The single-tube water heating system is used to heat private and municipal houses and apartments. It is chosen by homeowners who want to install a scheme that does not require large investments. This is a more profitable option compared to other types of wiring, for example, collector or two-pipe. When choosing such a system, it is useful to familiarize yourself with the principle of its operation, advantages and disadvantages, device options and connection methods in advance.
Principle of operation
Each water system works according to the principle of heat exchange between the coolant circulating along the circuit and the air contained in the heated room. Water supply to the batteries is carried out depending on the layout of the room where they are installed. Water is supplied using sunbeds in a horizontal pipeline of the main type or vertical risers. Types of system wiring are implemented taking into account how the heat carrier passes along the circuit, and are divided into two types:
- gravitational, when the coolant moves by gravity;
- with forced circulation.
For the stable operation of any system, it is necessary that the diameter of the distribution pipe exceed the size of the radiator inlets. This rule does not apply to upright risers in which the heat carrier flows downward due to gravity.
The difference between a one-pipe and a two-pipe system
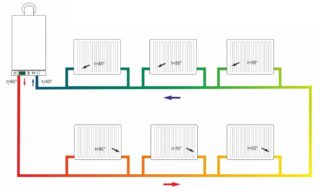
The one-pipe heating system operates by units connected by a single pipe. The coolant in it must be connected in series to each device. In the two-pipe scheme, there are two pipes designed for supply and return drain, in which case the heat carrier goes to the batteries through the pipe and goes to the boiler using the return output. The main difference between single-pipe wiring is that radiators are connected to a single distribution line.
Pros and cons of a single pipe system
A single-pipe heating system for any apartment or private house warms up faster when compared with a two-pipe one. If you follow the installation rules, the system will be well balanced, the heating of the rooms will begin evenly. This scheme is chosen for an aesthetic appearance, since only a single pipe is needed for wiring. In addition to the main advantages when wiring a single-tube type, you can connect the crane to the battery, which will allow you to remove it without having to turn off the entire heating system. It is advisable to install this type of scheme in small private houses, this is a more economical option, unlike the two-pipe method.
Of the minuses, schemes with a single pipe indicate difficulties with adjusting the temperature regime in the rooms. For this purpose, you need to use polypropylene thermo valves or radiator regulators. In addition to adjustment, you need to create strong pressure and install powerful pumps with tanks for expansion at the maximum point in the circuit. If the house is two-story, the heat carrier should go from above. In large houses, sometimes it is necessary to increase the number of sections in batteries, due to which it is necessary to increase their length and spend additional forces on placement.
Installation methods
One-pipe heating in a private house can be open or closed, vertical or horizontal, with lower or upper wiring, natural or artificial circulation of the coolant.
Natural and forced circulation systems
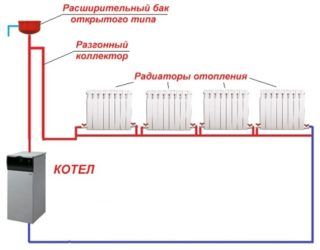
A system with natural circulation is considered the most common. Previously, single-tube standard heating of this type was installed in all one-story buildings, including with stove heating. Her plan includes a tank with expansion, located under the ceiling, into which water flows from the boiler. Then it flows by gravity into gas or automatic radiators through pipes.
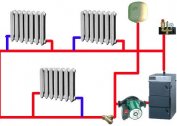
Now, in most multi-storey and private houses, automatic boilers with built-in circulation pumps are installed.
If you need to install a boiler with complex automation, a pump is installed for it separately to avoid overheating when the fuel flares up to extreme temperatures. Circuits with forced circulation make it possible to implement projects of increased complexity, they are often used for installation and connection of underfloor heating. Forced circulation is relevant for multi-storey buildings or houses with attic structures.
Open or closed heating system
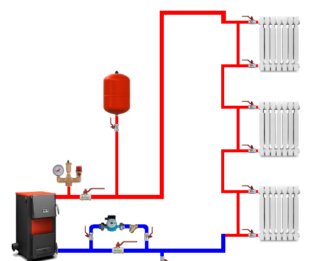
In open systems, which are very widespread, the water level inside the tank increases after overheating and decreases with cooling. They are supplemented by tanks with nozzles to discharge excess steam and atmospheric pressure. Automated devices that run on gas, pellets or fuel oil are complemented by compact expansion vessels that compensate for minimal pressure expansion.
Since the pressure itself will depend on the temperature, in the absence of malfunctions, the boiler switches itself off, the pressure in it drops. If the boiler runs on peat fuel, coal or wood, the combustion process in it cannot be stopped quickly, which can cause water overheating.
The design of an open or closed system must necessarily include an expansion tank, a polypropylene pump, a valve for releasing steam and a circuit for automatic water make-up. For solid fuel boilers, closed systems are more often used.
Horizontal and vertical layout
The choice of option for a single-pipe single-circuit type scheme completely depends on the type of structure, the number of floors in the building and other factors. For small houses, horizontal piping of the required diameter is considered an ideal option. In buildings with an area of more than 60 sq.m. and with the number of rooms more than three, it is recommended to use a horizontal scheme, if we are talking about a building with one floor, and vertical for a two-story building. In the second case, the wiring is installed on the second floor, then stretches from the top to the bottom, after which it is brought to the boiler.
The vertical layout in a single-pipe heating system is mainly used in multi-storey buildings, where water goes to the attic or to the upper floor and pours down into separate risers, after which it passes through radiators. Such a scheme is called Leningrad.
With a horizontal connection, the pipes are located horizontally, and the heating devices are connected one after another. This method is relevant for single-story buildings, since it delivers much less complexity.
Options for connecting the radiator to the highway
To connect the batteries to the highway, various options and schemes are used. The efficiency of supplying a thermal carrier depends on the method, so it is so important to choose the most suitable one.
Diagonal
Diagonal connection is considered the most effective, this scheme is used by manufacturers when testing heating appliances. Other options give off heat worse. Also, the diagonal method is quite universal, which allows it to be used both in a single-pipe and in a two-pipe scheme.
Side
If we compare with the diagonal one, if there is a side connection, the heating efficiency will be slightly lower, by about 2%, if the battery has no more than 10 sections. If the radiator has a large length, its far edges will not warm up completely or remain cold. To avoid problems in panel batteries, flow extenders are installed - special tubes that bring the heat carrier to the middle. Similar devices can be placed in batteries made of aluminum or metal alloys to improve thermal efficiency.
- Bottom connection
- Diagonal connection
- Side connection
Lower
The lower or saddle connection is considered the least effective, heat losses during it reach 12-14%. Moreover, this option is the most aesthetic, since the pipes are laid on the floor or under it. The problem with heat loss is solved by buying more powerful batteries to increase the temperature in the room.
Perfectly matched wiring diagram eliminates heat loss and helps prevent excessive fuel consumption. A one-pipe heating system for a private house or a multi-story building is a profitable and affordable option for those who want to save money and provide premises with heat.