During the construction of any engineering systems, the developer needs to look for trade-offs between effective work schemes and the cost of work. So, when laying sewage in a private house, namely, calculating the depth of laying, it is necessary to take into account such nuances as the level of freezing of soil in a given area, the slope of the relief, the sewage scheme (the presence and number of bends), the cost of land work. Manual only regulatory documents do not always give the desired result. So how to correctly determine at what depth the sewage system will work perfectly, but at the same time require minimal installation and maintenance costs in the future?
Why is this point so important
 The correct calculation of the laying depth allows you to avoid many troubles during the operation of the sewage system, as well as increase the life of the system. When laying pipes to a lower level, there is a risk of freezing of effluents in the winter. In this case, you cannot use the sewage system until it gets warmer and the wastes in the pipes freeze and pass through them. The freezing level for each region is different, and the colder the winters, the deeper the pipes should be laid.
The correct calculation of the laying depth allows you to avoid many troubles during the operation of the sewage system, as well as increase the life of the system. When laying pipes to a lower level, there is a risk of freezing of effluents in the winter. In this case, you cannot use the sewage system until it gets warmer and the wastes in the pipes freeze and pass through them. The freezing level for each region is different, and the colder the winters, the deeper the pipes should be laid.
To avoid unnecessary clogging of the pipes, it is recommended to arrange as few bends as possible and observe the recommended slope of the pipes, which will allow the waste to pass on its own with ease. If possible, it is recommended that bends be eliminated and pipes laid right up to the treatment facility. But, as practice shows, this is not always realistic.
Note. If it is not possible to avoid bends, it is recommended to make wells at the joints. This will allow, if necessary, to get to the junction and clean them.
Depth standards and what affects them
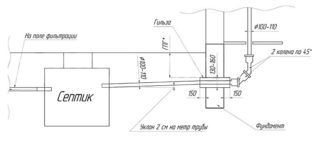 It is believed that the main criterion for choosing the depth of installation of the sewage system is the level of soil freezing. What does it depend on and how to calculate this parameter?
It is believed that the main criterion for choosing the depth of installation of the sewage system is the level of soil freezing. What does it depend on and how to calculate this parameter?
To do this, you need to familiarize yourself with the established standards. These norms are contained in document SNiP 2.01.01.82. It is here that you can find a map indicating the depth of freezing for each region of the state.
So thanks to this map, it can be seen that in the Moscow region the soil freezes to a depth of 1.4 meters, but Sochi and other southern regions are only 0.8 meters.
It is worth noting that these standards apply more to large facilities, while private facilities require other calculations. When laying sewers for housing, gravity systems are mainly planned, for the functioning of which a certain level of slope is required:
- with a pipe diameter of up to 50 mm - the slope according to the regulatory document should be 3 cm per meter;
- with a pipe diameter of more than 50 mm - 2 cm per linear meter.
If these norms are not observed, the landlord may encounter the following problems: with a small slope, the waste will pass too slowly, which can lead to clogging of pipes, and with a larger slope, the flows will be too fast, which will affect the life of the sewer.
Another important point when taking into account the level of depth is what structure will be at the end of the pipeline: so the deeper the pipes are located, the more you need a foundation pit. Strongly deepening the container is not recommended - the lid should be at ground level. If this condition is not met, then you will have to make a large throat for the septic tank.
Note. It is worth considering that the structure can fail and require repair, and a deeply laid system makes it difficult to access it, especially in winter.
Given these nuances, when laying sewers in a private house, you can not rely solely on the depth of freezing of the soil. Moreover, there are reasons that allow you to lay pipes slightly above this level:
- The drains that pass through the pipes have room temperature, and in some cases even higher. This allows you to wash off the frost that forms inside the pipe.
- If the sewage system is not used for a certain time, then the pipes will be empty, which means there is nothing to freeze.
- In the septic tank, during the treatment and decay of the effluent, heat is generated that enters the sewer.
Based on this, you can take the pipe out of the house slightly higher than the level of freezing of soils specified in the norms of SNiP 2.01.01.82, and then be guided by the angle of inclination and the depth of the treatment plant.
Calculation Example
 The SNiP states that the sewer pipe should go at least 30 cm above the average level of soil freezing for a given region. However, the minimum depth for laying sewers for a private building is the norm of 70 cm.
The SNiP states that the sewer pipe should go at least 30 cm above the average level of soil freezing for a given region. However, the minimum depth for laying sewers for a private building is the norm of 70 cm.
So you can lay pipes in the Moscow region at a depth of 1.1 meters. But, assuming that the skeptic is at a distance of 20 meters from the house, given the optimal level of inclination, which is 2 cm in this case, it can be seen that the inlet pipe on the septic tank should be located at a depth of 1.5 meters (assuming an even relief) .
It is also taken into account that earthworks have their cost and implementation period. In this case, it is impractical to lay pipes according to the norms of freezing soil. So, for residents of central Russia, it is enough to lay pipes to a depth of 70 cm, since even in this case the system will function normally.
In addition, many when laying pipes they are immediately insulated, which allows them to increase the service life due to protection from external influences of the soil in which the sewage is located, as well as to maintain the temperature of the effluents when they move through the pipes.
Conclusion
Depth of laying of sewer systems depends on many factors. In this matter, it is not wise to be guided only by dry calculations according to regulatory documents. This can lead to additional installation costs and may not increase the efficiency of the sewer. When installing a sewage system in a private house, it is much more important to determine the depth at which the drains in the pipes will not freeze and the cost of excavation work during installation. Moreover, the deeper the pipes are located, the more difficult it will be to get to them if it is necessary to replace or repair elements of the engineering system.


