The room is heated by transferring heat from the coolant to air or objects in the room. Since direct contact of a heat source or heat carrier with air is excluded, heating devices act as intermediaries. The latter are classified according to many signs.
Varieties of heating appliances
The design and efficiency of the heater determines the methods of heat transfer. This is the main classification of devices.
- Convective - transmit at least 75% of the heat by convection - in jets. An example is convectors, ribbed pipes. The source is usually a heater, heats the air, it is transmitted to the room, and already from the warm air masses surfaces, furniture and people are heated. Devices can be very effective due to the speed of heating the air, but consume a lot of electricity.
- Convective-radiation - transmit from 50 to 75% of the heat by the convective method. These are the majority of traditional heaters: radiators, floor heaters, smooth-tube.
- Radiation - 50% of the heat is radiation. These include infrared heaters, ceiling and panel appliances. The heater generates infrared radiation, in this case, first the surfaces, objects and people in the room are heated, and only then the air. Eliminating air from the heat transfer chain reduces heating costs.
Convection-radiation heaters are installed most often. Devices have high efficiency, cheap and practical.
By type of coolant
The traditional heating system implements the following scheme. The heat source is a boiler - gas, electric, solid fuel. It heats a certain amount of coolant, it enters the system and gives off heat through the surface of pipes and heating devices.
The coolant must meet many requirements: absorb and give a sufficient amount of heat, not cause corrosion, heat up to the required temperature.
- Water is the only option for central heating. The reason is the large distances between the heat source and the consumer. Replacing with any other option increases the price of heating by tens of times.
- Steam - the so-called dry. Used in vacuum-steam systems, in low and high pressure systems. Plus - the room warms up 3 times faster, there is no risk of freezing pipes. The disadvantage is high fuel consumption.
- Antifreeze - "non-freezing". Glycerin solution, a solution of ethylene glycol, propylene glycol and others. Liquids prevent freezing even in pipes with the smallest diameter. Antifreeze is recommended to be poured into a warm water floor. The coolant during the circulation acts as a lubricant, which increases the life of pipes and radiators. The disadvantage is the need to select antifreeze to the type of boiler.
- Transformer or mineral oil - heat carrier in oil heaters. This is a viscous, heat-absorbing liquid that can give heat to the air in the room for a long time.
It is possible to choose a coolant and a corresponding heating apparatus only when organizing an autonomous heating system.
According to technical characteristics
To evaluate the efficiency of a particular model, it is necessary to analyze technical indicators.
- Heat transfer is the main criterion. On this basis, the radiation apparatus is better than convective.Of the radiators, cast iron is distinguished by the highest thermal inertia, and aluminum transfers heat best.
- Work surface - it is important to consider the total area of the battery, and not the number of sections. Calculation of the dimensions of the heater is performed taking into account the volume of the room.
- Corrosion resistance - ceramic heaters are most resistant. Of the metal models, the best are aluminum.
- Resistance to pressure - convectors are the most stable, since such a load is absent in them. Of the radiators, the best are cast iron and bimetallic.
- Ease of maintenance - convectors and aluminum panels only need to be cleaned periodically. Cast iron and steel must be painted.
- Service life - cast iron batteries last the longest - 50 years. Bimetallic exploited 30-40 years. The least durable steel - no more than 10-15 years.
Thermal performance is not the only parameter of choice. Radiators must meet the requirements of the selected heating system.
Materials for water heating radiators
The most popular heating method is water heating. The heat source can be a gas, electric, coal boiler, coolant - water or antifreeze, batteries - tubular or panel heaters made of different materials.
Cast iron batteries
This is the most famous type of water heating device, adapted to the conditions of central heating. Cast iron batteries are cheap, durable, and can withstand pressure drops. With a small heat transfer - only 40%, they have a large working surface. Cast iron accumulates heat, so the batteries cool slowly even after the heating is turned off.
Modern designer models are very interesting and beautiful. However, caring for them is difficult.
Steel

Most often used in the arrangement of autonomous heating, where high pressure or water hammer are excluded, since steel is sensitive to them. The heat transfer of the alloy is higher; it heats up much faster than cast iron. It is easier to regulate heating due to low thermal inertia. But for the same reason, steel batteries cool immediately after shutdown.
The disadvantage is the tendency to corrosion. The heater must be looked after, used for pouring clean water with additives, and painted on the surface.
Aluminum
The maximum heat transfer level is above 70%. The weight of the radiator is small, its installation is extremely simple, it can even be installed on a drywall. Bonus - a large working surface: the channels along which the coolant moves are placed in sections of a much larger area. Since aluminum conducts heat well, the section is very fast and very hot.
Aluminum is prone to corrosion. To perpetuate the term of operation, heating radiators, like other aluminum heaters, are coated with polymer paint.
