Apartment buildings and private houses, enterprises and service establishments use water, which after passing through the sewer mains must be brought to the required level of purity, then sent for reuse or discharged into rivers. In order not to create a dangerous ecological situation, treatment facilities have been created.
Definition and purpose
 Wastewater treatment plant is a complex equipment that is designed to solve the most important problems - ecology and human health. The amount of sewage is constantly increasing, new types of detergents are appearing, which are difficult to remove from the water so that it is suitable for further use.
Wastewater treatment plant is a complex equipment that is designed to solve the most important problems - ecology and human health. The amount of sewage is constantly increasing, new types of detergents are appearing, which are difficult to remove from the water so that it is suitable for further use.
The system is designed to receive a certain amount of effluent from a city or local sewage system, purify it from all kinds of impurities and organic substances and then send it to natural bodies of water using pumping equipment or by gravity flow.
Principle of operation
In the process, the treatment plants release water from the following types of pollution:
- organic (feces, leftover food);
- mineral (sand, stones, glass);
- biological;
- bacteriological.
The greatest danger is bacteriological and biological sewage. When decomposed, they release dangerous toxins and unpleasant odors. With an insufficient level of cleaning, an epidemic of dysentery or typhoid can occur. To prevent such situations, the water after a full cleaning cycle is checked for the presence of pathogenic flora, and only after the examination is drained into the reservoirs.
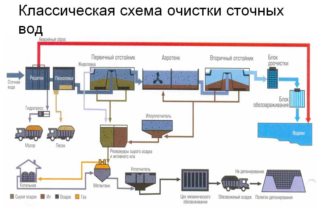
The principle of operation of treatment facilities is the phased separation of garbage, sand, organic matter, and fat. Then the semi-purified liquid is sent to sedimentation tanks with bacteria that process the smallest particles. These colonies of microorganisms are called activated sludge. Bacteria also release their waste products into water, so after they have disposed of the organic matter, the water is cleaned of bacteria and their waste.
Almost the most waste-free production takes place in the most modern equipment - sand is caught and used for construction work, bacteria are pressed and sent to the fields as fertilizers. Water goes back to consumers or into the river.
Types and arrangement of treatment facilities
 There are several types of wastewater, so the equipment must be suitable for the quality of the incoming fluid. Allocate:
There are several types of wastewater, so the equipment must be suitable for the quality of the incoming fluid. Allocate:
- Household waste is used water from apartments, houses, schools, kindergartens, and catering establishments.
- Industrial. In addition to organics, they contain chemicals, oil, and salts. Such wastes require appropriate treatment methods, as bacteria cannot handle the chemicals.
- Rain The main thing here is to remove all garbage that is washed into the sewer. This water is less polluted by organic matter.
In terms of the volume that the treatment plant serves, the stations are:
- urban - the entire volume of wastewater is directed to facilities with a huge capacity and area; located away from residential areas or made closed so that the smell does not spread;
- LOS - a local treatment plant serving, for example, a holiday village or village;
- septic tank - a type of VOC - serves a private house or several houses;
- Mobile installations that are applied as needed.
In addition to complex facilities, such as biological treatment plants, there are more primitive devices - grease traps, sand traps, grates, sieves, sumps.
The biological treatment plant
 The stages of water treatment at wastewater treatment plants:
The stages of water treatment at wastewater treatment plants:
- mechanical;
- primary sedimentation tank;
- aeration tank;
- secondary sump;
- tertiary treatment;
- disinfection.
At industrial enterprises, the system additionally contains tanks with reagents and special filters for oils, fuel oil and various inclusions.
In the process of receipt of waste, they are first cleaned of mechanical impurities - bottles, plastic bags and other garbage. Next, the wastewater is passed through a sand trap and grease trap, then the liquid enters the primary sump, where large particles are deposited to the bottom and cleaned with special scrapers in the hopper.
Then the water goes to the aeration tank, where organic particles absorb aerobic microorganisms. In order for bacteria to multiply, oxygen is additionally supplied to the aeration tank. After clarification of drains, it is necessary to dispose of the excess mass of microorganisms. This happens in the secondary sump, where bacterial colonies settle to the bottom. Some of them are returned to the aeration tank, the excess is compressed and removed.
