Utility payments are growing every year. Special metering devices — water, gas and electricity meters — help to save on them. Another way to not overpay utilities is to install a wastewater meter. High-tech product provides high measurement accuracy.
Definition, scope of equipment
A flow meter is a device designed to accurately calculate the volume of wastewater passing through it. Depending on the type of device it is used in the following areas:
- metering of sewage at municipal and private facilities;
- calculation of clean water consumption;
- monitoring the filling of sewer networks;
- industrial sector for accounting volumes of discharged effluents.
Sewer counters are equally intensively used for pressure and pressureless pipelines.
Types of metering devices
All flowmeters are divided into types according to the type of device and principle of operation. Each of them is most relevant for operation in specific conditions.
Ultrasonic
This type of device is used only for gravity gravity lines. The principle of operation of such a device is based on a built-in sensor that reads the volume of passing effluents by the area-speed method. That is, it determines the depth of the stream and the speed of its movement. The sensor is installed directly in the transported medium. The ultrasonic wastewater flow meter has the following advantages:
- good amount of memory (saving previous data);
- the ability to install on pipes of different diameters from the smallest to a cross section of 350 cm or more;
- minimum percentage of errors in the calculation (0.1%);
- operation of the device from batteries or from a network of 220 W;
- service life up to 10 years (with the need to check every 4 years);
- the ability to remotely take readings;
- Russian language interface.
Mortise ultrasonic metering devices and invoices are isolated. The second are intended for installation in pressure systems, including. To take readings from such devices, you can use a wireless modem or conventional cable connection.
Lever-pendulum
The device works according to this principle:
- The lever in the device is equipped with a float. When the water flow moves with their help, a measurement of the depth of the effluent stream (level of filling of the pipe) takes place. If the volume of contaminated media in the channel increases, the float rises and thereby raises the lever of the device. Reducing the depth of flow leads to the reverse movement of the working elements. It is the angle of the lever that shows the depth of the wastewater.
- The flow rate is measured by a rotary blade specially integrated in the flowmeter. It also displays readings on the angle of its inclination.
Lever-pendulum metering devices are used in open channels and high-grade pipelines. Perhaps their use even for very polluted waters.
Electromagnetic
Such wastewater meters are used in non-pressure pipelines and pressure pipes. But provided that the optimal working pressure in the last collectors does not exceed 40 bar. The principle of operation of these types of meters is based on the use of magnetic induction. Here, the flow itself plays the role of a moving core that passes through a magnetic coil.
Electromagnetic devices can be used to account for the volume of effluents and clean water.
The advantages of this type of apparatus:
- simple installation and operation;
- high reliability indicators;
- resistance to vibrations;
- accuracy of measurements;
- permissible temperature limit of effluents or water +80 degrees;
- elimination of pressure loss.
Electromagnetic flowmeters are many times cheaper than previous ultrasonic and lever-swing devices.
How to choose a counter for drains

The main criteria for buying a flow meter:
- maximum temperature indicators of effluents;
- type of measured liquids (clean or dirty water);
- range of flow rates for a specific device model;
- section of a pipe or channel;
- the material of which the highway is made;
- the most admissible working pressure on a collector;
- the ability to narrow the pipe.
Also, experts advise to heed such recommendations:
- It is better to put electromagnetic or ultrasonic meters on waste water. For pure water - lever-pendulum.
- When installing an ultrasonic device, an extended straight-line section of the line is required. You need to remember this when buying equipment.
- It is advisable to abandon the ultrasonic counter with surface sensors. They are less whimsical in installation, but at the same time they are characterized by low accuracy of readings.
- For pressure systems, it is better to choose electromagnetic meters.
Using these recommendations, the master can buy and install the best flowmeter for your conditions.
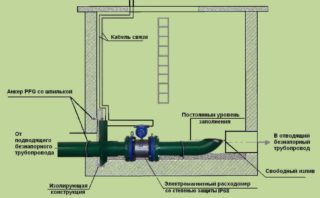
Installation Features
To obtain the most accurate readings, you must follow the rules for installing meters.
- The legislation allows mounting devices only on long, straight sections of pipelines.
- The installation of the device in non-pressure highways must be carried out on its lowered areas. At the same time, a flow meter is not placed at the bottom of the pipeline if its effluents are discharged from a height precisely at this point and first enter the atmosphere.
When installing the meter on a gravity gravity drainage system, it is important to remember that the fullness of the pipe and the flow rate are constantly changing.
Possible errors in the calculations
It is not uncommon for an installed mechanism to show many times less or more discharged water than it enters an object. A priori this cannot be. Therefore, it is worth looking for the causes of inaccuracies.
- Wrong location of the flowmeter in the collector - its installation without taking into account third-party cut-in to the highway. The equipment stands after the point of location of another outlet for the discharge of effluents into the general network.
- Damage in the pipeline in front of the location of the flowmeter. As a result of this, groundwater enters the collector assembly, which increases the amount of waste.
- Incorrect determination of the water balance by the object. For example, the master can only consider the ratio of incoming cold water and the formation of effluents. But after all, they also include the resources of the hot water supply.
- Failures in the operation of the equipment itself (sensors, levers, blades, coils).
To avoid serious errors in the readings of the meter, its installation must be carried out with strict observance of the above rules.