Hydrocarbon liquefied gases are used in heating units, water heaters and are a mixture containing propane and butane. The composition is transported and stored in liquid form in storages or cylinders, and before use, the fuel is vaporized and fed to the boiler burner. From the energy efficiency of the building depends on the consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house 100 m2 and consumption costs.
Liquefied gas description
Gas belongs to the substances of the alkanes group, is found in the form of components in natural analogues. Propane without impurities is odorless, but additives with a strong aroma are added to the technical mixture. Toxicity is little manifested, but there is an effect on the nervous system.
Liquefied petroleum gas (LHG) differs from its natural counterpart in that it is a product of high-temperature processing of petroleum fractions and chemical processes. Natural methane is extracted from the bowels of the earth. Both types are used for heating private buildings, but differ in chemical properties, characteristics and method of transportation.
LPG is characterized by high calorific value, but its cost is higher than that of natural gas. Methane is supplied to the consumer only through a centralized pipeline.
Propane use
 The substance has the formula C3H8 and belongs to the low toxicity category with a specific odor. Air becomes explosive if it contains a concentration of 1.8 - 9.1% butane vapor, 2.3 - 9.5% propane, and a pressure of 0.1 MPa at a temperature of +15 to + 20 ° C. Propane spontaneously ignites at + 470 ° С, butane - + 405 ° С.
The substance has the formula C3H8 and belongs to the low toxicity category with a specific odor. Air becomes explosive if it contains a concentration of 1.8 - 9.1% butane vapor, 2.3 - 9.5% propane, and a pressure of 0.1 MPa at a temperature of +15 to + 20 ° C. Propane spontaneously ignites at + 470 ° С, butane - + 405 ° С.
Chemical and physical properties of propane:
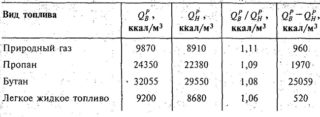
- molecular weight - 44.097 kg / kmol, molecular volume - 21.997 m3 / kmol;
- the consumption of liquefied gas per 1 kW of heat is 0.16 dm3 (liter);
- gas density at 0 ° С - 2.0037 kg / m3, at + 20 ° - 1.87 kg / m3;
- density in the liquid phase - 528 kg / m3;
- the volume of air required for the combustion of 1 cube is 23.8 m3.
Despite the higher cost, the liquefied type of gas fuel is more convenient to use. It goes into a liquid state and can thus be stored. To save natural methane, it is necessary to compress it under a pressure of 200-250 atm, and transportation in a liquefied form is possible only at cryogenic temperatures (below 120 K).
Centralized gas pipeline
 Natural gas is supplied in the gas pipeline. The construction of a centralized highway requires certain costs, therefore methane is used by residents of densely populated regions and areas with a large consumption. The suburban population does not always have access to the gas pipeline and fuel is delivered to them in cylinders.
Natural gas is supplied in the gas pipeline. The construction of a centralized highway requires certain costs, therefore methane is used by residents of densely populated regions and areas with a large consumption. The suburban population does not always have access to the gas pipeline and fuel is delivered to them in cylinders.
The line is built of steel pipes with a diameter of up to 1.42 m and is designed for pressure up to 10 MPa. Pipelines pass about 55-60 billion cubic meters of gas per year. Highways are laid underground or pass on the surface. Comprehensive services include compressor stations, cleaning and drying stations, gas distribution points.
Gas holders
For the continuous supply of LPG, underground and above-ground gas tanks are used, which are installed in a multi-story sector or in a private housing estate. From the tank, fuel is supplied to apartments and houses, used to heat the room.
Gas tanks have a control system and record the filling of the sump. The sensor determines the gas supply and transmits a signal to the service when the fuel level in the tank decreases to 30%. The operator sends a tanker to fill the tank.
Liquid is constantly accumulating at the bottom of the gas tank, which has not turned into a gaseous state, the tank needs to be cleaned. Storage facilities are convenient to use, as they provide a continuous supply of fuel.
Balloons
 Balloon gas is used in heating a home if in winter tenants do not regularly visit a country house. Propane or its mixture with butane is supplied in containers. The downside is the increase in the cost of fuel when removed from the supplier of the product. A standard propane tank holds 22 kg of gas and weighs 19 kg. Composite containers are used, they are lighter, but they are more expensive.
Balloon gas is used in heating a home if in winter tenants do not regularly visit a country house. Propane or its mixture with butane is supplied in containers. The downside is the increase in the cost of fuel when removed from the supplier of the product. A standard propane tank holds 22 kg of gas and weighs 19 kg. Composite containers are used, they are lighter, but they are more expensive.
Parameters of gas cylinders:
- unit length 28 - 95 cm;
- diameter - 20 - 30 cm;
- wall thickness - 3 - 4 mm;
- weight - 4 - 22 kg.
Using statistics, you can calculate how much gas is needed to heat 80 square meters of the home. In case of small cold weather, heating of such an area requires 2 forty-liter cylinders when using antifreeze in the heating system. This is 25-30% higher than gas costs for centralized deliveries. The combination of 15 cylinders in a closed metal cabinet is allowed.
Factors Affecting Liquefied Gas Consumption Calculations
Most of the heat leaves the room through the walls. Heat flows are characterized by a complex trajectory of movement and leave the house through the ceiling, floor and windows. The building envelope should be insulated from energy losses, otherwise the gas consumption will be large.
Fuel consumption depends on factors:
- terrain climate - to calculate the flow rate, the lowest temperature values are taken;
- heated area, layout, number of storeys, ceiling height;
- the degree of insulation of the roof, walls, floor;
- building material (concrete, wood, brick);
- type of filling window openings;
- the presence of organized ventilation of rooms;
- boiler power.
The geometry of the house affects heat loss. A complex perimeter with many wall protrusions and a combined roof increase the risk of cooling. The boiler power does not affect heat loss, but the correct selection of the parameter is required for efficient fuel consumption.
Formula for calculating
Theory and practice show that 169.95 kW of heat is needed for heating 1 m2 and heating the liquid in the water supply system per year. For calculation, the calorific value of LPG is used - 12.88% and boiler efficiency - 98%.
Gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 is made according to the formula ((169.95 * 0.1288) / 0.98) x Swhere S means the area of the house. To calculate the cost of heating, the obtained flow rate is multiplied by the price of gas per 1 kg.
The calorific value of the fuel is important, which shows how much heat is produced when a unit of fuel is burned. For LPG, this indicator is always higher than that of natural gas, firewood, coal.
Ways to reduce fuel consumption
The energy efficiency of a home must be increased to reduce gas consumption for heating a house. Using these methods, you can save up to 5 - 15% of fuel. During the winter period, the home is made as airtight as possible so that the internal energy does not go outside.
Clogging and insulation of the house leads to the need to install an organized ventilation system. The use of a recuperator is recommended. This device is an efficient heat exchanger that reduces heat loss, but delivers fresh air to the rooms.