A large amount of heat is left through the uninsulated attic, for which money is paid. As a result, the temperature in the room does not rise, and utility costs are rising. The only way out is to warm the cold attic with inexpensive building materials. If there is time and extra money, it is possible to insulate the roof, but this is not necessary, because it is enough to isolate the ceiling from the attic and all the heat will remain in the room.
Why do you need attic insulation
The floor area in a private house is equal to the area of the ceiling through which most of the heat escapes. More moisture forms in a cold living room, so the likelihood of fungus formation increases, which leads to respiratory diseases in the future. The most unpleasant sensations arise in the bathroom, the floor and walls of which do not have time to dry out, discomfort is created, in addition, the cold in the bathroom contributes to colds, when there is a sharp change in temperature. Children in these conditions are more likely to get sick.
Insulating materials for the most part drain water well, so condensation will not accumulate on the walls during insulation. Warm air dries out excess moisture, while the walls and floor warm up.
If you insulate the roof slopes and pediment, the attic will not form moisture and you will not hear the smell of mold. This is more difficult work, but doable, as the materials are light in weight.
It is best to carry out work on warming the attic with your own hands, so as not to spend extra money on wages. It is necessary to choose a heater according to technical characteristics, calculate its amount and lay it according to available technologies. All work may take 1 day.
Materials for thermal insulation
In the market of insulation you can find both natural and artificial materials. Their difference lies in cost, efficiency, service life, coefficient of thermal conductivity.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool or its varieties - glass wool, basalt insulation, slag wool - have a high coefficient of thermal conductivity due to the structure of randomly arranged fibers. Cold air in winter does not penetrate the room from the outside, and in summer it is cool in it, since cotton wool does not let air-flows cooled by the air conditioner.
Of all the varieties of mineral wool, it is recommended to choose basalt insulation for the following reasons:
- The material does not crumble and does not cause an allergic reaction. You can work with stone wool without protective equipment.
- Service life about 50 years.
- Mineral wool from volcanic rock can be of different densities - you can choose the right option for any region, including the coldest.
- Basalt cotton wool is a lightweight material, so one person can cope with its installation.
- Mineral wool from basalt does not burn. It can be melted at very high temperatures, so the attic will be safe.
Additional advantages of basalt insulation are the reduction of noise level in the room, since sound waves cannot pass through a layer of air located among the fibers. At the same time, the denser the material, the smaller the air gap and the more sounds it lets through, so the insulation can be chosen with average heat conductivity and sound insulation.
With a basalt heater, you can isolate the chimney, then even more heat will remain in the room where there is a stove or fireplace.
When using glass wool and slag, you will have to wear a protective suit, glasses and gloves, as thin fibers break and can get into the respiratory system, eyes and skin. These materials are also not combustible, but they melt at significantly lower temperatures. In this case, the material loses its structure and useful properties.
Styrofoam

Attic insulation in a house with a cold roof can be done using polystyrene foam. This material also has advantages:
- Low weight and cost.
- It does not emit harmful substances when heated, therefore it is chemically neutral and safe.
- Contains flame retardant, which does not support combustion.
- Microorganisms, mold do not start in the foam.
- Does not burden the design of the ceiling.
Of the disadvantages:
- Low coefficient of strength, therefore, additional protection of the material is required in the form of boards laid on top with support on the logs. This will require extra costs and time.
- The material does not let air through, so dampness and condensation may form in the room.
- Rodents that are found in private homes damage the foam, build holes out of it, so you need additional coverage.
Polyfoam is most often used for outdoor work under plaster. As insulation for the attic in a private house is not profitable - it requires large investments to protect the material itself.
Insulating the ceiling with foam in a house with a cold roof is more profitable to do from the inside, but this can reduce the ceilings.
Penoplex (expanded polystyrene)
Heater Penoplex is produced from granules of synthetic material polystyrene or polystyrene foam. This is a heater, which is a porous structure with separate cells. Cells do not touch each other, which on the one hand is a positive quality, on the other - a negative point. The fact is that polystyrene foam does not pass moisture well, it will accumulate indoors, causing dampness.
The advantage of polystyrene in its cost and small thickness. The air inside is 98% of the total volume of the material, so it is so cheap. Compared to stone wool, the thermal conductivity is lower. To achieve good thermal insulation, it is necessary to buy expanded polystyrene of greater thickness, which will cost more.
Penoplex is flammable, therefore, in terms of fire safety, it is absolutely useless. The melting point is 75 degrees, so it can not be laid next to heating appliances. In the attic, it may be a chimney from the stove.
Polyurethane foam
By service life, as well as heat-preserving characteristics, it is worth paying attention to polyurethane foam, which is applied by spraying. In this case, there is no need to build logs for laying mineral wool or expanded clay, save, acquiring cheap fragile materials.
