Natural pressure drops do not always provide the required coolant pressure in heating systems with one or more circuits. Get it will help a water pump for heating, built directly into the boiler equipment. Before using it, it is important to understand the device and the technical characteristics of the units, as well as understand the basic criteria for choosing the right sample.
Purpose and device
Water pumps for heating a private house are built into the circuits in order to create pressure sufficient to circulate the coolant. They contain the following elements:
- a housing with a working chamber located therein;
- electric motor with an impeller;
- air bleeding mechanism;
- distribution (terminal) box with wiring diagram.
The last of these elements includes additional electromechanical equipment designed to control the operation of the electric motor.
The simplicity of the design of the pumping units guarantees their reliable operation during the entire operating period declared by the manufacturer (approximately 5-10 years).
Types of Water Pumps
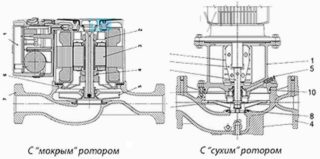
Modern circulation pumps for heating boilers, in accordance with their design features, are divided into “dry” and “wet” models. Their differences are manifested in the nature of the interaction of the drive elements with the coolant.
Dry Rotor Units
The design of circulation pumps of this type does not provide for direct contact of the coolant with the motor rotor. Its working part is separated from the movable elements by rings of a special design. The latter are made on the basis of the following materials:
- graphite or ceramics;
- Wolfram carbide;
- classic stainless steel;
- aluminium oxide.
The principle of operation of the pump is to rotate the blades in a coolant medium. In this case, the hole for water intake is located in the center of the working chamber. The system of channels diverting it is located in the peripheral zone. Thanks to this device, the working area is connected to the engine only through the shaft seal, which allows, if necessary, to replace the drive without complete disassembly.
The advantages of dry pumping equipment include:
- high efficiency, reaching 70-80%;
- minimum probability of water hammer at the time of launch;
- permissible vertical engine mounting;
- the ability to pump significant volumes of fluid (due to high power).
Due to a number of shortcomings, dry-type aggregates are mainly used in industry and in heating systems of office buildings. In residential buildings, use is limited. Negative sides:
- high level of noise;
- the need for frequent replacement of o-rings;
- the possibility of leakage of coolant in violation of the tightness of the chamber;
- the need for motor cooling.
Due to their considerable size and weight, dry-type pumps are either installed directly on the floor or suspended on special brackets.
Wet Rotor Pumps
The heating system pump with a wet rotor is similar in principle to the model described above with one difference: the motor shaft is in contact with the coolant, which is also used to cool the engine. Such devices are not able to work without additional lubrication, in the absence of which they overheat and become unusable. Since all elements of the pump are a monolithic unit, its repair in case of failure is physically impossible. The product in this case is completely replaced by a new one.
The advantages of wet rotor units include:
- noiselessness;
- compact sizes;
- low power consumption (no more than 30-50 watts);
- the ability to work without maintenance;
- low cost and easy installation.
The disadvantages of pumps with a wet rotor are limited power, the impossibility of eliminating a motor failure and a relatively low efficiency (40-60%). The disadvantages are the permissible installation of the unit only in a strictly horizontal position.
Advantages and disadvantages of pumps
Previously, heating systems of various classes, as a rule, did not have a water pump in their composition. The coolant moved through the pipes by gravity, the continuity of circulation was ensured by the differential pressure at different points in the circuit. Systems with natural circulation are still used in heating private houses, although they are much less common.
The advantages of pumping systems with forced circulation include:
- reducing the load on the equipment by reducing the difference in temperature in the inlet and outlet pipes;
- uniform distribution of heat fluxes;
- the ability to adjust the temperature of the coolant;
- fast heating when starting a cold boiler.
To this should be added the ability to integrate the pump into the system that controls the operation of the unit. Despite all these advantages, circulation devices are not without drawbacks, which are manifested depending on the power supply and high cost.
