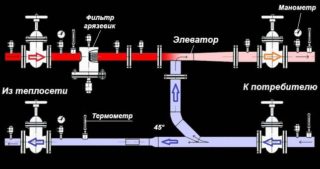
Elevator - was installed on the TP of the old model. The unit mixes the liquid from the main network and the cooled water from the return pipe to obtain a coolant with a temperature suitable for secondary networks. The temperature is maintained at a certain level regardless of the temperature of the air outdoors or indoors. When overheating, the only way to remove excess heat is to open a window. In case of underheating, it is necessary to connect electric heaters.
The circuit of the thermal unit with the controller is much more efficient. The heat exchanger and control equipment allows you to adjust the temperature of the water in the heating circuit according to real air readings. There are 2 systems of this kind:
- Dependent scheme - increases or decreases the temperature of the supplied liquid by mixing the cooled coolant from the return pipe. The controller monitors temperature changes and automatically turns on pumps and valves. Mandatory installation of pressure regulators, since this indicator is different in the primary and secondary networks.
- Independent - the water used to heat the house circulates in a closed circuit, heat from the heat carrier from the main is transferred only through the heat exchanger. Pressure regulators are not needed here, temperature control is more accurate and faster. The cost of a TP with an independent circuit is higher, but it is more economical to use: water is not polluted, does not overheat, and does not lead to corrosion of pipes and radiators.
Hot water supply is also implemented according to 2 schemes:
- Single-stage - water from the water supply is supplied to the heater. Heats up by the network heat carrier which came from a source. The cooled network is transferred to the source, and the heated tap is supplied to the consumer.
- Two-stage - the water is heated in 2 stages. First, due to the coolant from the return pipe - up to + 5– + 30 C, then it is warmed up using the supply heat pipe - up to +60 C. In this case, the waste energy of the return pipe is used - it's cheaper.
The more efficient the TP reduces the cost of the heat supply service, the more expensive it is to install.
System balancing
The calculations of any hydraulic circuit are very complex. During installation, features and deviations are manifested, which are impossible to take into account in the calculations: blockages, scale, narrowing. In practice, hydraulics are connected at the design stage, and then they are adjusted using balancing valves. This device is an adjustable washer. With its help, the valve capacity is changed, that is, hydraulic resistance. Thus, the work of all the circuits is connected.
Balancing valves are installed on all nodes and TP systems: heat exchanger, pumps, water supply, ventilation, and heating circuits. Additional devices are required to coordinate the operation of the circuits and compensate for the operation of the pumps.
Installation efficiency
An individual heating unit in an apartment building reduces the cost of heating and hot water:
- The heat meter itself does not affect its consumption, but it correctly takes into account. Heating companies often raise the cost of services without supplying enough heat. With accurate accounting, it turns out that before installing the TP, residents overpaid.
- Automation reduces maintenance costs.More precise temperature control also reduces costs.
- A closed heat supply system is more profitable: there is no need to constantly purify water, repair pipes and radiators. Heat loss in a closed system is less.
- ITP works according to the schedule: reduces the temperature at night, stops the pumps, and increases in the morning.
The heat point in 5 years saves from 1.5 to 8 million rubles.
Fields of application
TPs are necessary for the proper distribution of heat between consumers. These include:
- Hot water supply. Part of the heat, since hot water is supplied through pipes, is spent on heating the bathroom and kitchen.
- Heating systems - maintain a comfortable temperature in residential and public buildings.
- Ventilation system - before entering the building, the air is heated.
- Cold water supply - refers not to consumers, but to the elements of support. Cold water serves as a regulator.
Install TP for heating, water supply, air conditioning of both old and new buildings.