The regulation of energy consumption for heating is planned taking into account the climate, the type of residential building. The material of the enclosing structures, the number of storeys of the house and the degree of wear of the heating main are taken into account. Therefore, the heating standard for 1 square. m will vary in different cities and regions. The norms are introduced by the authorized body of the local council on the basis of the calculation of the supplying organization and are constant for three years.
The value of the heating standard and calculations per 1 sq. m
Heat consumption regulations are calculated in accordance with the conditions for the quality provision of services, which are prescribed in the legislation of the Russian Federation. The rules are changed in the prescribed legal order.
Reform Cases:
- reorganization of technical equipment and the construction of an apartment building, climate change, in which the consumption of resources in a residential building changes by 5% or more;
- modification of existing rules regarding the composition of heat consumption standards, methods and conditions for calculating cost and expense indicators.
The company, which supplies heat to the district, submits settlement documents to the local authorities with a strong justification for the new standards. Authorized services analyze the materials and make additional requests, if necessary.
The city council holds a meeting at which it discusses whether it accepts or refuses to improve the organization. On the basis of the decision, recalculation is made, modified tariffs for consumers are introduced.
The decision of the authorities within 10 days is published in local information media, the date is indicated when the new standard for the consumption of thermal energy begins to apply.
Comfortable room temperature
 Indices of comfortable temperature are regulated by the state. In Russia, the rules are prescribed for all regions.
Indices of comfortable temperature are regulated by the state. In Russia, the rules are prescribed for all regions.
Standards of temperature parameters are contained in the document GOST 30.494 - 2011 and include indicators depending on the type of premises:
- in rooms the temperature at the level of +20 - + 22 ° C is considered comfortable;
- in the kitchen - +19 - + 21 ° С;
- in the bathroom - +24 - + 26 ° С;
- in the toilet - +19 - + 21 ° С;
- in the hallway - +18 - + 20 ° С.
If the temperature does not reach these values, the heating rate per 1 m2 of the house is not fulfilled, you can complain and demand a recalculation of the energy consumed.
The rules take into account the purpose of the premises. The bedroom should be ventilated, after which it should be the standard temperature. In the nursery, the temperature of the upper limit is considered normal, and as the child grows older, he moves to the lower bar. In the bathroom, the increased rate is due to dampness, due to which there is a chilliness.
Calculation of a payment for heat taking into account standards
 Calorie is used in calculating the heat consumption of residential buildings and the multi-apartment sector. The unit is 4.1868 J. This amount is enough to heat one gram of water at 1 ° C. To get 1 cube m of hot water with a temperature of + 60 ° C (the lowest energy carrier in the heating main) requires 60 Mcal. To heat 100 m3 of liquid, 6 Gcal is already needed.
Calorie is used in calculating the heat consumption of residential buildings and the multi-apartment sector. The unit is 4.1868 J. This amount is enough to heat one gram of water at 1 ° C. To get 1 cube m of hot water with a temperature of + 60 ° C (the lowest energy carrier in the heating main) requires 60 Mcal. To heat 100 m3 of liquid, 6 Gcal is already needed.
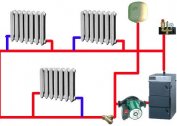
Multi-apartment buildings are considered as indivisible objects that consume energy to heat the premises in their composition. Rules of standards for heating 1 sq. Km. m provides for the calculation of thermal energy for the whole house during the year, on the basis of which the average value is obtained.
The multi-apartment building includes non-residential and residential premises and common areas (cellars, attics, stairwells) and the payment is distributed to the owners of the apartments. The size is determined in proportion to the area of the premises of individual owners.
To account for the amount of heat that home users could consume, city-wide heating standards per 1 square meter are applied. In 2019, the government established new standards for accounting for heat consumption for heating utility rooms, the line “common house needs” appeared on the receipt.
Calculation of your heating fee
To save money, consumers put separate meters in apartments, which allow measuring the amount of energy consumed without an average calculation according to the norms. Devices are supplied by specialists and sealed before use.
The number in the payment document depends on the calculation method:
- according to the testimony of an apartment meter with the addition of a share of heat energy consumption for heating common areas of use;
- based on the calculated share for a separate apartment according to the figures of a common house heat meter;
- according to local regulations, if there is no common and individual device.
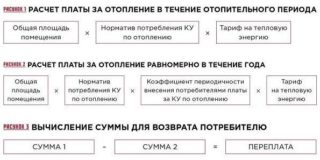
According to the law, the fee is considered only for the period of actual heating or spreads out for the whole year. Option chooses the district or city government. In the second version, an additional correction factor is applied. In houses with common meters, residents of which pay all year, a recalculation is done for the summer months.
With a common house meter
 If there is a meter in the high-rise building, and individual apartments are left without them, Gcal is calculated for heating its own area and the heat costs for heating the common space are added. The values of the device, the area of the house and the quadrature of the apartment are taken into account.
If there is a meter in the high-rise building, and individual apartments are left without them, Gcal is calculated for heating its own area and the heat costs for heating the common space are added. The values of the device, the area of the house and the quadrature of the apartment are taken into account.
The collective meter readings are submitted to the management office, and they are indicated in the next receipt. Information about the general quadrature of the house can be found in the housing and communal services in the acceptance documents. The area of the apartment is registered in the technical passport, and tariffs can be found in the heating system.
Calculation of consumption is carried out according to the formula: P = V x S / S1 x Twhere:
- V - the amount of energy used by the control device.
- S - squaring your own apartment.
- S1 - the area of non-residential and residential buildings.
- T - The legal tariff for heat.
The total amount of heat used in the house is divided into square meters of housing. It turns out the share for a separate apartment, this value is multiplied by the heating system tariff.
There is no common house appliance, no individual meters
In this case, the current standard for heat consumption per 1 sq. Km is used. m. The regulated indicator determines the amount of heat for heating the square of housing per month. The climate in the regions of the Russian Federation is different, so local authorities set different quotas in the subjects of the Federation. The type of housing and the state of communications in the building matter.
Costs are calculated by the formula: P = S x N x Twhere:
- S - the area of the apartment or non-residential premises.
- N - consumption rate.
- T - heat tariff.
The area of housing is multiplied by the current norm, the estimated amount of heat required for heating is determined. Such calculations sometimes do not correspond to the actual energy costs. The government obliges residents to install common meters in apartment buildings.
There is a meter and meters
 The installation of the meter in the apartment allows the owner to pay for the heat actually supplied to the housing. The rules provide for the compulsory acceptance of testimonies of individual devices by communal services if there is a collective meter in the house, and at least 50% of personal premises (by area) are equipped with separate devices.
The installation of the meter in the apartment allows the owner to pay for the heat actually supplied to the housing. The rules provide for the compulsory acceptance of testimonies of individual devices by communal services if there is a collective meter in the house, and at least 50% of personal premises (by area) are equipped with separate devices.
The fee paid by individual owners is cumulative. A part of each is calculated in accordance with the readings of the instruments. The share of consumption among the rooms equipped with meters is calculated.The resulting value is multiplied by the allocated amount of payment for Gcal for apartments with individual accounting and the payment for heat in a monthly period is displayed.
The amount of the payment may be less or more than the one already paid. The calculation of an additional fee in the next period or the allocation to a lower contribution depends on this.