If a heating scheme for a one-story house with forced circulation is selected, a pump crashes into the system. The pump is responsible for the speed of movement of water, and its operation depends on electricity. Heating the home can be achieved without a circulation pump, but it will be necessary to observe the slope of the pipeline so that the energy source can move in a natural way.
Advantages and disadvantages of a forced circulation heating circuit
The coolant speed increases in an organized supply system, water consumption increases and the diameter of the collectors can be reduced.
Advantages of the system:
- radiators heat up faster, there is no inertia;
- pipeline branches are made longer and laid in convenient places;
- a minimum slope of the collectors is arranged, which is required only for draining the coolant;
- expansion tank is located in the boiler room;
- It is possible to connect a heating branch of a warm floor.
The disadvantage of the circulation system is its dependence on the supply of electricity. Stopping the pump leads to a quick cooling of the radiators and overheating of the boiler. Spare supply options are used to avoid an emergency. Electric pumps are noisy during operation.
For a one-story private house
In residential buildings, a one-pipe or two-pipe heating system is arranged, the water supply in which is organized using a pump. Labor costs for installation of circuit elements are reduced, because it is not necessary to build an uncomfortable upper wiring.
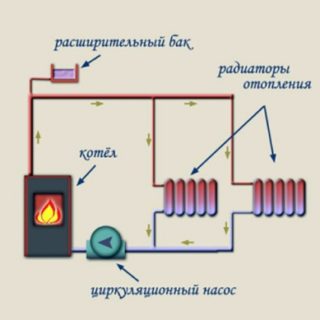
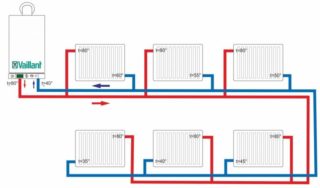
Piping according to the collector circuit ensures simultaneous heating of the batteries, even if they are located far from the boiler. The pump is placed in front of the heating unit on the return branch. There you need to connect the expansion tank, which is necessary in a closed system.
Elements of the coercive system
The expansion tank can be open or closed (expansomat). A closed system with a compensator is used more often, because in an open circuit, water evaporates. Atmospheric oxygen enters into such a system and leads to corrosion of internal steel parts.
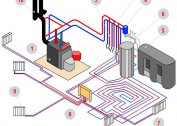
Elements of the heating system of a private house with forced circulation:
- gas, solid or liquid fuel boiler;
- membrane expansion tank;
- circulation pump of appropriate capacity;
- batteries
- pipes;
- connections and adapters;
- valves for various purposes, cranes;
- air vents;
- Filters
- fixing devices.
Pumping equipment must ensure the movement of energy, so it is selected by power. An excessively strong pump creates additional noise and overspends electricity.
In a closed highway, a security group is provided, which is placed at the outlet of the supply branch from the heating unit. It coordinates the pressure and relieves excess pressure in an emergency, and normally removes air from the pipeline.
Principle of operation
The pump in the construction has a stainless steel housing with a rotor located inside and a shaft with an impeller. The electric motor is driven by a rotor. The energy carrier is absorbed on the one hand, and on the other hand is pumped into the trunk. The pump pushes water if resistance appears in the pipe.
In forced systems, heating is controlled in rooms and groups of batteries.A well-thought-out system contains multi-way taps and valves, automatic regulators and thermostatic units that facilitate the management of home heating.
The breakdown of the heating main into sections does not affect the quality of heating, convectors, radiators are selected for rooms, and the contours of a heated floor can be connected. With an organized supply of energy, you can make many branches from the main circuit and separately connect different floors.
Heating options
In a private building, you can apply one heating system or combine several types. The choice is determined by the climate, the material of the walls of the building, economic feasibility.
As a result, an optimal system is selected that meets the requirements of:
- uses convenient and affordable fuel;
- it is maintained and operated inexpensively;
- reasonably gives off the received heat in the conditions of high energy efficiency of the house.
