Housing made from a log house does not need additional thermal insulation. But the joints of the logs need to be insulated so that heat does not pass out through the cracks. As such material is used interventional insulation. To choose it correctly, you need to deal with the features and basic principles of thermal insulation of joints.
The need for insulation joints

The joints of the logs are the weakest and most unstable parts in the construction of the house. Here the smallest wall thickness and there is a gap through which wind penetrates into the structure and creates a draft. To protect this area, a special interventional heater is used. It allows you to reduce heat loss and prevents the penetration of moisture inside.
Also, a heater for a log house between logs performs other functions:
- Protection of the house from blowing.
- Compensation for changes in the volume of wood. Under the influence of temperature and humidity, the tree can change in volume.
- Extends the life of the building.
- Waterproofing.
The beam can be insulated during construction work or after finishing the house.
The principles of choice of insulation
Serious requirements are made to a heat insulator:
- The insulation must be resistant to moisture - to prevent the formation of mold and harmful fungi, rot and insects. The best materials for these properties are linen and jute. They incorporate natural resin, which performs waterproofing tasks.
- Risk of fire. Wood is more susceptible to burning than other materials. If you choose the wrong insulation, you can complicate the situation. Natural materials burn better, especially flax. Synthetics are less prone to burning. To improve the refractory properties, flame retardants are used.
- Lifetime. It is recommended to take a heater with the same declared service life as the material of the house itself. This is due to the fact that installation is usually carried out at the repair stage, so it is difficult to replace the insulation during use of the house.
- The influence of birds and rodents. The material should not be interesting to them. Birds are one of the main problems for owners of wooden buildings, as they can organize their own home there. Most often, they take flax and moss from the heaters for building the nest. For this reason, when using them, you must periodically check the integrity.
- Good density with a small thickness. The optimal values are 40 g / cm2 with a thickness of 5 mm, 600 g / cm2. with a 6-10 mm layer.
- The form. It is better to take tape insulation during construction. It is convenient to roll out and fix it with a stapler. Tow is used to seal the cracks between the crowns.
- Thermal resistance. Natural materials retain heat better than artificial materials.
- Safety for human health. The material must not emit toxic substances or allergic dust. Many modern insulators meet this requirement.
- Elasticity. When expanding or narrowing the wood, the insulation must compensate for this distance.
- Width. It is determined by the climatic conditions of the region. Also, the material should not be visible from under the log.
There are materials that have been used since ancient times and are still popular. These include interventional insulation jute, moss, linen, felt. To understand what is best suited for warming, you need to understand their properties.
Varieties of materials
Moss
There are hundreds of varieties of moss, but only two are used for construction - sphagnum and cuckoo flax. The first is white, and the second is red. Sphagnum has good thermal insulation properties. It also contains antiseptic materials, which is why it is also used in medicine.
Moss can be collected manually or bought in special organizations. They supply an insulator in the form of finished briquettes.
If the moss was collected by hand, he needs to dry. The process takes 1-2 weeks. But it is impossible to completely dry it - when laying, the moss should let the juice in for additional protection of the log house from rotting and insects.
Stacked on the crowns in large piles. From above, another log presses them. If you put an insufficient amount, the moss will dry out and holes will appear.
Benefits:
- Nice smell. Even people with asthma find it easier to stay in a room warmed by moss.
- Hygroscopicity. The insulation between the timber absorbs moisture, so that the log remains dry.
- Environmental friendliness.
The disadvantages of moss include the complexity of laying and interest from birds.
Flax
This insulation is made in the form of a tape from natural linen. Next, he is working out on a needle machine. As a result, the material has improved properties.
The composition of technical flax includes cellulose, water, wax and lingin. Thanks to the use of lingin, the structure is combined into a single wear-resistant composition. Flax is the most durable natural heat insulator.
Avaterm
Synthetic material avaterm has Finnish roots. It is based on polyesters. The main characteristics include:
- Duration of operation. The declared service life reaches 200 years.
- Not interesting to birds. They use only natural materials to create the nest.
- Fire resistance.
It is made in the form of tapes with different lengths and widths, which can be selected for any conditions. There are also options for glued beams.
Jute
Jute insulation is a good solution for houses made of logs and timber. It has good strength, high density and hygroscopicity. Resistance to water is due to the presence in the composition of lignin - a resin that connects the fibers.
Also positive qualities include windproof, low thermal conductivity and lack of dust during installation. Jute insulation is sold in the form of rolls with different lengths and widths.
When choosing a thickness, they rely on the development of the bars. The less they are worked out, the thicker the jute tape should be.
Flax and jute insulation is not only sold in its purest form. There are mixtures with different ratios of raw materials.
Thermojack and termolen
New types of interventional heaters have their own characteristics. A biocomponent is added to the feedstock, which melts and connects the fibers. As a result, the material has improved density, high elasticity, low thermal conductivity. It is not interesting for birds and animals, as well as insects.
Tow
Tow is waste from different species of plants. The composition includes cellulose, lignin, pectin, wax. It absorbs moisture well and dries quickly. It is safe for human health. Sold in the form of bundles of different lengths and shapes. It is inexpensive.
The disadvantages include difficult uniform laying, the interest of birds and the need for re-laying a year after shrinkage.
Synthetic insulation
Synthetic insulation materials are made from polyester fibers that are bonded to each other using hot air. High-quality materials do not use harmful synthetic resins, so it is important to choose a professional insulation. The brands of synthetic insulation include Ecotherm, Avaterm and others.
The positive aspects include:
- Long service life. It can reach 200 years.
- Low thermal conductivity.Heat will remain in the house for a long time.
- Elasticity. It can recover its volume by more than 90% after compression.
- Fire safety.
- Lack of interest from birds.
- Frost resistance.
Experts note one drawback with synthetic materials - moisture resistance. Due to poor water transmission from the tree, a greenhouse effect can be created. To get rid of this drawback, you need to create a good ventilation system in the house. Also, wood must be carefully treated with special tools before construction work.
Laying interventional insulation
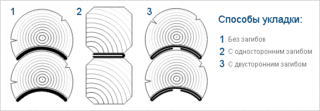 Installation of interventional thermal insulation is carried out in several stages. First, prepare the wood, choose the right tools and the material itself. The tree must be well dried and worked out. Tools do not have to be very sharp, otherwise they can damage the logs.
Installation of interventional thermal insulation is carried out in several stages. First, prepare the wood, choose the right tools and the material itself. The tree must be well dried and worked out. Tools do not have to be very sharp, otherwise they can damage the logs.
Next, the insulation is laid. When working, use the following rules:
- Laying should be uniform. Thickness is determined in advance.
- Insulation is placed around the perimeter of the house. Otherwise, there is a risk of building skewing during shrinkage.
- The material is laid in the middle so that it protrudes slightly beyond (no more than 4-5 cm). Additionally, it is fixed with a construction stapler.
- If a tape of insufficient width is used, put a second overlap on top.
The last stage is a digging. All gaps must be carefully sealed with a harness. This process should be repeated one year after the construction of the building, since shrinkage occurs during this time.