Sewerage system is a complex consisting of pipelines, pumping station and treatment facilities. It is designed taking into account the volume of moving effluents and the possibilities of their treatment. But they do not exclude that a situation may arise when the treatment plant cannot cope with a large unforeseen amount of sewage. Therefore, the project necessarily takes into account the security zone of sewage treatment plants. This is the area around designated structures of a certain area, which protects the environment and soil from sewage discharges.
What is prohibited in the security zone

There are strict requirements for the protection zone of water supply and sewage networks. This mainly relates to its possible operation, in particular, the construction of buildings and structures for various purposes. The requirements are as follows:
- not to carry out the construction of residential buildings;
- not organize sports and playgrounds, recreation and entertainment areas;
- plant trees near laid pipe lines at a distance of at least 3 m;
- it is impossible to change the amount of soil inside the zone, because the sewer system is designed for the landscape of the territory;
- Do not drill, pile, or explode;
- some types of construction are possible, but permission is required;
- construction within the security zone should be carried out by specialized companies, therefore, obtaining a permit will require a license for construction work;
- you can not change the line of the shore and bottom of nearby reservoirs, because this can lead to displacement of the soil layers, which will create pressure on the laid pipes and tanks;
- it is forbidden to block access roads, which in extreme situations (fire, sewage discharge) are the only highways; rescue services arrive along them.
Sewer networks located underground are not provided with any warning signs. The only element that designates them is a cast-iron hatch with the letter "K" on the front plane. That is, pipes and tanks laid underground are a latent threat to the environment. Any actions near them, even out of ignorance, can turn into a big catastrophe. Therefore, before starting any work, especially construction, permission is required. It is confirmed by architectural bureaus or research institutes for construction, Vodokanal trusts or the district administration (its construction department).
Unauthorized construction in protected areas is stipulated in legislative acts. If this happens, the producer of the work, as well as the customer, will be administratively punished. Usually these are fines for large amounts.
If permits for the construction of facilities in the security zone are received, you must strictly follow the recommendations:
- strictly comply with building regulations and rules;
- Do not harm sewer systems;
- if during the construction process any discrepancies were found in the issued design documentation, work should be stopped immediately until clarification.
After completion of work, it is necessary to invite a representative of the organization that issued the permit so that it approves the conformity of the measures taken with the design and estimate documentation. Be sure the contractor at the end of the work carries out garbage collection, and in the winter dirty snow.
Regulations
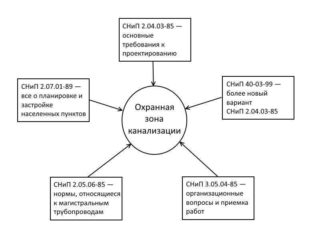 Create a protection zone of the sewer collector according to SNiP.They indicate the requirements for the formation of protective areas, as well as other rules and regulations.
Create a protection zone of the sewer collector according to SNiP.They indicate the requirements for the formation of protective areas, as well as other rules and regulations.
- SNiP 2.04.03-85. Here are the requirements for the design of security zones. Today they use its updated version under the number 40-03-99. But the first document can be used.
- SNiP 2.05.06-85. This code contains standards that apply to pipelines.
- SNiP 2.07.01-89. This document contains everything related to the planning and development of settlements.
- SNiP 3.05.04-85. Organizational work associated with the formation of security zones and acceptance of work carried out within the zone is indicated here.
There is a main requirement for the creation of protective and security zones. It is related to local conditions and features. All work is carried out based on the relief of the site, the type of soil, the remoteness of open water bodies, the depth of groundwater, and more.
There are special requirements that determine the operating conditions of sewer systems and the formation of security zones. These include regions with abnormal temperature differences: regions of the Far North, desert regions. Special conditions include seismically hazardous areas, as well as areas where soils are soft or very wet.
Additional requirements for security zones
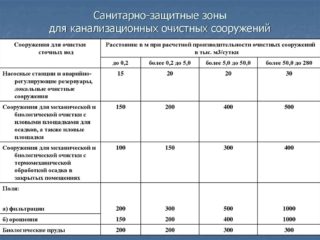 There are certain standards that define the protected area of the laid pipelines:
There are certain standards that define the protected area of the laid pipelines:
- If the soil is dry, the protection zone along the pipe should have a width of 10 m, 5 m on each side.
- If the ground is wet, this parameter increases to 50 m.
- If engineering networks are laid inside the built-up area, the security zone can be reduced or increased, coordinating this with the SES, which will act on the basis of SanPiN.
- If the diameter of the pipe being laid does not exceed 600 mm, the width of the zone does not exceed 10 m.
- If the pipe diameter is 1000 mm, the security zone increases from 40 to 100 mm.
Requirements for the size of the security zone must be taken into account when creating a project for sewage and treatment facilities. In some cases, you can depart from the rules. But all changes will have to be coordinated with the sanitary-epidemiological station.
Distances between water supply and sewerage
If there is a breakthrough of the sewer network, and a water supply branch is located nearby, there is a high probability of contamination of drinking water. To prevent this from happening, the SNiPs set standards for the mutual arrangement of these two communication networks, as well as sewage systems with other engineering systems.
The most important thing is to place the water supply system above the sewer. During a breakthrough, the last runoff will begin to be absorbed by the soil. If there is no possibility of such laying, sewer pipes must be laid in tight casings.
The distance between the water supply and sewerage varies in the range of 1.5-5.0 m. It all depends on the material from which the pipes are made. The distance between the sewer system and other utilities:
- storm sewer - 0.4 m;
- gas pipe - 1-5 m;
- voltage cables - 0.5 m;
- heating system - 1 meter.
Between the security zone of the sewage system and water bodies, the distance determined by SNiPs must also be observed. To the river - 250 m, to the lake - 100 m, to the level of lying of aquifers - 50 m.


