Installation of the air conditioner consists in hanging the outdoor and indoor units and holding pipelines between them. The installation diagram for air conditioners is an installation guide. The fulfillment of the basic requirements ensures the normal functioning of the device.
Basic requirements for installing an air conditioner
The installation scheme of air conditioners allows:
- Mounting the indoor unit on any strong wall of the room;
- Installation of the outdoor unit under the window, between the windows, inside the balcony or outside it;
- The installation scheme of air conditioners allows you to lay pipelines both inside the apartment and along the street;
- When hanging the outdoor unit between the windows, mount it in the middle.
Technical requirements:
- Between the indoor unit and the ceiling should be at least 6 centimeters;
- Between the exit of the road to the street and the window there must be at least 50 centimeters when hanging the outdoor unit on the street and at least 20 centimeters when hanging on the balcony;
- The installation scheme of air conditioners prohibits installing the outdoor unit close to the window opening, balcony fencing.
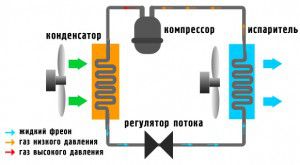
The scheme of the air conditioner
The air conditioner performs its functions due to the ability of liquid media to absorb heat during evaporation and to give it off during condensation.
The refrigeration circuit is created by a condenser, compressor, expansion valve, evaporator. Between them are copper tubes passing through the refrigerant.
The scheme of the air conditioner:
- From the evaporator, refrigerant is supplied to the compressor in the form of a gas of temperature from 10 to 20 degrees under low pressure;
- In the compressor, the refrigerant is condensed, its temperature increases by 60 - 70 degrees, after which it is supplied to the condenser;
- According to the control scheme of the air conditioner, the fan delivers a stream of room temperature air, the refrigerant cools, liquefies and transfers heat to the air in the condenser. The temperature of freon at the outlet is on average 15 degrees higher than the ambient temperature;
- Next, the refrigerant goes to the expansion valve (thermostatic valve), which is a copper tube curled by a screw. Here the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant fall;
- From the valve, refrigerant in the form of gas and liquid is supplied to the evaporator, where it completely becomes gas, absorbing heat from atmospheric air. Thus, a decrease in room temperature is achieved. The operation of the air conditioner provides an endless repetition of cooling cycles.
Air conditioner control principle
The control circuit of the air conditioner includes a control circuit: microprocessor, the location of the boards of the indoor unit, power circuit, control board and working unit.