To comply with sanitary and hygienic standards, it is necessary to ensure high-quality discharge of sewage from all residential and industrial facilities. For this purpose, a sewage system is mounted. Its pipelines, as communicating vessels, eventually occur in VOCs (local treatment facilities). The sewage from a private collector flows into a pre-mounted septic tank or cesspool.
Definition and purpose
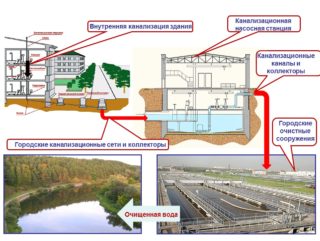 Sewer system is called a special sanitary facility. It is an integral element of VOCs. With the help of sewage, all water contaminated with feces, industrial and household waste is discharged here. In VOCs, effluents are pre-treated before they are discharged to nearby water bodies.
Sewer system is called a special sanitary facility. It is an integral element of VOCs. With the help of sewage, all water contaminated with feces, industrial and household waste is discharged here. In VOCs, effluents are pre-treated before they are discharged to nearby water bodies.
Violations and malfunctions of the city collector can lead to serious environmental disaster.
Classification and device
The collector for drainage is divided into types according to purpose, location relative to the building and type of construction. According to the location zone, such systems are distinguished:
- Internal sewage: a network of pipelines mounted inside the building. From each plumbing fixture there is a branch towards the central riser. In the future, sewage is transported to the public network.
- External sewage: piping and other communication elements outside buildings, due to which sewage is sent to a local sewage treatment plant. As a rule, the external collector is mounted underground. The diameter of the pipes varies depending on the amount of dirty water transported.
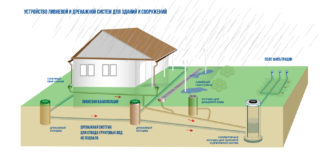 By purpose, the sewer is divided into such types:
By purpose, the sewer is divided into such types:
- Heavy rain. Serves to divert rainwater from buildings, from roads, autobahns, runways.
- Drainage. Allows you to remove excess groundwater from the site.
- Fecal. Sewerage through which household and industrial effluents are removed.
By design, the collectors are divided into three groups:
- Separated. It implies separate transportation of domestic, industrial and storm drains and separate receivers for them.
- Semi-separate. Discharge of sewage along different lines and their further accumulation in a single tank.
- Alloyed. Rain and household sewage are transported through one collector to a common treatment basin.
For household (fecal) sewage, the marking K1 is applicable; for storm - K2; for industrial - K3. Do not confuse the city fecal highway with cable ducts. Under it also arrange underground collectors.
Elements of the sewer system
 Any local sewage system or public / industrial system has a number of components. Moreover, for external and internal networks, they differ.
Any local sewage system or public / industrial system has a number of components. Moreover, for external and internal networks, they differ.
For the collector in the building, the following elements are used:
- pipes;
- water locks;
- bends and tees;
- fitting;
- fecal pump (if necessary, if it is not possible to transport wastewater by gravity due to the peculiarities of the structure or relief on the site).
For outdoor sewage use:
- Pipes made of polymer, cast iron or concrete.
- Wells (revision, overflow, storage, drainage) depending on the type, extent and configuration of the collector (straight, curved). The inspection well helps to eliminate blockages in certain sections of the pipeline.
- The receiver, it is a septic tank, shambo, cesspool, aeration tank. Everyone chooses a tank for themselves according to available means. Sometimes they build a septic tank from car tires or reinforced concrete rings. The drive is installed with a private sewage device.
- Caisson. It is necessary if a fecal pump is installed in the collector area.In this case, the sewage system is considered pressure head.
When installing an external network, it is better to use plastic pipes in the corrugation. Here the rings play an additional role of stiffeners, the soil will not exert pressure on the collector.
Current requirements
When designing and installing the collector, it is important to adhere to sanitary norms and rules (SNiP). Otherwise, the efficiency of the system will be zero.
