For heating private homes and summer cottages are widely used installation of autonomous heating. A common option is with two pipes and a small generator that can run on different types of fuel. There are different schemes of a two-pipe heating system. One of the most common is Tichelman's scheme. It is characterized by stability and uniform heating of the radiator elements.
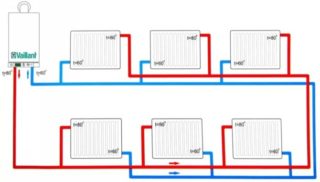
Tihelman heating scheme
The system has other names: it is often called a passing system, characterizing the movement of a liquid coolant along two circuits included in it. In addition, there is a name for this circuit reverse with reverse movement. One of the main features of the installation is the same length of the supply and return pipes. Since the hydraulics in different elements of the system will be identical, the extreme radiators receive the same amount of heat. In this case, the return originates from the first of them, and the feed ends on the last.
Features of the internal structure of one-story private houses are often such that they do not have to hang heating pipes on the walls. Typically, they are usually laid under the floor and protected with thermal insulation. The installation of the Tihelman heating loop, in particular, the vicious circle on the distribution element, is then simplified.
In rooms with high window frames, the use of floor convectors is common. Compared with the radial design, the Tichelman heating loop is better suited for connecting these elements due to lower fuel consumption and reliability.
In a two-story house, a common riser is installed and two rings are made for the first and second floors. It must be borne in mind that their energy loss will turn out to be very different, and select radiators and diameters of the pipes used based on this. The use of separate structures will allow for their mutual balancing. In a two-story house, two cranes are conveniently placed in the boiler room next door to each other.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of plants of this type include uniform heating of the entire network and the ability to adjust heat transfer by radiators. The scheme is reliable, it rarely fails, especially when compared with the operation of other systems with a large number of heating elements. This makes it a good option for use in a private home.
The main drawback of the design is the limitations associated with the internal features of the device premises. The scheme involves bypassing the perimeter of the building with a return to the boiler. In many buildings, organizing this is not easy - they do not give doors, flights of stairs and other barriers. Also, the installation of thick pipes involves an increase in the cost of configuration.
System installation process
The installation of Tichelman’s heating begins with the installation of a boiler, which should be placed in a room of at least 250 cm. The power of the device depends on the area to be heated: 1000 watts per 10 m2 of area.
After that, you need to perform the following steps:
- Hang sections of radiators. Having determined the required number of elements, mark their future localization - usually they are placed under the windows. Fix radiators with brackets.
- To stretch pipes made of metal-plastic, along which the flow and return will go.Such material is recommended due to its ease of installation and resistance to high temperatures. Diameters should be 20-25 mm (for main pipes) and 16 mm (battery connection).
- Mount the circulation pump on the return next to the boiler. Before it you need to place the filter device. Cut the pump through a bypass with three cranes.
- Install the expansion tank and safety parts that are responsible for the safety of the system.
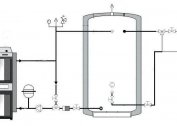
The simplest and cheapest method of water treatment is the use of an indirect boiler in the Tjhelman loop. Automated boilers are usually easily switched and controlled by a heating device. Otherwise, the inclusion of a boiler will require the creation of a strapping.
In utility and outbuildings, it is considered acceptable to place a bypass pipe directly above the doors. In this case, at the highest point of the configuration, you need to place the air exhaust device, and at the bottom, equip the drain mechanism.
Associated pipes and pumps

Since buildings in the private sector are distinguished by a compact layout and the absence of long main heating paths, high hydraulic resistance for such systems is uncharacteristic. To determine what diameter should be in the pipelines, you can use the table that describes the relationship of this parameter with the required energy.
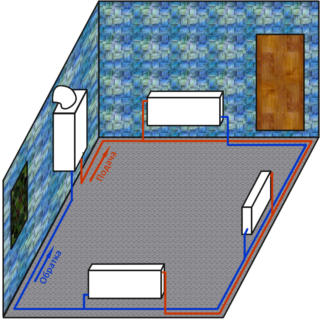
Double pipe system
In small areas (150 m2 or less), heat loss does not exceed 15 kW. In this case, it is recommended to choose products with an internal diameter of 2 cm and connect a 25-40 pump. In structures that heat large areas where 15-30 kW is expended, an indicator of 25 mm is used in the main routes. In looped configurations and branches, it is slightly reduced. To connect the radiator elements and supply to the last of them, the minimum parameter value is 16 mm. For such an installation, a 25-60 pump is suitable.
DIY Tichelman loop
When installing this design yourself, you need to pay attention to the following points: the type and size of the pipes used, the selection of the capacities of the components involved and their strapping. It should also be borne in mind that a configuration with height differences (with laying pipes above the doorway) requires air exhaust and drainage. Sometimes, instead of arranging such an installation, a choice is made in favor of a dead-end scheme, characterized by a longer path length.
The feed contains the components responsible for the security of the system. They include a manometer, a bleed valve and an automatic air mass release device. An open configuration assumes a vertical route to the route before the start of the dodging, with an expander placed at the highest point. After that, the trunk is led to the remaining network components.
On the way back, a pump is installed, the power of which should be enough to neutralize the resistance of the hydraulic system. The boiler binding system includes shutoff valves installed next to it on both pipes and in the vicinity of the expansion tank. They are also attached to the sides of the pump and to the make-up pipe located near it.
Hydraulic calculation

An important component of the circuit is a hydraulic pump, which creates supply pressure and vacuum on the way back. The calculation data demonstrate that the values of both parameters decrease with increasing distance from the pump in the direction of movement of the coolant. If you measure the data on a hundred-meter pipe, it turns out that with a distance of 10 m, the supply pressure will be 90% of the nominal value, and the reverse vacuum will be 5%.With a range of 20 m, these parameters will be 75% and 20%, respectively, and the drop on the radiator element in both cases will be 95%. At a distance of 50-60 m, the numbers are shifted to the middle (45 and 40, 40 and 45, respectively), and the decline on the radiator is 85%. With further distance from the pump, the proportions continue to change in the direction of increasing vacuum; pressure reduction at a distance of 70 m will be 90%, and at 80 m and more - 95%. Thus, in the middle part the pressure loss will be slightly greater than at the beginning and end. Proportionally changing indicators allow maintaining approximately equal pressure differences of radiators.
With proper installation, the absence of differences in the cross section of the main pipe and the same height of the location of the radiators, the system functions smoothly. The power of the batteries involved will be equal to each other.