Propylene glycol for heating is used as a filler for heating circuits and radiators. In a closed system, the energy carrier must not contain impurities, chemicals, alkalis and salts that contribute to corrosion. The use of the finished heat carrier increases the operational characteristics of the boiler, reduces the destruction of the inner surface of pipes, batteries.
Features of a water heating system
The structure includes a heating boiler, a network of pipelines, batteries, a circulation pump, collectors, external temperature meters, thermostats. Water passes through the heat exchanger of the unit, heats up and through pipes enters the radiators of the heated space. The energy source transfers heat through the batteries and returns to the source. The coolant moves in a natural way or with the help of a pump.
Heating in the house happens:
- gravitational (natural);
- forced.
Work is controlled by sensors and thermal heads in automatic mode or coordinated manually. In the system, the temperature is regulated separately on all devices, which saves fuel. The heat carrier based on propylene glycol is used in the main line, this extends the service life of equipment and devices. No precipitate is deposited in the pipes, so 80–90% of the heat is lost.
The lack of water is that it freezes in unheated buildings, tears collectors and radiators. Adding salt does not solve the problem, because it leads to increased corrosion, the inclusion of antifreeze in the coolant increases the cost of heating.
Propylene Glycol Description
The substance is actively used in heating circuits due to non-toxicity and safety. It is a viscous liquid without color with a characteristic odor, which is used in many industries.
Fluid properties:
- the solution can withstand without changing the state of temperature from -40 to + 100 ° C, for a pure substance, operating parameters in the range of -60 - + 185 ° C;
- the substance contains up to 5% carboxylates that protect the inside of the pipe from destruction;
- anti-corrosion, anti-scale and stabilizing additives are introduced into the glycol for heating.
The density of propylene glycol is lower than that of glycerol and ethylene glycol, but higher than that of ethanol. The viscosity of the substance is greater than that of alcohols and ethylene glycol, especially in cold conditions. A substance is produced from propylene oxide by hydration at +160 - + 200 ° C under a pressure of 1.6 MPa.
The reaction proceeds in a vacuum, in the process it is released:
- propylene glycol - 85%;
- dipropylene glycol - 13%;
- tripropylene glycol - 2%.
The finished product is stored for a year without changing the quality. After that, the substance is divided into additives and a base, which reduces the heat capacity of propylene glycol.
Specifications
The product finds application as a basis for energy, with which the system is not afraid of freezing. Inexpensive pipes can be used since the substance contains anti-corrosion components.
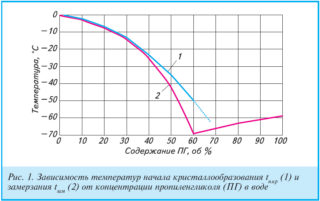
Freezing temperature depending on the concentration of propylene glycol:
- contains 54% of the substance - the energy carrier freezes at -40 ° C;
- 48% - -30 ° C;
- 39% - -20 ° C;
- 25% - -15 ° C;
- 15% - -5 ° C.
In the system with the substance, storage boilers are used; in heating with ethylene glycol, the use of such units according to the instructions is not allowed. The disadvantage of propylene glycol, like ethylene glycol, is considered to be increased fluidity, due to which the liquid penetrates into cracks inaccessible to water. Welding joints and fittings are done carefully to prevent leaks.
The propylene glycol coolant is used only in a system with the appropriate technical characteristics, so replacing water does not always lead to good results. Manufacturers of radiators indicate in the passport the conformity of products to one or another type of energy carrier.
The product is mixed with water, alcohols, ethylene, acids, organics of the carbonyl group, amines and nitrogen-containing solutions.
Advantages and disadvantages
In water at temperatures above + 75 ° C, carbonates decompose, scale is deposited. Propylene glycol inhibits the corrosion process, ideally if the substance is added to a distilled liquid.
Advantages of using an energy carrier with additives:
- protects the heating circuit and appliances from rupture in frost, freezing occurs slowly with gradual crystallization;
- the frozen substance in the pipes gets a working consistency when the heating unit starts;
- the second ecological carrier after water, prolonged inhalation of vapors, ingestion, and skin contact are not dangerous;
- in contact with the finish of the floor and walls does not damage the materials;
- promotes fast heating and slow cooling of the system;
- reduces hydraulic resistance and improves the functioning of the pump in the return branch;
- reduces electricity consumption when pumping energy, due to its low density.
The disadvantages include the high cost compared to other types. But the high cost is justified by minimizing repairs, reducing the amount of fuel and labor costs. The substance is not used in heating mains where there are galvanized elements.
Differences between propylene glycol and ethylene glycol
Ethylene glycol is an organic acid-containing solution, a representative of polyhydric alcohols. It is a colorless, transparent, odorless, oily-thick liquid. Ingestion causes toxic poisoning.
Differences from propylene glycol:
- when freezing, the volume of water with propylene glycol increases only by 0.1%, and the coolant with ethylene glycol becomes more by 1.5%;
- the energy carrier with propylene glycol withstands the evaporation of water from the solution and does not freeze to -60 ° C, ethylene glycol crystallizes at -13 ° C, glycerin - + 17 ° C;
- toxicity of propylene glycol LD50 from 20 to 30 thousand mg / kg, a similar indicator of ethylene glycol - LD52 - 4700 mg / kg.
The toxic substance is rapidly absorbed into the body, causing pulmonary edema and heart failure. The substance is not used in open systems, because it penetrates the skin and when breathing. Spent energy carrier based on ethylene glycol is not poured into the soil or sewer, but is given for processing.
Criterias of choice
When determining the type, the operating temperature is taken into account at which the energy carrier exists for a certain time without decomposition. The properties of the liquids are described and allow you to make the choice of additive according to the characteristics of the heating system.
The indicators are taken into account:
- heat capacity indicates the amount of energy that will provide the desired heat per unit time;
- corrosive activity indicates the need for the choice of pipes and batteries and the impossibility of using some materials;
- viscosity determines the speed of fluid movement, affects leakage, heat transfer coefficient, the indicator changes when heated or cooled;
- the lubrication index limits the use of certain materials and structures of various mechanisms in contact with the product.
Safety for humans, the ability to cause burns, toxic poisoning matters. The flammability limit and the possibility of damage to objects during spill from the system are taken into account.
Scope and features of propylene glycol use
The substance is used in the production of polyester unsaturated resins for the construction and automotive industries, in the production of alkyd mastics and polyurethanes. The product is used in the manufacture of creams, pastes, detergents in cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. The food industry uses propylene glycol to dissolve additives, uses bactericidal and preservative characteristics.
The substance is used in the manufacture of antifreeze, brake, anti-icing fluids, serves as a plasticizer in the production of polyvinyl films and cellophane. Propylene glycol is seasoned in visual smoke devices at stage performances.
Due to loss of fluid in the circuit, there is often a need to mix ethylene glycol and propylene glycol in a heating system. Before filling, you need to conduct a compatibility test. These substances are combined, but manufacturers use different additives, which when combined can give a precipitate. The ideal solution is to completely drain the coolant before new filling.
An energy carrier based on propylene glycol can be used in heating mains, which partially pass outside the house or in the attic. The coolant is poured into the circuit under pressure or manually, but previously the system passes hydraulic tests. During operation, energy samples are taken and suitability in the laboratory is checked.