Floors in modern apartments need both insulation and soundproofing. Rockwool Flor Butts basalt floor slabs are a material with equally high sound and heat insulation properties. The company produces mineral plates suitable for soundproofing floating floors, under screed, for warming a wooden floor on logs.
Description of insulation Rockwool Flor Butts
The material is obtained by melting rocks - basalt and gabbra. Use secondary raw materials, which reduces the cost of the product and contributes to the preservation of the environment. In a special furnace, thin fibers with a length of 1.5 cm are obtained. A fabric is formed from them, and then, under pressure and after heat treatment, a material of a certain density is obtained and cut into lengths.
Adhesive is not used to connect the fibers, so the Rockwool basalt wool is very durable.
The heat and sound insulation qualities of the plate are determined by the structure. Thin stone fibers are located horizontally, vertically, at different angles to each other. They form many tiny air cavities. A Rockwool thermal insulation board with a width of 100 millimeters passes the same negligible amount of cold as a brick wall 196 cm thick or a 43 cm bar.
Floorboards are designed for soundproofing rooms. Material 25 mm thick reduces the level of acoustic noise - loud music, street noise, up to 43 dB. It also absorbs structural noise, especially shock noise, up to 35 dB. In addition, Flor Butts dampens up to 40% of vibrations.
Insulation Rockwool - the first of the heat insulators that received the certificate of environmental safety EcoMaterialGreen. They finish any premises, including children's rooms.
Specifications
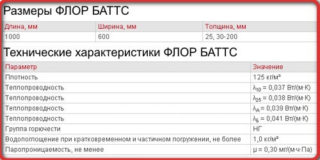 Technical indicators of Rockwool Flor Butts plates:
Technical indicators of Rockwool Flor Butts plates:
- The density of basalt wool reaches 125–150 g / sq. m. With high thermal insulation qualities, the plate is quite rigid, does not deform, does not crack, but at the same time remains flexible.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient is 0.037–0.041 W / (m · K).
- With vertical compression, a dry mineral plate withstands pressure of 33 kPa. If higher resistance is required - up to 50 kPa, choose a type of insulation such as Flor Butts I.
- Basalt cotton wool does not absorb water, water absorption does not exceed 1.5%. Even having wet a plate Rockwool does not change its properties.
- The vapor permeability is 0.30 mg / (m * h * Pa). The insulation is laid under a wooden floor, wall varieties are used for thermal insulation of the house and timber.
- The material is fireproof: it does not burn and does not support combustion.
The cost of the plates depends on the type, sheet thickness and density.
Advantages and disadvantages
All varieties of plates - Rockwool Cavity Butts, Flo Butts, Light Basst Scandic, have all the advantages of basalt insulation and all the advantages of Rockwool products:
- Although the material is positioned as acoustic, its soundproofing properties are in no way inferior to thermal insulation. 25 mm slabs replace 50 cm bricks.
- Flor Butts boards are tough but flexible and slightly springy. When laying, the material compensates for irregularities in the base floor and does not deform under load.
- Flor Butts does not shrink.
- The weight of the plate is small, laying is very simple and takes a matter of hours.
- Basalt wool is not to the "taste" of rodents, molds, fungi.
- The Rockwool company guarantees that floors insulated with mineral wool will last at least 50 years.
This material has limitations:
- When the load exceeds 33 kPa, the structure of basalt wool changes. It can withstand a short-term load of up to 17 kPa, but under pressure it flattens and loses its insulating properties.
- The insulation must be waterproofed. Although the miniplate itself does not get wet, moisture retention inside will not lead to anything good.
Apply material to insulate only floors and floors. For insulation of walls, roofs, building structures, Rockwool produces other models.
The use of insulation
Use mineral wool plates in the following areas:
- in the construction of floors on soils in private buildings;
- under a wet or dry screed for thermal insulation when arranging floors indoors, on balconies or loggias;
- when warming wooden floors - the plates are vapor permeable and prevent the appearance of condensate;
- under the heating system "warm floor";
- for heat and sound insulation of floors of any type.
The material is used for insulation of floating floors. Such a solution is rare, but leads to resonance. Together with plywood or OSB mineral wool boards, instead of suppressing sounds of a certain frequency, it transmits them. Usually these are structural noises - slamming doors, the noise of an elevator shaft.
Range of insulation sizes
The dimensions of the plate are standard: length - 1000 mm, width - 600 mm. The minimum sheet thickness is 25 mm. The next value is 30 mm, then the parameter increases in increments of 10 mm to 200 mm.
The thicker the layer of material, the better its thermal insulation properties. Resistance to pressure remains the same - no more than 33 kPa.
Range of insulation Rockwool Flor Butts
2 types of material are produced: Flor Butts with a base density of 125 kg / cu m and the “I” series with a density of 150 kg / cu. m. The latter is taken for thermal insulation of loaded areas, where the assumed constant pressure can reach up to 50 kPa.
Plate mounting
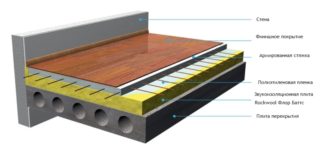
Laying technology depends on the type of floor: dry screed, reinforced screed, floating floor, wooden on the logs.
The most popular option in apartments is a floating floor. It virtually eliminates deformation under any fluctuations in temperature and humidity.
Installation of the structure is performed as follows:
- The concrete base is cleaned, if necessary, impregnated with antifungal and hydrophobic compounds. Lay with sheet soundproofing material.
- Stripes are cut from the plates, with a width slightly exceeding the height of the floor. They are laid around the perimeter of the room.
- Installation of inserts and plates is carried out simultaneously: first, an insert is placed on the wall, and then they are pressed with a mineral wool plate.
- Lay a screed of plywood or OSB. Sheets are laid in 2 layers so that the seams of the lower and upper layers do not match. They put the plywood end-to-end, fasten together with masking tape. A gap is left between the substrate and the wall.
- The inserts along the wall are trimmed to the height of the screeds. After that, the final coating is mounted.
If a cement screed is made, the technology changes. To protect the plates from moisture, they are covered with plastic wrap. Then the structure is poured with cement, a layer of at least 30 mm, and reinforced.
Insulating a wooden floor on logs is just as easy.
- The base floor is cleaned of dust, dirt, and the remnants of the old finish. To make the surface of the base more uniform, do not primer. You need to wait until the soil dries.
- Install wooden logs. The distance between them is equal to the width of the sheet. Plates should fit snugly between the bars.
- The floor and logs are covered with plastic wrap and fixed with construction brackets. Then put the floors of Flor Butts.
- It is recommended to cover the thermal insulation with plastic wrap, or better, with the Rockwool vapor barrier membrane.
- At the last stage, a finishing floor is laid.
To warm the attic floor, you can use Light Butts Scandic or Light Butts. They are less dense, withstand less load, but in a non-residential attic, high pressure resistance is not needed. The cost of lightweight plates is lower, and the level of heat conservation is equally high.