In a short time, you can create a monolithic floor in the attic, in which rodents do not settle, mold does not start, cracks do not appear. When using polyurethane foam it is not necessary to buy additional steam and waterproofing.
Expanded clay bulk
You can insulate the attic with expanded clay. It is a durable material that is used in bulk with prepared cells. If you need to move around the attic, you will have to build a floor on wooden logs from above. Advantages of expanded clay:
- strength;
- durability;
- does not absorb moisture;
- keeps heat well;
- passes air;
- can be used in combination with other materials, which is preferable.
Most often, expanded clay is combined with mineral wool or polyurethane foam is sprayed on it, so as not to waste time on the construction of the frame.
Thermal Insulation Layer Thickness
To warm the attic in a house with a cold roof, you can use heat-insulating materials of any density, since the room is not residential. If you plan to lay mineral wool on the roof slopes, you can prepare material of lower density and thickness, since as a result the ceiling insulation will be double, but laid in two places.
Builders recommend a thicker layer of insulation to be placed around the perimeter of the attic, since the greatest heat loss occurs in the corners.
For ease of movement along the soft insulation, it is necessary to build paths of wood or other material so as not to violate the properties when compressing the insulating layer.
Preparing the attic for insulation
Before starting work, it is necessary to calculate the area of the premises and the amount of building materials. The main thing is the thickness of the insulation, which is needed in the middle band, where the temperature can drop to minus 30 degrees. The thickness of the mineral wool should be at least 20 cm.
After calculations:
- Remove all debris and dust so that the seal does not absorb it.
- Close up cracks in the roof using construction foam.
- Remove sharp objects. They can damage the protective layer of cotton wool.
After cleaning, you can bring in building materials, tools, as well as an additional lamp for lighting.
Vapor barrier
According to the laws of physics, warm air saturated with steam will always rise upward, passing through walls and ceilings. This process is called diffusion.
Different materials have different degrees of vapor permeability. Condensation or the accumulation of moisture between floors can have a high resistance to diffusion. In such places, floors are usually made of wood, and wood, saturated with moisture, loses its strength.
When the lower room warms up, and the upper one is cold, vapor barrier is necessary. In the case of using stone wool, you can buy a material with a hydrophobic coating that will not let steam into the cold room at the top, where water drops form from it.
There are two concepts in technical documentation: steam resistance and vapor permeability coefficient. These are different concepts.
To organize vapor barrier, two materials are used - a film to cover the entire area and adhesive tapes to connect the layers of hydrophobic insulation, so that steam does not penetrate into the cracks.
The characteristics by which vapor barrier is chosen should take into account strength (a plastic film is not suitable), resistance to ultraviolet, since sunlight can sometimes get into the windows, which can damage materials.
Waterproofing
To protect the attic from flooding, and ceilings and repairs from water drips, it is recommended to lay a layer of waterproofing material on the roof slopes.
- Surfaced - overlaps and connects using a torch. The cheapest option is synthetic materials.
- Sprayable. An integral membrane film is created.
- Powder. Water is added to it immediately before installation.
- Liquid - suitable for concrete floors, soaking into their surface.
- Bituminous based.
Before you buy waterproofing, you must re-read the properties: the material must let air through, but retain water. Some cheap films create a greenhouse effect in a cold, unheated attic, causing the walls to become moldy.
How to carry out the work
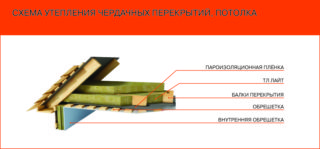 Do-it-yourself attic insulation in a private house is carried out as follows:
Do-it-yourself attic insulation in a private house is carried out as follows:
- If the attic is not planned to be inhabited, it must be ventilated. To do this, install air ducts in the roof.
- It is recommended that the old roof be insulated with a waterproofing layer of any type described above. This is necessary to protect mineral wool.A wooden structure, on which the film is pulled, or a sprayer will do.
- If you simultaneously warm the slopes, it is recommended to start with them. Plates on one side are smeared with glue and attached to the inside of the roof. You can use self-tapping screws, substituting square wide plates under them. Roll insulation can be cut after it is laid between the rafters.
- A vapor barrier film is mounted on top of the slabs.
- When installing the insulation on the floor, lags are first built - a wooden frame, between which a roll or tile layer is laid.
- In front of the plates, vapor barrier is laid, then the plates and waterproofing.
To be able to move freely throughout the attic, the lags are covered with durable material - wood or sheets of gypsum board. This makes the appearance of the room more accurate - if you wish, you can equip a workshop or a storage of things there. If you want to save money, you can equip only paths to important objects, for example, to a chimney, dormer, ventilation.