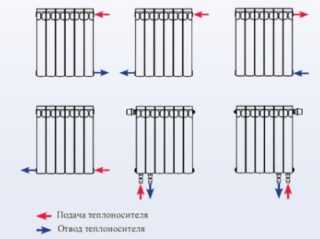
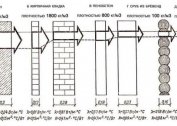
Connecting the batteries in the lower way provides for the location of the nozzles at the bottom of the structure, on both or one of the sides. The bottom connection of the radiator is most often used in private homes to mask communications.
Need a connection point
The connection of heat sources with the route from below provides for the presence of pipes at the inlet and outlet. One of them is used to supply water, the second - to drain. The circuit is intended for:
- easy docking of heating elements;
- ease of replacing radiators if repairs are needed;
- compact decoupling;
- hiding ugly communications;
- equipping the heating main with a cooling valve with a tube probe;
- simplification of installation of sectional batteries with bottom nozzles of heaters.
When the system is withdrawn from the walls, lower L-shaped structures are formed.
Pros and Cons of Technology
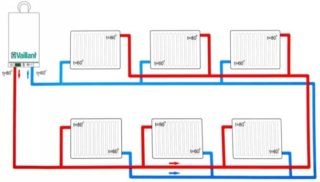
The best option for using the unit for connecting a heating radiator with a lower type of supply is a two-pipe system. Communications exclude heat loss and have several advantages:
- uniform heating of the top and bottom of the batteries;
- ease of serial connection of pipes;
- high-quality heating of rooms, which allows you to implement only the two-pipe method;
- masking of radiator elements in the floor or walls;
- quick dismantling and replacement of elements;
- the ability to install a pipeline of polypropylene, copper, PEX, bimetal, aluminum, steel.
The disadvantages of the lower supply include the need for additional equipment for each battery with air vents, the impossibility of arrangement in the presence of a circulation pump.
Bottom heating system compatibility

The organization of the bottom supply is not carried out in communications with the natural type of circulation. The reason is the direction of the water - from bottom to top, against gravity. If there is a two-way system, it is required to place the valve on the return pipe. The element is characterized by greater throughput compared to the standard foot, which allows the use of powerful circulation pumps.
One-sided lower connection is complicated by the hydrodynamic resistance of radiators due to the presence of two oncoming channels and a small conditional passage. It is problematic to select stop valves - it is represented mainly by models with external thermostats.
One-way injectors are equipped with a built-in bypass, so it is difficult to adjust the water flow. An injection device with a separate choke and a thermostat head cannot be supplied due to lack of space.
Types of connection nodes
An H-shaped assembly located at the bottom facilitates the process of tuning, shutting down radiators and draining coolant from them. Depending on the type of contour reinforcement, there are several types of designs.
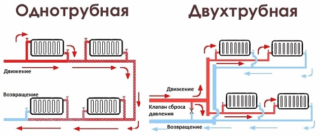
Single tube
The coolant moves along the line to the heating appliances. Due to the drop in water temperature, the battery warms up well only in the first circuit, the latter remain cold. Bypass distribution is used to equalize the temperature difference.The thermal compensation system divides the input streams into two parts. One goes to the radiator devices and starts heating the case. The second at this moment moves to the next device.
Double pipe
Radiators warm evenly without bypass. If there is a lower node, the “binoculars” design is used in the form of fittings with adjustment and closing taps. One nozzle is output to the feed, the second to the return.
Combined
The main with a bypass channel inside is used in single-pipe and two-pipe wiring. On the heating main from one pipe, the bypass slightly opens, from two - it completely closes.
Types of fittings for the assembly
You can connect communications in the lower way using three types of fittings:
- Direct. They are used to bring the radiator modules to the pipes leaving the floor in an upright position. A direct fittings scheme provides for fittings with an “American” (union nut) or compression adapter sleeve.
- Corner Pipes are removed from the wall at a minimum height from the floor surface. The corner fitting is connected by an American, located at the ends of the nozzles.
- Faucets to close the system and adjust the temperature. The fitting is built into the battery housing and provides the speed of connection to a two-pipe wiring. Using ball or valve taps with recessed tips, you can adjust the return, flow, turn off the radiators.
