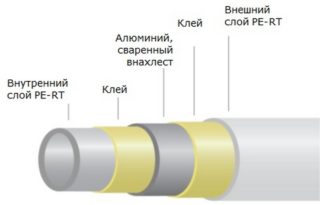
When installing typical water heating systems, it is impossible to do without water pipes. Modern requirements for heating equipment make it necessary to carefully choose products suitable for these purposes. Cross-linked polyethylene for heating is a good option when choosing a material that can replace obsolete steel water pipelines.
Types of pipes by the method of crosslinking polyethylene
Crosslinked polyethylene (SP) is a synthetic material having a modified mesh structure. Its molecules are additionally linked together by the lateral bonds that are absent in the ordinary polymer. The crosslinking effect gives the material extra strength, while reducing the rate of thermal ductility.
Crosslinking Technology
Crosslinking of polyethylene materials is organized according to one of the following technologies:
- peroxide method;
- chemical method;
- physical option.
In the first case, hydrogen peroxide is used as a reagent. The process proceeds at a temperature of 200 degrees, so that the crosslinking is more uniform.
The chemical (or silane) method is characterized in that polyethylene of the required quality is made with the addition of water, silane and special catalysts. This method is considered the most common in industrial practice, although the percentage of crosslinking is only 65-70 units.
By the physical or radiation method is meant the sweeping of a polyethylene mass through an accelerator in which it is exposed to x-ray and gamma radiation. Free atoms of the same elements take part in this process, forming new bonds. The degree of crosslinking achieved is 60%.
Feature Comparison
Crosslinked polyethylene has an ordered structure resembling a crystalline lattice of solids. Moreover, in each case, the finished product acquires original properties. The most uniform crosslinking is obtained with the peroxide method, which is considered unproductive and expensive. This approach is also completely inapplicable in the production of multilayer pipes. The silane method makes it possible to achieve a high production speed of not very flexible products, and the use of the radiation method guarantees the simplicity of manufacturing products from cheap raw materials. The selection of the appropriate material in this case depends on the particular application of the pipe products.
Specifications
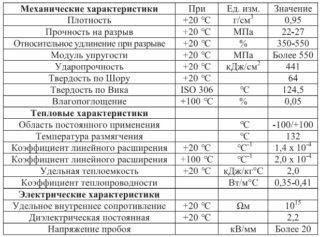
In addition to the claimed high strength index, cross-linked polyethylene pipes have inherent properties that determine their technical parameters. Crosslinking of molecules allows to increase the melting point of this material. Its modified samples have the following indicators for heat resistance:
- softening limit is 150 degrees;
- melting limit is 200 degrees;
- such polyethylene begins to burn only after reaching 400 degrees.

With the crosslinking of a plastic material, its strength increases, but at the same time, the tensile elongation decreases. It almost does not respond to sudden changes in environmental parameters, while revealing similarities with metals. In terms of resistance to chemical reagents, it is also not inferior to them, and even superior in resistance to deformations. The main characteristics of cross-linked polyethylene include:
- structure density reaching 940 kg / m³;
- operating temperature range from 0 to +95 ° С;
- resistance to mechanical stress (shock loads) at temperatures up to -50 ºС;
- thermal conductivity;
- flexibility factor;
- tensile strength (from 350 to 800%);
- life time.
The service life of the joint venture is from 10 to 50 years, depending on the temperature in the pipes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of polyethylene pipes made using the PEX and PE-RT technologies include:
- temperature resistance (frost resistance), especially pronounced for PE-RT pipes;
- high strength indicators, due to which these products are not susceptible to external damaging effects and internal stresses;
- plasticity of the material, allowing their use on complex laying routes with many turns;
- immunity to corrosion, as well as aggressive inclusions present in the coolant, and environmental cleanliness.
Smooth walls inside the pipe channel provide minimal hydraulic resistance to the moving coolant, so that the probability of deposits is minimal. Some of these advantages are fully manifested when comparing a joint venture with metal-plastic, from which pipes for floor systems are also made. The latter does not withstand freezing of the coolant and poorly restores its shape. Otherwise, these two competing species are equally good for arranging warm floor coverings. The disadvantages of the joint venture include the inability to bend them along the radius above the limit value and the complexity of the design of the rotary zones, since the joints in these places have to be firmly fixed.
Fields of application
The universal properties of the joint venture, including resistance to destructive effects and temperatures, determine the areas where this material is most often used. For example, the Uponor pipe for domestic heating is ideal. However, it is often used for the following purposes:
- production of pressure pipes for cold and hot water supply;
- use as elements of industrial heating structures;
- use in drinking water supply systems.
The high-quality Uponor heating pipe obtained by the stitching method is allowed to be used in the arrangement of warm floor structures, as well as in air conditioning systems for domestic and office premises.
Principles and nuances of pipe installation
Proper installation of polyethylene pipes is possible only subject to the following rules:
- pipes from the joint venture are mounted so as to prevent the possibility of freezing;
- for the arrangement of pipelines of heating systems or FGP, a material suitable for water heating of floors is selected;
- the choice of the method of connecting pipes from the joint venture depends on the diameter of the workpieces used.
- fittings are used for pipes with a diameter of up to 32 mm, and for large sizes they are mounted by welding.
The basis of the joint venture pipe laying procedure is the principle of using compression fittings. These connectors, if necessary, are easily dismantled and, after replacing the gaskets, are put in place. To install such a fitting, two adjustable wrenches are required, with small diameters of the workpieces, they are dispensed with an ordinary tool.
Operation tips
When commissioning products based on the joint venture, their throughput increases markedly. This is due to the peculiarity of the material used, which has the property of gradually expanding. Upon reaching the maximum service life, the diameter of such pipes increases by about 3%.
Another factor influencing the increase in fluid pumping volumes is a change in the structure of the pipe material, after which the surface acquires additional ductility.This helps to reduce the resistance to movement of the water carrier and accelerate its movement. Taking these factors into account during the operation of pipes will allow avoiding troubles in the form of leaks at the joints.