To equip a water-heated floor with your own hands, you need to deal with all the subtleties of its installation, taking into account the main characteristics of the heated structure. It will be necessary to take into account the number of rooms in the house and the total area of all its rooms. Based on this, they are determined with the need for consumables, as well as with the general costs of arranging the heating system.
Styling schemes

Before you begin installation of a water heated floor, you will need to prepare a diagram indicating the location of the following working elements:
- heating boiler - a physical source of heat;
- distribution node - collector;
- a set of copper or polypropylene pipes forming the wiring of the heating circuit.
Heat sources in the house are boilers for the kindling of which solid or liquid fuel is used. The option of using gas equipment, which is notable for its low cost, or its electrical analogue, is not ruled out. At the same time, an existing heating system operating in the house is considered as an extreme case. As a collector, sets of fittings mounted on the input and output are usually used. System elements are stacked according to the following schemes:
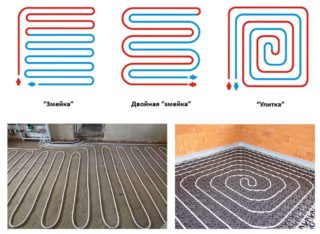
- a snake (several options);
- a snail;
- according to a more complex combined scheme.
Each of the installation operations is implemented in a special way.
Snake
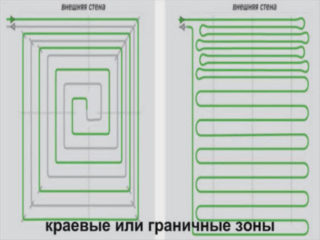
In the first version, the floor installation with a snake starts from the walls around the perimeter of the room, after which it narrows towards the center and gradually closes the usable area in the apartment. Having reached the middle, the laid track goes back to the boiler. Due to this, one half of the floor is heated during operation, and the second is cooled. This technique allows you to evenly distribute heat during operation of the system.
You can achieve the same result if you start laying the snake in the form of a pipe folded in half. One half is responsible for the supply of hot water, and the second, leading from the opposite wall, is used as a return.
Snail
In the case of the cochlea, the pipes folded in the same way as in the case of a “snake” are laid along a spiral path in the form of a square structure. First, they are led along the walls, and then gradually shifted to the center of the room. The use of this technology ensures uniform heating of floor surfaces. Sometimes they use a combined scheme that combines elements of both of these approaches. At the same time, sections of the floor located closer to the walls are heated more intensively, which allows reducing the boiler power while maintaining the heating intensity.
 You can control the distribution of heating zones in the following ways:
You can control the distribution of heating zones in the following ways:
- the use of a variable pitch pipe laying;
- displacement of the entire structure in one of the parties;
- combination of various laying schemes.
If you want to more intensively warm the floor near the outer walls, the gaps between the threads in this place need to be done less, and closer to the center, on the contrary, increase.
The installation scheme of the warm floor is prepared taking into account the material of the existing base. It displays the points of connection to the coolant source, the installation option and the removal of pipes to the walls of the room and between them.
Styling technology
Upon completion of the calculation of all components of the system and the selection of a suitable scheme, they proceed to the preparation of building materials, additional equipment and tools. After that proceed directly to the installation.Sometimes the elements of such floors are laid on polystyrene plates, placed in a certain order on a rough basis. In addition, for these purposes the following methods are allowed:
- placement of polypropylene pipes directly on a concrete base;
- installation of the system in the grooves of wooden plates remaining after the arrangement of the flooring;
- laying on a previously embedded screed base.
It is better to retain heat on the plane laid on the plates, it is possible due to the use of a substrate of foil, the working side laid to the side of the floor. According to the instructions, during the installation of the docking zone of the individual elements, they are sealed with special tape.
Collector Installation and Connection
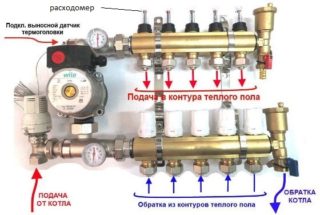
The collector used to distribute the hot water carrier through the pipes of the system is installed in a separate room or in a special distribution cabinet. It is made in the form of 2 stainless steel cylinders welded on both sides. One of these blanks through a pipe system first receives and then distributes the heated water along the working circuits. At the same time, the second cylinder draws chilled water from there, returning the carrier to the heat source.
