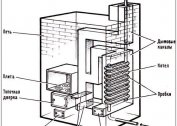
Non-combustible insulation helps prevent heat exchange between the room and the street and guarantees safety: the probability of fire and fire in the house is reduced to an absolute minimum. Refractory thermal insulation can be used in industrial and domestic conditions.
Characteristics of non-combustible insulation material
All varieties of refractory insulation must meet certain criteria:
- when burning, non-combustible thermal insulation should not lose more than 50% of its weight;
- with a visible flame, combustion should last no more than 10 seconds - the material may ignite but not burn;
- when burning, the temperature of the non-combustible insulation for walls and floors should not exceed +50 degrees;
The concept of the oxygen index deserves special attention. This criterion characterizes the fire safety of the material, which indicates the minimum oxygen content per unit volume of the insulating substance.
In construction, several flammability thresholds for the oxygen index are shared:
- 20% - materials that burn well in air;
- 31% - cellular and fibrous non-combustible materials;
- 40% are composite polymers.
There are several types of non-combustible heaters, the characteristics of which must be familiarized with before purchase.
Varieties of fireproof insulation
Thermal insulation materials can have a different production technology and basis, which is reflected in the technical characteristics and appearance:
- loose;
- cellular;
- fibrous;
- liquid.
- Loose
- Liquid
- Fibrous
- Cellular
Loose
Bulk heat-insulating materials are stones of various fractions that fall asleep in the cavity of a building structure. To ensure greater heat efficiency, it is recommended to use bulk heaters of different sizes: large ones provide thermal insulation, and small ones fill the cavities between them.
Non-combustible bulk insulation includes:
- Expanded clay is an environmentally friendly and completely safe material based on clay. It is mainly used for warming hard-to-reach places. The substance has high thermal insulation characteristics and moisture resistance. Expanded clay is recommended for insulation of fire hazardous facilities. Previously, it was used in the construction of industrial furnaces.
- Perlite is a heat-resistant insulation based on volcanic glass, due to which the material is characterized by low weight and low thermal conductivity. 30 mm perlite in terms of heat efficiency is equivalent to 150 mm of masonry. The main disadvantage is poor moisture resistance.
- Expanded vermiculite consists mainly of hydromica, which is subjected to high-temperature firing at the production stage. As a rule, vermiculite is used for warming low-rise buildings, external thermal insulation and attic rooms. Characteristic features are improved biostability and high environmental friendliness, the inability to withstand the effects of moisture. Leveling this significant drawback is possible only with properly installed waterproofing.
- Perlite
- Vermiculite
- Expanded clay
Cellular
Visually, such varieties of insulation are similar to hardened soap foam. The most common material from this group is foam glass.It is produced by sintering coal with glass chips. Characteristic features of the material are durability (operating life exceeds 100 years), low thermal conductivity and mechanical strength.
Foam glass does not ignite even at record high temperatures. The material melts, while not releasing toxic substances into the atmosphere.
Fibrous
Visually, the materials are similar to ordinary cotton wool, because they consist of randomly arranged fibers. A heat insulator in the form of mats and rolls is produced, also non-combustible mineral wool is sheet. Compared with analogues, sheet products have less rigidity.
Types of non-combustible mineral wool:
- Ecowool for 80% consists of recycled cellulose, which was subjected to flame retardant treatment at the production stage. The material is environmentally friendly, has a low weight and low coefficient of insulation. The only drawback is its low moisture resistance.
- Basalt wool consists mainly of rock fibers, which are pre-heated to more than 1300 degrees. Due to this, the material does not ignite and does not burn even under the influence of abnormally high temperatures. Minvata has a low coefficient of moisture absorption, does not shrink, biostable and completely environmentally friendly.
- Glass wool can withstand temperatures up to 500 degrees, while maintaining all its technical characteristics: light weight, durability and heat efficiency. Glass wool also has a drawback - it is prone to shrinkage and when working with raw materials, special protection must be used, otherwise damage to the skin can not be avoided.
Liquid
Liquid non-combustible thermal insulation for walls is sprayed using special equipment. After time, the liquid solidifies, forming a mass that visually resembles a non-combustible expanded polystyrene.
The most common and popular type of liquid insulation is polyurethane. The raw materials are environmentally friendly, have improved adhesive characteristics, are evenly distributed over the entire surface, even in the most inaccessible places.
Scopes of heat-resistant thermal insulation
Non-combustible heaters are used in all areas of construction, including domestic buildings and industrial facilities. Especially relevant is the use of materials in rooms with a low level of fire safety.
In the domestic market, basalt cotton wool is most widely used. It is most often used for external thermal insulation of facades. The advantage of the material is the ability to effectively use under the plaster and in the curtain wall system.
Glass wool is also used for this purpose, but much less frequently. This is due to low vapor permeability and moisture resistance, a tendency to shrink.
Criterias of choice
Before purchasing heat-insulating materials, you need to decide what goals are set for the raw material and whether it will meet the standards.
The main selection criteria:
- To achieve maximum heat efficiency, you need to choose a heater with a low coefficient of thermal conductivity. No more than 20-25% of heat loss occurs on the walls, so the issue must be approached comprehensively and create the most airtight design.
- Price policy. High-quality building materials can not be cheap. Unreasonably low cost indicates a violation of production technology and low quality of feedstock.
The material must be biostable and have excellent moisture resistance indicators. For interior decoration, it is important that the insulation is environmentally friendly and safe.