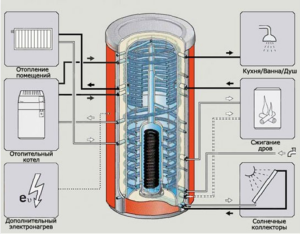
Any heating system has a number of important characteristics - nominal heat output, fuel consumption and volume of components. The calculation of the latter indicator requires a careful and comprehensive approach. How to make the correct calculation of volumes for heating: water, tanks, coolant and other system components?
Heating calculation required
First, you should determine the relevance of calculating the volume of water in the heating system or the same indicator for batteries and an expansion tank. After all, you can install these components without complex operations, guided only by personal experience and the advice of professionals.
The operation of any heating system is associated with a constant change in the parameters of the coolant - temperature and pressure in the pipes. Therefore, the calculation of heating by the volume of the building will allow you to properly complete the heat supply, based on the characteristics of the house. In addition, one should take into account the direct dependence of work efficiency on current ferries. Since you can calculate the volume of water in the heating system yourself, it is recommended to perform this procedure in order to avoid the following situations:
- Incorrect actual thermal operating mode, which does not correspond to the calculated one;
- Uneven heat distribution across heating devices;
- Emergencies. After all, how to calculate the volume of the expansion tank for heating, if the total capacity of the pipelines and batteries is not known.
To minimize the occurrence of these situations, the volume of the heating system and its components should be calculated in a timely manner.
Calculation of heat supply parameters is carried out before installation work. They serve as the basis for the selection of components.
Calculation of the volume of coolant in the pipes and boiler
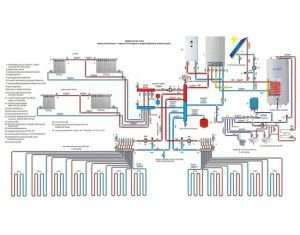
The starting point for calculating the technical characteristics of the components is calculating the volume of water in the heating system. In fact, it is the sum of the capacity of all elements, from the boiler’s heat exchanger to the batteries.
How to calculate the volume of the heating system yourself, without involving specialists or using special programs? To do this, you need a layout of components and their overall characteristics. The total capacity of the system will be determined precisely by these parameters.
The volume of water in the pipeline
A significant part of the water is located in the pipelines. They occupy a large part in the heat supply scheme. How to calculate the volume of coolant in the heating system, and what pipe characteristics do you need to know for this? The most important of them is the diameter of the highway. He will determine the capacity of water in the pipes. To calculate, just take the data from the table.
| Pipe diameter mm | Capacity l / m |
| 20 | 0,137 |
| 25 | 0,216 |
| 32 | 0,353 |
| 40 | 0,555 |
| 50 | 0,865 |
In the heating system, pipes of various diameters can be used. This is especially true of collector circuits. Therefore, the volume of water in the heating system is calculated by the following formula:
Vtotal = Vtr1 * Ltr1 + Vtr2 * Ltr2 + Vtr2 * Ltr2 ...
Where Vtotal - total water capacity in pipelines, l,Vtr - heat carrier volume of 1 m.p. pipes of a certain diameter,Ltr - the total length of the highway with a given section.
In total, these data will allow you to calculate most of the volume of the heating system. But besides pipes, there are other components of heat supply.
In plastic pipes, the diameter is calculated by the size of the outer walls, and in metal pipes, by the inner. This can be significant for long-distance heating systems.
Calculation of the volume of the heating boiler
The correct volume of the heating boiler can only be found from the data sheet. Each model of this heater has its own unique characteristics, which are often not repeated.
Floor boiler can have large dimensions. This is especially true for solid fuel models. In fact, the coolant does not occupy the entire volume of the heating boiler, but only a small part of it. All liquid is located in the heat exchanger - the design necessary to transfer heat energy from the fuel combustion zone to water.
If the instruction from the heating equipment has been lost - the approximate capacity of the heat exchanger can be taken for miscalculations. It depends on the power and model of the boiler:
- Floor models can hold from 10 to 25 liters of water. On average, a 24 kW solid fuel boiler contains about 20 liters in the heat exchanger. coolant;
- Wall mounted gas is less spacious - from 3 to 7 liters.
Given the parameters for calculating the volume of coolant in the heating system, the capacity of the boiler heat exchanger can be neglected. This indicator varies from 1% to 3% of the total heat supply of a private house.
Without periodic cleaning of the heating, the pipe cross-section and the passage diameter of the batteries are reduced. This affects the actual capacity of the heating system.
Calculation of the volume of the expansion tank heating
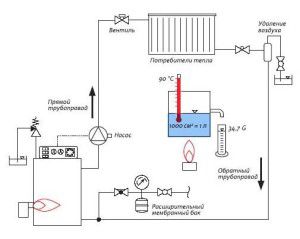
For the safe operation of the heating system, the installation of special equipment is necessary - an air vent, a drain valve and an expansion tank. The latter is intended to compensate for the thermal expansion of hot water and reduce the critical pressure to normal values.
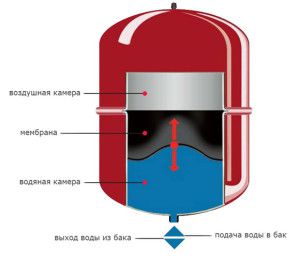
Closed tank
The actual volume of the expansion tank for the heating system is not constant. This is due to its design. For closed heat supply schemes, membrane models are installed, divided into two chambers. One of them is filled with air with a certain pressure indicator. It should be less than critical for the heating system by 10% -15%. The second part is filled with water from a pipe connected to the highway.
