During the construction of a residential building, an important detail is the installation of a heating structure. The modern market offers the use of a warm water floor and warm water walls. Consider the pros and cons of this system and the features of the installation.
Advantages and disadvantages of water floors and walls
 This type of space heating has several advantages:
This type of space heating has several advantages:
- economic benefits compared to electrically heated surfaces;
- safety in use (electric shock and burns are excluded);
- long period of operation (from 25 years);
- does not dry out the air in the room;
- saves space;
- It is combined with any other types of heating.
It has the following disadvantages:
- installation on stairs is impossible;
- obtaining permission for a device in a multi-storey building is extremely difficult (the project is almost always denied);
- the risk of damage to the system, which can lead to flooding of neighbors from below;
- installation of a water floor and walls is more expensive than electric.
Installation of underfloor heating
The first stage of installation is to create a project. At this stage, you need to decide: will the underfloor heating supplement the heating from the radiator or will become the main source of heating.
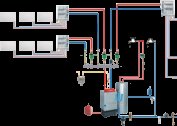
If the installation will be carried out in a private house with several floors, it is necessary to provide for the installation of mixers and collector assemblies on each floor. At the same time, they must be connected to the central riser. The assembly is most preferably located in the central part of the floor so that the length of the pipes is approximately the same for all rooms.
It is recommended to use ready-made, assembled in the production, manifold cabinets. They are factory tested, have a warranty and are easy to install. Their main drawback is the high cost, but often their reliability pays for itself completely.
Next, pipes are selected, they are of several types:
- polypropylene;
- metal;
- metal-plastic based on cross-linked polyethylene.
Polypropylene pipes are the cheapest on the market, but they also have a relatively short period of operation, metal pipes have a higher price and are difficult to install, but their advantage is in a long service life. The most optimal pipes for price and quality are products based on cross-linked polyethylene.
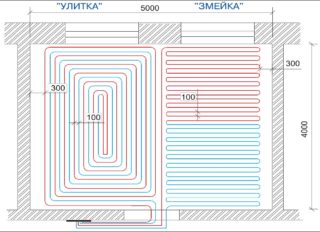
The project of insulated floors also provides for the type of pipe laying:
- spiral;
- A snake.
The type of masonry is selected depending on the size of the premises. In addition to the main types, there are various variations: a double “snake”, a simple “snake”, a double spiral, etc. Experts recommend laying pipes with a spiral - although this is a more time-consuming method, the heating will be uniform and the structure will not be subjected to additional bending stresses . "Snake" is more suitable for small rooms - up to 10 square meters. m. You can also use combined styling methods.
After all design work and material selection, installation begins. The initial stage is the preparation of the foundation. The surface for laying should be flat, for this you can use a self-leveling bulk floor or cement-sand mortar. After the concrete base has dried, thermal insulation is laid. For these purposes, polystyrene or penofol is used.
The thickness of the insulation layer depends on the floor:
- for the first or ground floors, under which there is soil, a layer of 6-8 cm thick is laid;
- for rooms under which there is an unheated room, the insulation layer is 2 cm;
- the upper floors, located above the warm rooms, a layer of insulation 3-5 mm is enough.
A reinforcing mesh is laid on a heat-insulating base for fixation, and then pipes. For ease of installation, it is recommended to apply a pipe layout to the insulation layer. During installation, excessive kinks must be avoided. Pipe cutting - only in place. To avoid possible leaks, do not place them in an interference fit or join segments.
After all the above works, the pipes are connected to the distribution combs and the heating system is tested:
- pipes are filled with coolant;
- system pressure rises to 5 bar;
- after that, a spontaneous decrease in pressure to 2-3 bar will occur;
- increase the pressure to 5 bar and wait until it drops to 2-3 bar;
- repeat this cycle several times;
- during testing, carefully inspect the system contours for possible leaks;
- then a working pressure of 1.5-2 bar is set and left for a day, the pressure during this time should not decrease.
After that, if the operation of the system is satisfactory, final tests are performed, for this the maximum operating temperature is set on the boiler, and the circulation pumps are adjusted to the operating pressure. The entire heating structure should heat up. Next, the test is repeated after a day.
After checks, the heating is completely turned off for filling with screed. The system must be completely cooled. It is recommended to use a special solution for underfloor heating. For residential premises, the thickness of the floor above the pipes should be 20 mm, and for household or industrial - 40 mm. It is important to wait until the floor has completely dried before restarting the heating, usually this period is 28 days.
Installation of heating in the walls
Installation, material selection and structural testing in the walls is carried out according to the above algorithm. The difference is that the system is fixed with a layer of plaster. The first row of the mixture fills the voids between the pipes. Then another reinforcing mesh is fastened and finishing with plaster is carried out.
Conclusion
Built-in water heating designs fit well into the heating of a private house, utility and industrial buildings. It is important to follow all the rules for installing the system and its operation.