Post-treatment is an additional filtering. Not all structures have filters - coal or membrane, but they allow you to completely remove organic particles from the liquid.
The last stage is exposure to chlorine or ultraviolet light to kill pathogens.
Water purification methods
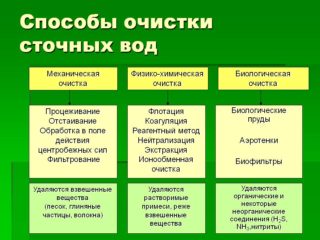 There are a large number of methods with which you can clean the effluent - both domestic and industrial:
There are a large number of methods with which you can clean the effluent - both domestic and industrial:
- Aeration - forced saturation of effluents with oxygen for the quickest weathering of odors, as well as for the reproduction of bacteria that decompose organic matter.
- Flotation is a method based on the ability of particles to trap between gas and liquid. Bubbles of foam, oily substances raise them to the surface, from where they are removed. Some particles are capable of forming a film on the surface, which is easy to merge or assemble.
- Sorption is a method of absorption by some substances of others.
- Centrifuge - a method using centrifugal force.
- Chemical neutralization, in which the acid interacts with alkali, after which the precipitate is disposed of.
- Evaporation is a method in which heated steam is passed through dirty water. Volatiles are removed with it.
Most often, these methods are combined into complexes to conduct cleaning at a higher level, taking into account the requirements of sanitary and epidemiological stations.
Design of treatment systems
The scheme of the treatment plant is designed based on the following factors:
- Groundwater level. The most important factor for autonomous treatment systems. When equipping a septic tank with an open bottom, the drains after sedimentation and biological treatment are removed to the ground, where they fall into groundwater. The distance to them should be sufficient so that the liquid clears when passing through the soil.
- Chemical composition. From the very beginning it is necessary to know exactly what waste will be treated, what equipment is needed for this.
- The quality of the soil, its penetrating ability. For example, sandy soils absorb liquid faster, but clay areas will not make it possible to dispose of runoff through an open bottom, which will lead to overflow.
- Waste collection - entrances for cars that will serve the station or septic tank.
- Possibility of draining clean water into a natural body of water.
All treatment facilities are designed by special firms that are licensed to carry out such work. For the arrangement of private sewage, permission is not required.
Installation of installations
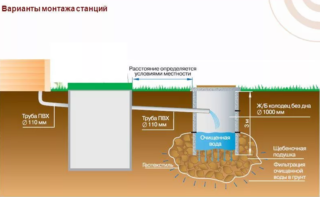 When installing water treatment facilities, many factors must be taken into account. First of all, this is the terrain and system performance.It is necessary to count on the fact that the volume of effluents will constantly increase.
When installing water treatment facilities, many factors must be taken into account. First of all, this is the terrain and system performance.It is necessary to count on the fact that the volume of effluents will constantly increase.
The stable operation of the station, the durability of the equipment will depend on the quality of the work performed, so public facilities should be well designed, taking into account all the features of this area and the system configuration.
Stages:
- Create a project.
- Site inspection and preparatory work.
- Installation of equipment and connection of nodes.
- Station management setup.
- Testing and commissioning.
The simplest types of autonomous sewage require the correct slope of the pipes so that the line does not become clogged.
Operation and maintenance
Scheduled maintenance prevents serious accidents, therefore, there is a schedule at large treatment plants, according to which the units and the most significant components are regularly repaired, and parts that fail, are replaced.
At biological treatment plants, the main points requiring attention are:
- amount of activated sludge;
- oxygen level in water;
- timely removal of garbage, sand and organic waste;
- control of the final level of wastewater treatment.
Automation is the main link that participates in the work, therefore, a specialist checking the electrical equipment and control units is a guarantee of uninterrupted operation of the station.
Of particular importance is the power of ultraviolet lamps, which need periodic replacement. The purity of water ultimately depends on their work.
The cost of treatment facilities
For a private house, you can order the most advanced cleaning system, but it will cost quite a lot, so the owners of several houses combine and build a local local station, which allows you to do quality work, but the price of the treatment plant decreases the more the more houses are connected to one device.
It is cheaper to equip a septic tank with two chambers using plastic materials. Such a system will be cheap, but it will not be able to work for full-fledged treatment - it is impossible to drain water into the river.