Bimetal batteries
The channels through which the coolant circulates are made of steel: it is stronger and more durable than aluminum. The working area of the section is made of aluminum to improve heat transfer to the air. A bimetallic device combines the advantages of steel and aluminum, but is devoid of their disadvantages, such as a short life or a tendency to corrosion.
There are limitations. Antifreeze must not be added to the water used in bimetallic batteries.
The price of bimetal heaters is the highest and is second only to copper radiators.
Electric types of heaters
Electric heaters work on a different principle. The coolant is replaced by heating elements that function when an electric current is applied.With rare exceptions, the heating element has a small area. To make the heat supply more efficient, use 2 solutions:
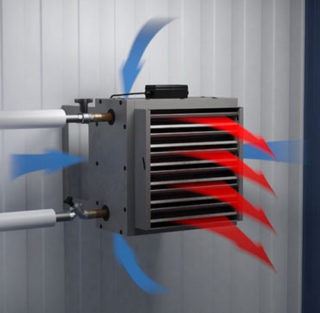
- air flows pass through the heating device - any kind of convector;
- create a case with a large working area - panel heaters.
Electric heaters include appliances that are a heating element. Such a heating appliance, like the Evan boiler, is not. It is a heat source, but not a heating design.
The main drawback of electric heaters is their exactingness to the quality of electric current. If the total power of the heaters exceeds 12 kW, it will be necessary to lay a network with a voltage of 380 V.
Convection devices
Heating elements - heating elements, are placed inside a flat housing. The surface of the housing heats up and transfers heat to the air. However, this mechanism provides only 20% of the heat transfer. There are inlets at the bottom of the device. Through them, air enters the device, heats up and exits through openings in the upper part. Convection provides 80% of heat transfer.
Convectors quickly heat the room, but do not burn oxygen as much as fan heaters. At minimum temperatures, the device can be left turned on for the night. Power varies from 0.25 to 2.5 kW. The calculation of the indicator is performed by cubic capacity, since the convector heats the air. The disadvantage is that the comfortable temperature is maintained in the room only while the convector is working.
Oil devices
The heating element is a heating element, however, the coolant - oil, is also present. A warm, viscous substance fills the sections and transfers heat to the surface. The larger the working surface, the higher the efficiency of the device. Oil-heated electric heating devices are close in efficiency to radiation ones.
Plus - high thermal inertia. The appliance heats up slowly, but also gives off heat for a long time after a shutdown. This mode of operation is more economical. The devices produce power up to 4.5 kW, but oil radiators consume less electricity. The disadvantage is the large mass and bulkiness.
Infrared heating
The efficiency of the infrared heater is close to 100%. The basis of the device is a film with resistor conductors, carbon spirals and plates, which generate thermal radiation when electric current passes. At the same time, it is not air that is heated, but surfaces, objects and people in the room. Even at lower air temperatures, people in the room already perceive it as comfortable.
IR heaters consume 30% less electricity. Heating is faster than convection. The air does not get too dry and does not lose oxygen.
Gas heating
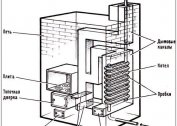
Efficient and cheap heater, but difficult to maintain. The gas air heater or convector works on the principle of a gas furnace. Gas is supplied to the burner. The products of combustion through the chimney are discharged to the outside. The air entering through the holes is heated in the heat exchanger and flows back into the room.
The power of the heaters reaches 8 kW. Since gas is an affordable and cheap fuel, heating costs are minimal. There are many shortcomings: in the house you need to install good ventilation, equip the chimney, periodically clean the nozzles. In case of device malfunctions, carbon dioxide poisoning is very likely.
Installation Requirements
Operational safety is ensured by competent installation of the system. Installation recommendations depend on the type of radiator and the material of execution:
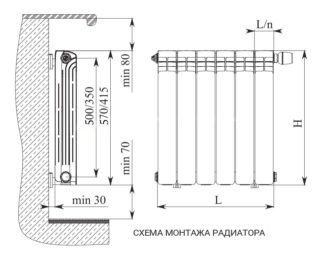
- Batteries of any kind are installed at a distance of at least 6 cm from the floor, 5 cm from the window sills and 2.5 cm from the wall.In rooms of category A. B, C, the distance to the wall should be at least 10 cm.
- Heaters are best installed under window openings, where access to them is provided for inspection and repair.
- The surface temperature of the open radiator should not exceed +70 C. Otherwise, the batteries are protected by a grill.
- When connecting pipes, parts and radiators made of different metals, threaded adapters made of bronze or stainless steel are used.
- Batteries must be filled with water at all times. Fluids are drained only in case of accidents.
- Heating appliances are equipped with shut-off and control valves, with some exceptions. The fittings are selected taking into account the type of system: one-pipe, two-pipe, fan.
The requirements for the installation of gas heaters coincide with the recommendations for the installation of any gas appliances. Build and run only by special services. Convectors and oil radiators are located indoors, observing the usual fire safety requirements.