For its circulation, a separate pump is used, supplemented by a set of bypass valves, as well as a manifold valve and thermostat. In addition to the distribution function of the coolant flows, the installation of this unit allows you to adjust:
- water temperature through a thermostatic valve;
- the state of the carrier entering the heating circuit;
- his pressure in the system.
In the latter case, an electric drive and a set of manifold valves are used for regulation.
Installation procedure
 To equip the underfloor heating with water in your own home, you will need to prepare an absolutely flat surface. If roughness is clearly distinguishable on a rough concrete base, a screed should be made. The sequence of installation of a water heated floor on concrete substrates or on a dried screed can be represented as the following step-by-step instructions:
To equip the underfloor heating with water in your own home, you will need to prepare an absolutely flat surface. If roughness is clearly distinguishable on a rough concrete base, a screed should be made. The sequence of installation of a water heated floor on concrete substrates or on a dried screed can be represented as the following step-by-step instructions:
- Along the perimeter of the floor, edge insulation is set based on a damper tape, which is attached to the walls of the room. In thickness, it overlaps the plane of the structure, including the insulation layer, pipes and screed with reinforced reinforcement.
- A protective layer of foil is laid on the concrete floor, which allows you to keep heat in the heat insulator and concrete screed. It is placed with its protective plane in the direction of the coating (tiles, for example).
- The joints between the individual elements are closed with adhesive tape based on foil.
- The insulation is mounted on the insulation material in the form of plates up to 50 mm thick. The rows of heat insulator are stacked with a slight offset.
- The insulation layer is covered by a steam insulator - a polyethylene film of the usual type.
A reinforcing mesh with a step of 10x10 cm or 15x15 cm is placed on the insulation plates. It is fixed on the stop brackets, mounted every 0.5 meters from one another. In height, the stops are calculated for the installation of 2 grids: one under the water floor, the other above it. Pipe laying begins by connecting a prefabricated collector to the outlet.
All further operations look like this:
- On the mounted grid, pipe wiring is laid, fixed on it by tightening clamps.
- The pipes themselves are not fixed on the floor rigidly, taking into account the tolerance for changing the temperature of the coolant.
- When laying polypropylene according to the "snail" scheme, the removal between the pipes is maintained within 10-15 cm - so the floor heating near the walls will be better.
- If a single circuit is not enough, its area is divided into two parts with equal pipe lengths.
- Upon completion of laying, one of the ends is connected to the inlet of the manifold.
- On top of the laid pipes, it is also mounted on a reinforcing mesh, which gives the protective coating additional strength.
Before arranging the screed, the system that is not yet completely ready is tested for leaks, for which it is tested with compressed air. For this, a compressor is used, which creates a pressure of 4 bar. If there are leaks, the air leaves the system and the pressure drops.
In addition to checking with a compressor unit, hydraulic tests with hot water are mandatory in accordance with current regulations. For this, the preheated liquid is fed into the system, which is then turned on for a couple of hours. With its serviceability, the pressure drops by no more than 0.03 MPa per hour.
Concrete screed will be installed at the end of the installation of the warm floor and the completion of the entire set of tests. Previously, polypropylene pipes were filled with cooled water, pumped into them under slight pressure. The screed is made using concrete M300. The thickness of the layer covering the second reinforcing mesh is 3-5 centimeters, the total thickness of the screed is 7-10 cm. Its surface is then leveled with a vibrating rail, for which beacons are first installed. Using a vibrating tool, air is removed from the concrete and the surface is prepared for laying tiles or linoleum, for example.
It is allowed to start the formation of flooring 25-30 days after curing of concrete. Dry it at a positive air temperature in the usual, natural way. When the floor area is more than 30 m2 or one wall of the room is more than 8 meters long, special shrink seams are used to prevent cracking of the coating. In rooms of significant living space, they are arranged between separate circuits in order to pass through polypropylene pipes in areas where the comb is equipped with a circuit. In places of their placement, pipe channels are specially protected by corrugation, and sections of the reinforcing mesh are neatly cut.
A shrink joint is made with a width of 10 mm, subsequently sealed with silicone sealant.
The correct approach to starting a warm floor includes one more leak test, which is carried out already at the end of all work. After a trial run of the system, the final decision is made on its admission to permanent operation.