Parts of the steel pipeline are fixed with a union metal-plastic nut with a Eurocone type connector.
The specifics of installing radiators with a bottom connection
It is required to connect radiator elements, regardless of the method, indented 5 cm from the wall surface, 5-10 cm from window sills, and 8-10 cm from the floor. For self-assembly, you will need:
- T-shaped or T-shaped tubes;
- level and pipe cutter;
- special multiflex nodes;
- FUM tape;
- thermal insulation material;
- nuts.
The approach is carried out at the stage of repairing the home or building underfloor heating in the walls, between heating appliances and the floor or in the floor. The sequence of work depends on the shape of the reinforcement.
L-shaped branch pipes
Heating elements can be connected as follows:
- Mounting the nipple and ball valve assembly.
- Putting on a pipe clamp fitting.
- Flaring the tube to prevent the rubber seal from slipping.
- Installation of an element in an angular clamp.
- Conclusion of the structure to the block of ball valves and bait.
- Marking under fixture of a clamp and dismantle of pipes.
- Drilling a hole and driving into it a complete dowel with a self-tapping screw.
- Reinstallation of connecting branch pipes with fastening on overlapping.
- Supply of the main pipe to the connecting pipes. It will be necessary to move the insulating layer 2 lengths of the sleeve.
- Fixing the sleeve and flaring the pipe.
On the ceiling, the structure is installed with dowel hooks. To prevent the pipes from popping out from under the screed, a step of 0.5 m is made.
T-branch pipes
The connection process is implemented as follows:
- Putting on the threaded connection on the nozzle.
- Flaring an element.
- Fixation with a sliding sleeve.
- Masking the knot with decorative overlays for the color and texture of the finish.
Before starting the connection, plastering and leveling are carried out.
After installation, manual or thermal valve adjustment is performed. In the first case, three-way or ball valves are used before and after the radiator. The temperature is set manually or programmed.For lower batteries control valves with a thermal head are best suited.
Node connection diagram
The lower node is connected in several ways.
Via bypass
Bypass is implemented by:
- Built-in channel with adjustable hole diameter. It can be connected to one-pipe communications for even distribution of water temperature. Using eccentric nuts, you can connect pipe bends with any axial distance.
- A remote element to increase the temperature at the inlet, followed by equalization in the system. The tube is connected through a fitting with a built-in thermostat. The coolant will flow through the bypass up to the battery and drain down. An air vent is integrated in the upper part to adjust the return.
Bypass reduces heat loss by 20%.
Through the injector
Injection, or lower side method provides for the availability of special devices. Injectors are made in the form of a pipe installed in the pipe body at the outlet. A feature of the circuit is the direction of the hot coolant into the battery through the inlet near the nozzle and return through it to the return. On the side of the injection device is a valve regulator, screw or automatic temperature controller.
Tichelman wiring
Actual for a single pipe heating system. The main line is equipped with a passing route with the same total distance for the supply and return lines.
Using Flow Extenders
The device is mounted at the bottom, does not have taps to the top. The coolant circulates, moving to the middle of the battery, and then exits at the end. It rises and pushes water through the outlet pipe. Flow extenders are not used in gravity communications.
Using an adapter
The element is screwed in at the bottom, a stainless pipe goes up. Heating pipes to the adapter are connected from below.
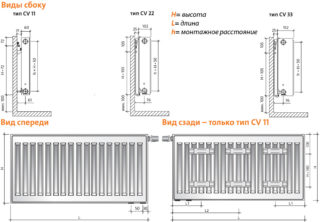
Which radiators fit
Manufacturers produce batteries for the bottom connection with outlet and entry pipes at the bottom. Universal models have 4 gaps under the trunk, so they crash in any way. Heating pipes are thrown at two entrances, the rest are hidden by plugs. It is allowed to connect radiators under the side insert in the lower way. You will need a special installation kit for fixing the pipes to the wall, into it or under the floor.
Fixing is made from below on arms. The element should be slightly inclined towards the reverse movement of the coolant. In this way, air congestion is quickly removed from the system.
The lower radiator connection method is suitable for single-pipe and double-pipe heating. Using special fittings and devices, the technology is implemented in an apartment and a private house.