Rockwool Roof Butts - insulation designed to protect roofs. To understand the features of its application, you will need to familiarize yourself with the varieties and technical characteristics of the building material. The user should also know how insulation boards are stacked correctly on the roof.
Description of the types of insulation
Rockwool produces a wide range of roofing insulation, among which the following stand out:
- Roof Butts N;
- Roof Butts B;
- Rockwool Butts S;
- Roof Butts Extra;
- Rockwool Butts Optima.
The first of these materials is used to protect the lower layer of the coating in combination with the samples used as the upper insulation layer (Rockwool Roof Butts B). Products with the “C” index are in demand when it is necessary to combine insulation with a sand screed, which guarantees reliable adhesion of various layers of protective coatings.
Rockwool Roof Extra refers to the original “H” type boards, consisting of two heat insulators: the lower thin with a density of 130 kg / m³ and the more durable upper with a density of 235 kg / m³. These products, unlike the “H” brand, have a lower weight, which facilitates their installation on any roof. Roof Butts Optima slabs differ from other options only in their lower density (only 100 kg / m³), which allows them to be used for warming the interior of buildings.
The main characteristics of the insulation
Rockwool's product specifications include:
- density;
- compressive strength;
- thermal conductivity;
- vapor permeability;
- moisture absorption by volume;
- dimensions of tiles.
According to the first indicator, most of the plates presented by the company are produced according to the principle of combined (double) density. Thanks to this, all Rockwool product samples are lightweight and easy to install. Products of Ruf Batts B have the highest density index of 190 kg / m3. Next are plates of the same type with a density close to 160 kg / m3. The product with the “N” index closes this row with an indicator of 115 kg / m3.
Compressive strength indicates the ability of a material to withstand the effects of external factors causing deformation and internal stresses. This indicator is affected by its structure (in particular, porosity). The most compressive are Ruf Batts B boards (at least 70 kPa). The least durable is Roof Butts N with an indicator of at least 35 kPa. This is enough to use it as an intermediate layer between the outer coating and thermal insulation with index “B”.
Thermal conductivity is determined by the amount of heat given through the area of the isothermal surface. Similarly, moisture absorption and vapor permeability are evaluated. These indicators are directly related to the porosity of the insulating material and its other characteristics.
Distinctive features
The specifics of insulation from Rockwool include the technology of obtaining material from the original product. Its raw materials are the rocks of the basalt group, distributed throughout the world and therefore differ in low cost. After mining, the stones are loaded into special furnaces, where at high temperature they turn into liquid melt.The resulting mass then goes to centrifuges, in which it is sprayed into small jets. When cooling, the latter turn into thin long fibers with a diameter of up to 15 microns and a length of up to 50 mm.
Frozen formations are first collected in a carpet film, which is then treated with binders and hydrophobic compounds. This is followed by pressing to give the material the desired density and molding mats of a given size. The use of this technology allows you to get a large number of cavities filled with air layers. The features of the structures under consideration, saturated with large volumes of air, are unique thermal characteristics.
Application area
Advantages of basalt heaters - the main reason for their widespread use in various fields:
- insulation of the external surfaces of building frame or wooden structures using modern technologies;
- reliable thermal insulation of socles of building facades;
- when certain conditions are met, they can be used to insulate the internal surfaces of buildings;
- protection of partitions, allowing to increase their sound and thermal insulation properties;
- insulation of floor coverings, including cement screeds and concrete floors;
- for the purpose of thermal insulation of pitched roofs and flat roofs, as well as for warming attic (attic) rooms.
A wide selection of materials for universal use allows the use of Rockwool products for the stated purposes.
Methods for laying roofing slabs
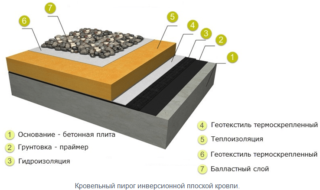 The main methods of installation of insulation:
The main methods of installation of insulation:
- laying between the elements of the rafter structures;
- mounting without mounting;
- ballast fixation;
- anchoring.
Laying between rafters
After accepting the natural form of mineral wool by the plates, they should be prepared for laying, for which they are cut with a construction knife into blanks of the desired size. The width should correspond to the distance between the rafters, minus a tightness of about 20-25 mm. All these operations are performed in protective equipment (gloves, a respirator and tight clothing), which eliminates the possibility of cotton particles getting into the respiratory system and skin areas. Sliced workpieces are then pushed into niches formed by adjacent rafters; while the edges of the material are slightly bent outward due to the difference in size. The method is best suited for medium hard boards.
Installation without fixing
The installation method without fastening is relevant for products with medium and low stiffness indicators. In this case, the workpieces are mounted across the entire overlapping area one next to another on a previously laid waterproofing layer. In adjacent rows they fit with a slight offset relative to each other. With this approach to warming, the attic is unsuitable for living.
Ballast mount
The ballast method is used only when using boards with a high density and stiffness index. Ruf Butts blanks are laid out directly on the vapor barrier film, and a waterproofing layer is laid on top. A ballast holding structure is placed on top. For unexploited attics, this function is performed by stone filling, and in residential premises - paving slabs.
To fix the blanks of the RUF BATTS insulation to the roof base, anchors or dowels with a wide hat are used. This type of fastening is in demand if the plates have to be laid in two layers, of which the upper is harder than the lower.
Competitive advantages of insulation Rockwool Ruf Butts
In terms of quality, Rockwool Ruf Butts basalt cotton wool successfully competes with the most common types of thermal insulators of this class.This possibility is primarily due to the environmental cleanliness of the feedstock, its processing and the final product itself. In addition, RUF BATTS insulation guarantees effective sound insulation, which reduces the level of external noise by 43-62 dB. Its competitive advantages are also manifested in the fire safety of the material belonging to the class KM0 (absolutely not dangerous).
In terms of combustibility, the heat insulator belongs to the NG category, which means absolutely non-combustible. Therefore, the plates are used not only for insulation work, but also with the aim of creating fire barriers.
The features of the fiber structure of basalt wool, in addition to good sound insulation, provide the plates with long service life with no signs of shrinkage. When using these products over time, dips and voids do not appear in the mass of the substance; its original form remains during the entire period of operation. According to the manufacturers, this period for ROCKWOOL heaters is approximately 50 years.