The owner is considering various options for systems depending on the time spent in the building (cottage or apartment building). This takes into account the power of the boiler, its efficiency, number of storeys of the house.
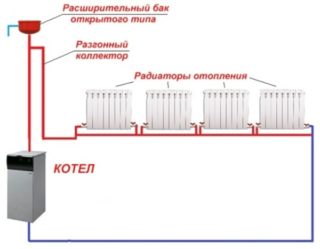
Single tube
In such schemes, the reverse supply and reception of the spent coolant is not provided. Vertical one-pipe heating is easier to install, requires less cost and relates to economical systems. Radiators are connected in series, there is no possibility of coordination of heating during operation.
A single-pipe scheme requires high water pressure, so more powerful pumps are installed. An increase in pump power leads to increased operating costs, increases the risk of leaks and requires regular replenishment of energy.
One-pipe heating is arranged according to the principle of the top spill when the expansion tank is placed in the attic or at the highest point of the room under the ceiling. If such a system is installed in a two-story house, additional automation is required to equalize the temperature on each tier.
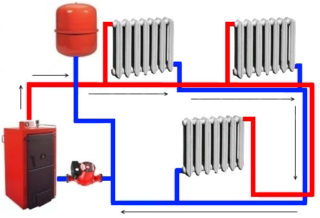
Double pipe
This arrangement contributes to an even distribution of heat. One line supplies the heated energy carrier, the second takes it back. The view allows you to set the temperature in the rooms with a control valve, suitable for a building of any size and different storeys.
The two-pipe system is:
- horizontal
- vertical.
The horizontal scheme is used more often, because the buildings have a large length, and the struts of its branches are arranged in utility rooms, stairwells and corridors. Batteries of one tier are connected to a common riser. In the vertical version, a larger number of pipes is used, installation is more expensive, but the appearance of air jams in pipelines and radiators is excluded.
Collector
In this system, the pump evenly distributes energy throughout the house, it is possible to adjust the temperature of each radiator. The collector is connected to the batteries using a pipeline, at the outlet and entrance to the highway there is a slight difference in heating. The system uses pipes from different materials, more often metal-plastic ones are installed.
The German engineer Tihelman developed the reverse system of reverse action, while changing the principle of return feed. According to his method, the first heat exchanger to receive hot energy was the last in the return circuit, and the first in the return received heated water last. As a result, the fluid circulated throughout the system and the radiators were heated evenly. The technique made it possible to equally heat the system at different points and refuse to use regulatory automation.
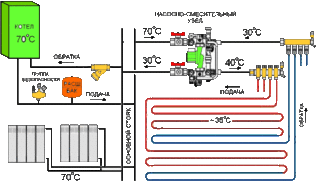
Water heated floors
The system belongs to the low-temperature types of heating, uses an energy carrier with a temperature 2 times less than the indicators for the radiator circuit (+30 - 35 ° С and + 70 ° С). The room is heated by transferring heat from the pipes to the surrounding area. Under the branch, materials with low thermal conductivity are placed, and layers that transfer energy well are arranged above the collectors.
The water is taken from the general heating system, the water temperature is regulated automatically at the entrance to the heating floor main. This type of heating acts as an additional or is the main in the room. On stairwells and in vestibules it is not always possible to carry out underfloor heating, so a branch with radiators is installed.
Choosing a heating boiler

For a one-story private house, an optimal heating system with a boiler that meets the required characteristics and parameters. The unit capacity is calculated in such a way as to satisfy the heating needs in the harsh conditions of the local climate and a small margin is provided (10 - 20%). In conditions of forced water circulation, it is easier to provide for boiling water in the heat exchanger of the unit.
Parameters taken into account when choosing a boiler:
- pipeline length and diameter;
- fluid velocity.
Electrical units do not require a chimney, easy to operate and manage. Oil boilers use diesel fuel, they are installed if there is no access to the gas main and there is no electricity. Gas units are almost 10 times more economical than the first two types, but fuel supply is needed. Solid fuel boilers operate on coke, coal, wood, automation controls the combustion of residues and emitted gases.