One of the characteristics of HVAC equipment is the type of refrigerant used. There are about 40 types of stable compounds designed for refrigeration systems. Freon R22 - a popular option for refueling household split systems. The composition copes with the heat transfer function, provides high cooling capacity of air conditioners. Consumer-friendly Freon R22 destroys the ozone layer of the atmosphere.
What is freon R22
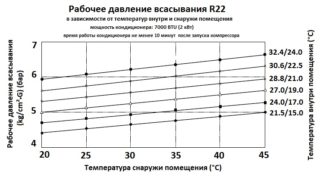 Until recently, difluorochloromethane or R22 refrigerant was used as a working fluid in 90% of air conditioners. Due to its physical characteristics, it is an excellent refrigerant. Inside the systems, freon changes its state of aggregation, taking away heat and generating cold. To perform the functions of the refrigerant, the substance must have a low boiling point, as well as the condensation pressure and the volume of steam that arise during this. Freon R22 meets the requirements, its boiling point is -40.8 ° C, and the pressure is 4.986 MPa.
Until recently, difluorochloromethane or R22 refrigerant was used as a working fluid in 90% of air conditioners. Due to its physical characteristics, it is an excellent refrigerant. Inside the systems, freon changes its state of aggregation, taking away heat and generating cold. To perform the functions of the refrigerant, the substance must have a low boiling point, as well as the condensation pressure and the volume of steam that arise during this. Freon R22 meets the requirements, its boiling point is -40.8 ° C, and the pressure is 4.986 MPa.
The refrigerant can be charged in domestic and industrial climate systems. It is compatible with mineral and alkylbenzene oils. Freon R22 has a low chlorine content, its ozone depletion potential is ODP = 0.05, global warming GWP = 1700. The substance is a transitional refrigerant, replacing R12 in all areas of application. Its cold performance is 60% higher.
The refrigerant is suitable for low temperature cooling systems with piston and screw type compressors:
- domestic, industrial and automotive air conditioners;
- refrigeration units, including automobile and marine;
- cryogenic equipment.
Difluorochloromethane is used as a low-temperature propellant in aerosol cans, a foam converter, and a component for producing fluoromonomers. R22 freon is used in stage I and II chillers to obtain temperatures of -40 ° and -60 ° C, respectively. It is a component of a mixture of refrigerants.
The connection of R12 and R22 freon is forbidden, since a dangerous azeotropic composition is formed.
A common gas sales option is a metal cylinder with a valve and safety valve.
Effects on the ozone layer
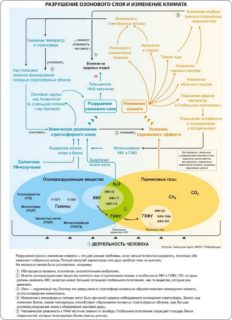 The effect of freon on the ozone layer is 20 times less than previously used freon R11 and R12. Gas belongs to the group of chlorofluorocarbons (HCFC). Refrigerants have a harmful effect on the ozone layer, enhance the greenhouse effect. After use in climatic equipment, aerosols, refrigerators, they enter the atmosphere. Under the influence of solar ultraviolet decompose. The free components of freons react with ozone, causing its decay. Under the UN Montreal Protocol, the production and use of HCFC freons is declining and phasing out. China has not joined the settlement agreement, the refrigeration equipment and air conditioners manufactured in the country operate on R22 freon.
The effect of freon on the ozone layer is 20 times less than previously used freon R11 and R12. Gas belongs to the group of chlorofluorocarbons (HCFC). Refrigerants have a harmful effect on the ozone layer, enhance the greenhouse effect. After use in climatic equipment, aerosols, refrigerators, they enter the atmosphere. Under the influence of solar ultraviolet decompose. The free components of freons react with ozone, causing its decay. Under the UN Montreal Protocol, the production and use of HCFC freons is declining and phasing out. China has not joined the settlement agreement, the refrigeration equipment and air conditioners manufactured in the country operate on R22 freon.