Features of marking water pumps
There are no unified labeling requirements for pumps of this class. Manufacturers themselves choose a set of technical parameters indicated on the nameplate of the device, which is mounted on the housing. It displays the following information:
- fixed direction of movement of the coolant;
- standard size (diameter) of the joined pipes;
- maximum pressure and temperature;
- manufacturer of the product and its model;
- degree of protection and characteristics of the power supply network.
Sometimes the manufacturer indicates additional information - symbols that comply with technical regulations, for example.
Rules for choosing water pumps for heating
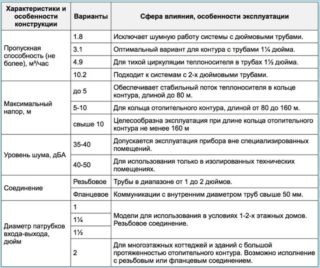
It is possible to choose the right pump for heating systems only after a careful study of its technical characteristics:
- Efficiency or the ratio of the energy lost in the pump to the useful work of moving the coolant;
- fluid pressure value characterizing the pressure difference between inlet and outlet openings;
- the maximum volume of coolant in the system pumped through the working chamber with a minimum circuit resistance (supply);
- power consumed by the device in kilowatts;
- nominal diameter of pipes of connected equipment.
Properly choose a pump - choose equipment specifically for the heating system, the temperature of the carrier in which does not exceed 130-150 ° C. Attention is also drawn to the maximum pressure (PN) in the working circuit at 20 ° C and the period for which the manufacturer's warranty is given. Usually this information is enough to make sure that the characteristics of the pump match the parameters of the installed heating system.
Device power
This parameter depends on the thermal power of the boiler equipment in which the pump is supposed to be installed. The latter is calculated on the basis of practical indicators sufficient to heat a room area of 100 square meters. meters, for example. The more heat you need to get from the heating system, the more powerful the pump must be, providing the pumping of the required volume.
When choosing this parameter is taken with a small margin, guaranteeing the receipt of the desired heat output. You should not save and try to strictly comply with the calculated ratio of pump power and equipment. In the future, this can lead to much greater costs. It is also not recommended to buy a product with a large margin of power, which inevitably leads to an excessive consumption of electricity.
Additional functionality
Before you purchase a pump unit suitable for boiler equipment, make sure that it contains the following additional options:
- the ability to operate with a fixed speed of rotation of the drive shaft;
- permissibility to work in several modes (usually three speeds);
- the presence of an electronic control module.
These capabilities allow a more flexible approach to the use of pumping equipment in any heating network. In addition, they allow you to work in economical modes, which significantly increase energy saving indicators.
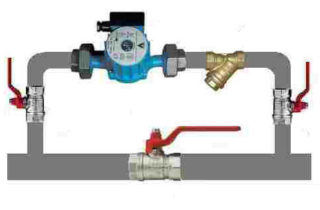
Water pump installation
The most common way to install a water pump is to plug it into the jumper between the straight branch and the return (in bypass). This approach allows you to get the following benefits:
- the convenience of dismantling or temporarily disconnecting the unit from the network in case of power problems, for example;
- the ability to move the pump outside the heating circuit;
- exception of idling;
- fine tuning of the entire system is permissible
For installation, you will need a standard tool kit, including open-end and adjustable wrenches, pliers, as well as tow or linen thread and sealant.
Nuts of the American type are usually supplied complete with a pump, but adapters (drives) and valves will have to be prepared independently.
Installation Order:
- Three working nodes with valves are assembled.
- Two of them are mounted on the sides of the pump, and the third is installed on a pre-measured section of a straight pipe.
- Before embedding in the bypass, a pump loop is prepared, the nuts of which are not yet tightened.
- Places for incorporating nodes into the pipe are outlined, after which a professional welder carries out all the necessary welding operations.
- The lower part of the loop is mounted on the return, and then all the nuts are tightened.
At the final stage of work, the pump is connected to the power supply.