To calculate the volume of the expansion tank in the heating system, you need to find out the fill factor (Kzap). This value can be taken from the table:
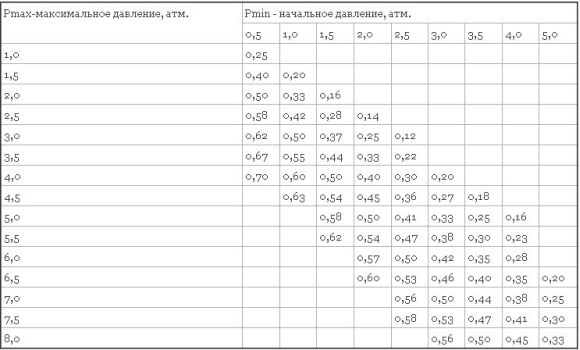
In addition to this indicator, you will need to determine additional:
- Normalized coefficient of thermal expansion of water at a temperature of + 85 ° C, E - 0.034;
- The total volume of water in the heating system, C;
- Initial (Rmin) and maximum (Rmax) pressure in the pipes.
Further calculations of the volume of the expansion tank for the heating system are performed according to the formula:
![f-1 [1]](https://home.htgetrid.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/f-11.jpg)
If antifreeze or other non-freezing liquid is used in the heat supply, the value of the expansion coefficient will be 10-15% higher. According to this technique, it is possible to calculate with great accuracy the capacity of the expansion tank in the heating system.
The volume of the expansion tank cannot be included in the total heat supply. These are dependent quantities, which are calculated in strict order - first heating, and only then an expansion tank.
Open expansion tank
To calculate the volume of the open expansion tank in the heating system, you can use a less laborious technique. Less requirements are imposed on it, since in fact it is necessary to control the level of coolant.
The main value is the thermal expansion of water as its degree of heating increases. This indicator is 0.3% for every + 10 ° С.Knowing the total volume of the heating system and the thermal mode of operation, you can calculate the maximum volume of the tank. It should be remembered that it can be filled with coolant only 2/3. Suppose that the capacity of pipes and radiators is 450 l, and the maximum temperature is + 90 ° C. Then the recommended volume of the expansion tank is calculated by the following formula:
V tank = 450 * (0.003 * 9) / 2/3 = 18 liters.
The result obtained is recommended to be increased by 10-15%. This is due to possible changes in the total calculation of the volume of water in the heating system when installing additional batteries and radiators.
If the open expansion tank performs the functions of monitoring the level of the coolant, the maximum level of its filling is determined by the installed additional side pipe.
Calculation of the volume of radiators and radiators
To perform an accurate calculation, you need to know the volume of water in the heating radiator. This indicator directly depends on the design of the component, as well as its geometric parameters.
As well as when calculating the volume of the boiler, the liquid does not fill the entire volume of the radiator or battery. For this, the design has special channels through which the coolant flows. Correct calculation of the volume of water in the heating radiator can be performed only after obtaining the following parameters of the device:
- The center distance between the forward and return lines to the batteries. It can be 300, 350 or 500 mm;
- The material of manufacture. In cast-iron models, the filling with hot water is much greater than in bimetallic or aluminum;
- The number of sections in the battery.
It is best to find out the exact amount of water in the heating radiator from the technical data sheet. But if this is not possible, approximate values can be taken into account. The greater the distance between the axles of the battery, the greater the volume of coolant will fit in it.
| Center distance | Cast iron batteries, volume l. | Aluminum and bimetallic radiators, volume l. |
| 300 | 1,2 | 0,27 |
| 350 | 0,3 | |
| 500 | 1,5 | 0,36 |
To calculate the total volume of water in the heating system with panel metal radiators, you should find out their type. Their capacity depends on the number of heating planes - from 1 to 2:
- For type 1 of the battery, for every 10 cm there is 0.25 volume of coolant;
- For type 2, this indicator increases to 0.5 l per 10 cm.
The result must be multiplied by the number of sections or the total length of the radiator (metal).
For the correct calculation of the volume of the heating heating system with designer radiators of a non-standard shape, the above method cannot be applied. You can find out their mono volume only from the manufacturer or its official representative.
Calculation of the volume of the heat accumulator
In some heating systems, auxiliary elements are installed, which can also partially be filled with coolant. The most capacious of them is a thermal battery.
The problem in calculating the total volume of water in the heating system with this component is the configuration of the heat exchanger. In fact, the heat accumulator is not filled with hot water from the system - it serves to heat it from the liquid in it. For the correct calculation, you need to know the design of the internal pipeline. Alas, manufacturers do not always indicate that parameter. Therefore, you can use the approximate calculation methodology.
Before installing a heat accumulator, its internal pipe is filled with water. Its amount is calculated independently and taken into account when calculating the total volume of heating.
If the heating system is being modernized, new radiators or pipes are installed, it is necessary to perform an additional recalculation of its total volume. To do this, you can take the characteristics of new devices and calculate their capacity according to the above methods.
As an example, you can familiarize yourself with the methodology for calculating the expansion tank: