The comfort of living in a private house and cottage depends on a well-planned, correctly constructed water supply and sewage system. However, these systems can fail in severe cold, when the ground freezes to the place of laying communications. In addition, even with an ultra-deep laying, there are areas that are close to the surface at the places of entry into the building. If you do not insulate the water supply with a heating cable, liquid will freeze in the pipes. This is fraught with a lengthy and costly repair.
Design and scope of heating cables
A wire for heating water pipes is practically no different from a standard electric cable externally and internally. The difference lies in the conductors used.
The wire for heating the pipes in winter has the following device:
- Inner wire. It is distinguished by good flexibility, made of alloys having high electrical resistance. The higher this indicator, the greater the heat release. Depending on the model, the electric cable for heating the water pipes has one or two cores.
- Polymer insulation. Designed to prevent current leakage into the ground or onto a steel pipe.
- Screen. It is made of aluminum foil or copper mesh. Serves to give the product extra strength.
- Outer shell. It is made of dense and durable polyvinyl chloride. Designed to protect the heating element from external damage.
Products vary in thickness, resistance and power per meter. To increase the service life of the heating wire for pipes, the inner conductor is coated with nickel, which prevents oxidation of the metal.
Varieties of heating cable
For heating the water supply, systems consisting of one or two internal conductors are used. In single-wire products, the core acts as a heater and line simultaneously. In two-core cables, one wire is heated, and the second supplies energy.
In addition, heating wires for water supply are divided into two categories that determine the principle of their operation and scope of application:
- Resistive. They are simple cables in the device, consisting of one or two cores. Passing along the heating line, the current causes it to heat. Cable indicators are constant, do not change over the entire length of the line. The device is controlled manually by turning it on and off based on the weather and season. Improvement of systems is carried out by installing a temperature sensor, relay and temperature controller. Installation of a heating resistive cable on a pipe is carried out when laying highways of short length, up to 40-50 m. A plus of models of this type is their reliability, durability and low cost. The disadvantages are that the line cannot be shortened and increased, it is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature, since when it increases, the wire overheats and fails.
- Self-regulating. This type of product is equipped with a heating matrix that controls the power produced. Water pipes are heated by a self-regulating heating cable in an autonomous mode. The operation of the product is based on the principle of changes in the resistance of a material with a change in temperature. With its increase, the current decreases, which leads to a decrease in power. When cooling, everything happens the other way around, resistance increases, heating increases.The advantage of such models is that the heating of the pipeline with a heating cable occurs zonally, depending on the state of the environment. In critical places, it heats to the maximum, and in other areas it maintains the optimum temperature. To avoid unnecessary energy loss, the cables are equipped with automatic regulators, tied to the temperature of the street air. The minus of the product is only in its price, but the investment is worth it.
- Self-regulating cable works offline
- Resistive requires sensors or timely manual shutdown
When planning a pipeline heating, you need to approach this event differentially, competently selecting various types of heaters for certain sections. Read manufacturers instructions carefully.
Installation methods for water supply
There are several ways to equip the heating of a water pipe from freezing, each of which is best suited to a particular case.
Do-it-yourself installation of a heating cable for a water pipe can be carried out in the following ways:
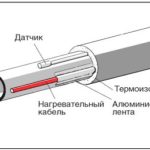
- Outside along the pipe. So fit both resistive and self-regulatory models. Single core cables are looped. The line stretches along the entire length of the highway, is fixed at its end, and then returns to the energy source. The wires must be placed on both sides of the trunk with an offset to the bottom, to enhance the thermal effect on the fluid passing through it. If there is plumbing fixtures on the track, 2-3 turns are made on it, depending on the size of the product. It is impossible to lay both lines near the bottom, as this will cause them to overheat. Fixing is carried out by heat-resistant plastic screeds or aluminum tape.
- In a spiral. The turns are made along the entire length, grasping to the pipes as they are wound. The distance between the turns is determined by the location of the route. Closer to the surface and above the ground, they are located as often as possible to ensure maximum heating even in extreme cold. At a depth, the pipe can be wrapped less often, but with the expectation of possible freezing of the soil. Winding is done in one or two directions, depending on the model purchased, the length of the line and the conditions for its operation. Overheating is excluded, since the contact of the lines occurs pointwise. This method is equally effective for both plastic sewer and metal water pipes.
- Interior. This option can be used for pipes with a diameter of 25 mm or more. You can use resistive and self-regulating single-core models. This is due to the fact that the adjacent cable arrangement causes induction and malfunctions of the product, up to breakage. The complexity of this method is the difficulty of pulling the wire into the channel. This is best done even at the installation stage, by inserting the cable into vertically arranged sections or using an exhaust cable.
- Outside along the pipe
- Inside the pipe
- Spiral cable winding
When choosing a method of placement of insulation, the intensity of the effluents should be taken into account. The internal arrangement can slow them down significantly, which will reduce the efficiency of the pipeline.
Thermal insulation of heating cables
Regardless of the cable used, a heated pipe for water supply needs to be insulated. If the trunk is not enclosed in an insulating sheath, the generated heat will be consumed on both sides, heating the soil, not the pipes.
As a heater, it is recommended to use such materials:
- polystyrene foam in the form of removable cylinders;
- mineral wool with a polymer substrate;
- polyurethane foam applied to the internal location of the cable;
- foamed polyethylene wrapped around a channel.
All these products are distinguished by the lack of hygroscopicity, excellent thermal insulation and a long service life. As for the thickness of the insulating layer, 20 mm is enough for buried places, 30-40 mm above the surface, and at least 50 mm in open areas.