Refrigerant Benefits:
- Freon R22 is stable, non-toxic and explosion-proof.
- The low discharge temperature during compression in the compressor prevents overheating of the mechanism.
- The refrigerant has excellent thermophysical and thermodynamic characteristics.
- Chemical inertness to most structural materials (copper, brass, nickel, steel).
- Freon 22 is offered at an affordable cost, cheaper than the R407c analogue.
- It contains one component, which simplifies the refueling of air conditioners in the event of a leak.
- The absence of a temperature glide does not change the composition of the substance in the liquid and gas phase.
Key Features and Features
Colorless gas is stable at normal temperature, does not burn, and is inert to metals.When interacting with plastic and elastomer leads to swelling. It has a slight smell of chloroform. Contact with fluorine-containing rubber is prohibited. The refrigerant is poorly soluble in water, penetrates through leaking surfaces.
Permissible concentration of freon in the air is 3000 mg / cu. m
The chemical formula of freon is R22: CHCLF2, the designation HCFC 22 is found. In terms of exposure to the body, it belongs to hazard class 4.
Characteristics table of freon R22
| Characteristics | Units |
R22 |
| Molecular mass | 86,5 | |
| Boiling temperature | ° C | -40,8 |
| Critical temperature | ° C | 96,13 |
| Critical pressure | MPa | 4,986 |
| Temperature drift | ° K | 0 |
| Steam pressure at 25 ° C | MPa | 1,04 |
| Flammability in the air | Not flammable | |
| Melting temperature | ° C | -146 |
| Ozone Depletion Potential | 0,05 | |
| ASHRAE Safety Class | A1 |
Contact with open flames or incandescent materials (temperature 330 ° C) decomposes into toxic components. Gas cylinders are stored in dry rooms without the possibility of heating by sunlight or heating devices. Allowed to transport by any means of transport.
Since 1987, a systematic transition to the use of safe refrigerants has begun. Industrialized countries have decided to abandon the use of ozone-depleting freon R22. His alternative was R407c freon. After a complete ban on chlorine-containing refrigerant, service centers will not stop servicing and refueling the equipment sold.
Refueling the air conditioner with r22 freon
 During prolonged use of the air conditioner or in the event of a refrigerant leak, the equipment loses power. Signs of insufficient Freon:
During prolonged use of the air conditioner or in the event of a refrigerant leak, the equipment loses power. Signs of insufficient Freon:
- weak blowing with cold air;
- the appearance of frost on the heat exchanger of the indoor unit;
- uneven compressor operation;
- freezing of the liquid port;
- emergency shutdown.
In such a situation, R22 freon refueling of the cooling system is necessary. The procedure requires a vacuum pump, a manometer, electronic scales, communication tubes. The equipment must be designed to work with the brand of Freon 22.
The manifold for R410a cannot be used due to the different type of oil.
Preparatory measures:
- Checking the tightness of the system by injecting high pressure. Special foaming liquid lubricates the joints of the blocks with the pipeline and soldered sections. If a leak is detected, repair it before refueling begins.
- Remove air from the device using vacuum. The pressure gauge and pump hose are screwed to the gas fitting. The vacuum unit is turned on for 10-20 minutes to completely remove air and moisture. The pump is turned off at a pressure of -1 bar. In some cases, the procedure is replaced by purging the system with gas - nitrogen or freon.
Refueling is done with pressure or weight control. In the first case, a pressure gauge is connected to the adapter between the gas cylinder and the air conditioner. Permissible refrigerant pressure is indicated in the instructions and characteristics of the climate technology. Gas is supplied in parts to the system, the pressure gauge and recommended data are periodically compared.
Complete refueling of the split system is carried out by controlling the weight of freon. When weighing the cylinder on an electronic balance, the amount of gas transferred to the equipment is determined. Previously, the tank is turned upside down. The refueling recommendations indicate how much refrigerant is per 1 m of the route. At the end of the procedure, the valves at the service ports are closed. The equipment is removed and plugs are installed. Performance testing of the split system is in progress.


