The efficiency of the heating equipment is directly related to the indicator of thermal power. Comfort and coziness in a room heated by gas, firewood or electricity depends on it. Therefore, it is important for the user to know what this physical quantity is and how it is calculated in each case.
Definition of thermal power
Under the power of heat generation is meant the amount of heat generated during the conversion of the source medium into heating energy. This indicator is different in magnitude for different types of energy carriers and is calculated individually for each of them. For gas boilers, it depends on the volume of natural or liquefied gas supplied to the burner per unit time.
When considering electrical analogues, this parameter is directly related to the power of electricity consumed by the unit from the 220 or 380 Volt network and its thermal efficiency. The ratio of thermal and electrical powers is set by special formulas that translate one value into another.
Required Features
Calculation of thermal power is very important, since its results are necessary to determine the parameters of the selected sample of heating equipment. The latter traditionally include:
- unit electrical power for volatile models;
- conversion efficiency (or boiler efficiency);
- productivity, defined as the amount of heat generated by the device per unit time.
Models of boilers connected to the power grid relate to equipment with the consumed power of the heating system, resulting in the amount of solid or gaseous fuel burned. For images independent of electricity, this parameter is determined directly - without recalculating the consumed electricity.
The efficiency of any heating unit to a large extent depends on the correct choice of the node that provides the conversion of thermal energy (heat exchanger). A competent solution to this issue allows you to get the required heat output and feel comfortable in the house even on the coldest days.
Surplus thermal power is undesirable, because in this case, part of the spent funds is wasted.
Factors affecting heat demand
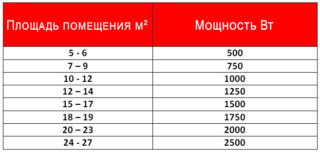
The main factors determining the need for thermal energy for a room include:
- full volume of heated spaces;
- type and quality of insulation material;
- The climatic zone in which the building is located.
The amount of air space in need of heating depends on the volume of the room. The larger the heated room, the more heat will be required to maintain the desired microclimate. With the same ceiling height (about 2.5 meters), a simplified calculation is usually used, in which the room area is taken as the basis.
The quality of insulation is judged by the methods of thermal insulation of the walls, as well as by the area and set of windows and doors. The type of glazing is also taken into account - a simple and a triple glazing are different in terms of heat loss. The influence of the climatic factor affects, ceteris paribus, and is taken into account as the temperature difference in the street and in the room where the boiler is installed.
For appliance (radiator)
When considering factors affecting the heating power of heating radiators, three main ones are distinguished:
- an indicator corresponding to the difference in heating of the coolant and the surrounding air - with its increase, the thermal power increases;
- surface area that gives off heat;
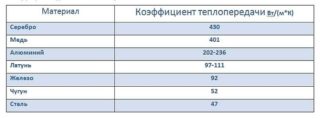
- thermal conductivity of the material used.
In this case, the same linear dependence is observed: with an increase in the surface of the battery, the magnitude of the thermal return also increases. For this reason, many modern heating radiators are supplemented by special aluminum fins that increase the overall heat transfer.
Why do I need to calculate the power indicator
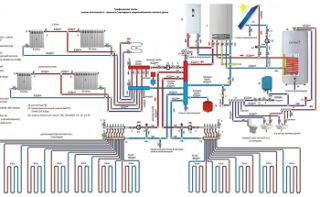
The need for determining the power is explained by the fact that the main characteristics of the boiler depend on the following factors:
- design features and purpose of the heated object;
- the size and shape of each room;
- total number of residents;
- location on the map of the country.
The calculated heat transfer power is used to determine the parameters of the boiler equipment planned for installation in this room. The future boiler must have a capacity sufficient to heat it even on the coldest winter days. It is also important to provide for the possibility of coordinated connection of the unit to the main pipeline. The calculations performed will help determine its length and tube size, as well as the type of radiators and parameters of the circulation pump.
Calculation of thermal power
 To evaluate thermal energy, there is a formula for determining power through the amount of heat: N = Q / Δ twhere Q Is the amount of heat expressed in joules, and Δ t - time of energy release in seconds.
To evaluate thermal energy, there is a formula for determining power through the amount of heat: N = Q / Δ twhere Q Is the amount of heat expressed in joules, and Δ t - time of energy release in seconds.
When evaluating the calculations, a special coefficient (COP) is also used, which indicates the amount of heat consumed. It is found as the ratio of useful energy to heat loss power and is expressed as a percentage.
The amount of energy spent for the premises depends on their construction features. The same indicator for batteries is determined by the materials used and their design features.
More accurate thermal calculation
A competent choice of heating equipment is possible only after familiarization with the procedure for calculating the thermal power required in each case. The formula used to determine it exactly is: P = V∆TK = kcal / hour:
- V - the volume of the heated room, measured in cubic meters.
- ∆Т - the difference between the temperature of the air outside and indoors.
- TO - heat loss coefficient.
The latter value depends on the material of the walls. Based on the measurements carried out by experts for an insulated wooden structure, it is 3.0-4.0. Exact values TO for various insulation options are given below:
- For buildings of single brickwork and with simplified window and roof structures (the so-called “simple” thermal insulation) K = 2.0-2.9.
- Thermal insulation of average quality (K = 1.0-1.9). This is a typical design, which means double masonry, a roof with a conventional roof, a limited number of windows.
- High-quality insulation (K = 0.6-0.9), which includes brick walls with enhanced thermal insulation, a small number of windows with double frames, a solid floor base and a roof with reliable heat insulators.
As an example, we will consider the exact calculation of power for a heated room with a volume of 5 x 16 x 2.5 = 200 cubic meters. ∆Т is defined as the difference of the indicator outside -20 ° С and indoors +25 ° С. Accepted option with an average specific thermal insulation (K = 1-1.9). According to average operating conditions, we take 1.7. We expect: 200 x 45 x 1.7 = 15 300 kcal / hour. Based on the fact that 1 kW = 860 kcal \ hour, in the end we have: 15 300 \ 860 = 17.8 kW.