Requirements for the location and installation of external sewage:
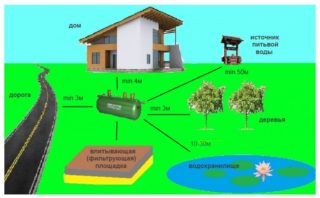
- A cesspool or septic tank is located at least 5 meters from the house. From wells or wells - at a distance of 20 meters.
- The pipe material must be durable and corrosion resistant.
- The depth of laying the collector is located below the freezing of soil in the area. Otherwise, the pipeline is qualitatively insulated.
- Turns and bends should not be mounted at an angle of 90 degrees. Sharp changes will lead to blockages in the reservoir.
- Bias. One of the most important points when installing a sewer system. In order for sewage to flow into the receiver by gravity, it is necessary to lay the pipes at a slope towards the septic tank / pit. The smaller the clearance of the tube, the greater the slope. With a cross section of 50 mm, the slope of gravity sewage is 3 cm per 1 linear meter of the collector. With a diameter of 100 mm - 2 cm / mp With a cross section of 160 mm and more than 0.8-0.7 mm / mp
According to Construction Norms and Regulations for sewer pipes and septic tanks, they must arrange a foundation. The heavier the collector, the more durable it should be. A concrete platform is poured under the plastic barrels and aeration tanks, a sandy pillow is enough for the pipes.
Preparing for the installation of an outdoor sewage system
 As preparatory measures, an initial assessment of the soil is carried out: its composition and depth of freezing, groundwater occurrence. Based on the data received, they necessarily make up the project. The drawing is applied to the length of the outer part of the pipeline, the location of its bends, the location of the wells. This will be useful in the future when carrying out repair and maintenance work.
As preparatory measures, an initial assessment of the soil is carried out: its composition and depth of freezing, groundwater occurrence. Based on the data received, they necessarily make up the project. The drawing is applied to the length of the outer part of the pipeline, the location of its bends, the location of the wells. This will be useful in the future when carrying out repair and maintenance work.
After all the calculations, it is important to prepare the trench and the removal of the pipe from the house. To do this, a hole is formed low (15 cm below the ground surface) in the foundation and a steel sleeve is necessarily inserted into it. A pipe is brought out through it.
They dig a trench in accordance with the intended scheme. In this case, observe a bias towards the septic tank. The bottom of the trench is carefully tamped and covered with a layer of slightly damp sand. It is also well compacted. If you can’t dig a trench for any reason (there is a building, there is a carriageway, etc.), use the method of horizontally directed drilling to lay the pipeline.
Installation Steps
As a rule, all tubes are joined into the socket - each end of the next element is inserted into the socket of the previous one until it stops. If it comes to the installation of plastic elements, all joints are sealed and laid with rubber seals. Cast-iron pipes are boiled or caulked with a special solution.
The fully assembled system is checked for leaks and only after that they are insulated if necessary and buried. It is important to ensure that the collector does not sag in any of the sections, otherwise over time this will lead to a break in communication.
It is forbidden to compact the soil over the laid pipes. Over time, he himself will sit down under the influence of precipitation.
Operation and maintenance
 As a rule, the outdoor sewage system laid in compliance with all norms works properly. The following service principles will help extend its life:
As a rule, the outdoor sewage system laid in compliance with all norms works properly. The following service principles will help extend its life:
- It is forbidden to dump large personal hygiene items into the toilet. This can cause blockage in one of the sections of the pipeline.
- Once a year, it is advisable to flush the external collector with a strong pressure of hot water (50-60 degrees). This will help prevent siltation of the walls of the system, the growth of fatty polyps on them.
- For the winter period, if no one will use the sewage system, it is advisable to insulate all plumbing fixtures in the house, or arrange regular heating of the room. Otherwise, the system will freeze from the side of the house, which can lead to a rush of the toilet and pipes. If freezing does occur, you need to wait until spring until the collector thaws at random.
Proper operation of an autonomous sewer system extends its service life by decades.